Curtis 1232E/34E/36E/38E & 1232SE/34SE/36SE Manual, os30
24 NOVEMBER 2015
APPENDIX B: EN13849 COMPLIANCE
B-2
in these startup tests, communication timing, crosschecks, or responses will
command a safe shutdown of the controller, disabling the driver outputs and
motor drive within 200 ms.
To mitigate the hazards typically found in machine operations, EN13849
requires that safety functions be dened; these must include all the input, log-
ic, outputs, and power circuits that are involved in any potentially hazardous
operation. Two safety functions are dened for Curtis Enhanced AC Motor
Controllers: Uncommanded Powered Motion and Motor Braking Torque.
e Uncommanded Powered Motion safety function provides detection
and safe shutdown in the following circumstances: faulted throttle; improper
sequence of forward/reverse switches, throttle, and interlock; incorrect direc-
tion of travel; loss of speed control or limiting; uncommanded movement; or
movement at startup. e Braking Torque safety function provides detection
and safe shutdown in the event of the loss of braking torque, position/hill hold,
or emergency reverse.
Curtis has analyzed each safety function and calculated its Mean Time
To Dangerous Failure (MTTFd) and Diagnostic Coverage (DC), and designed
them against Common Cause Faults (CCF). e safety-related performance of
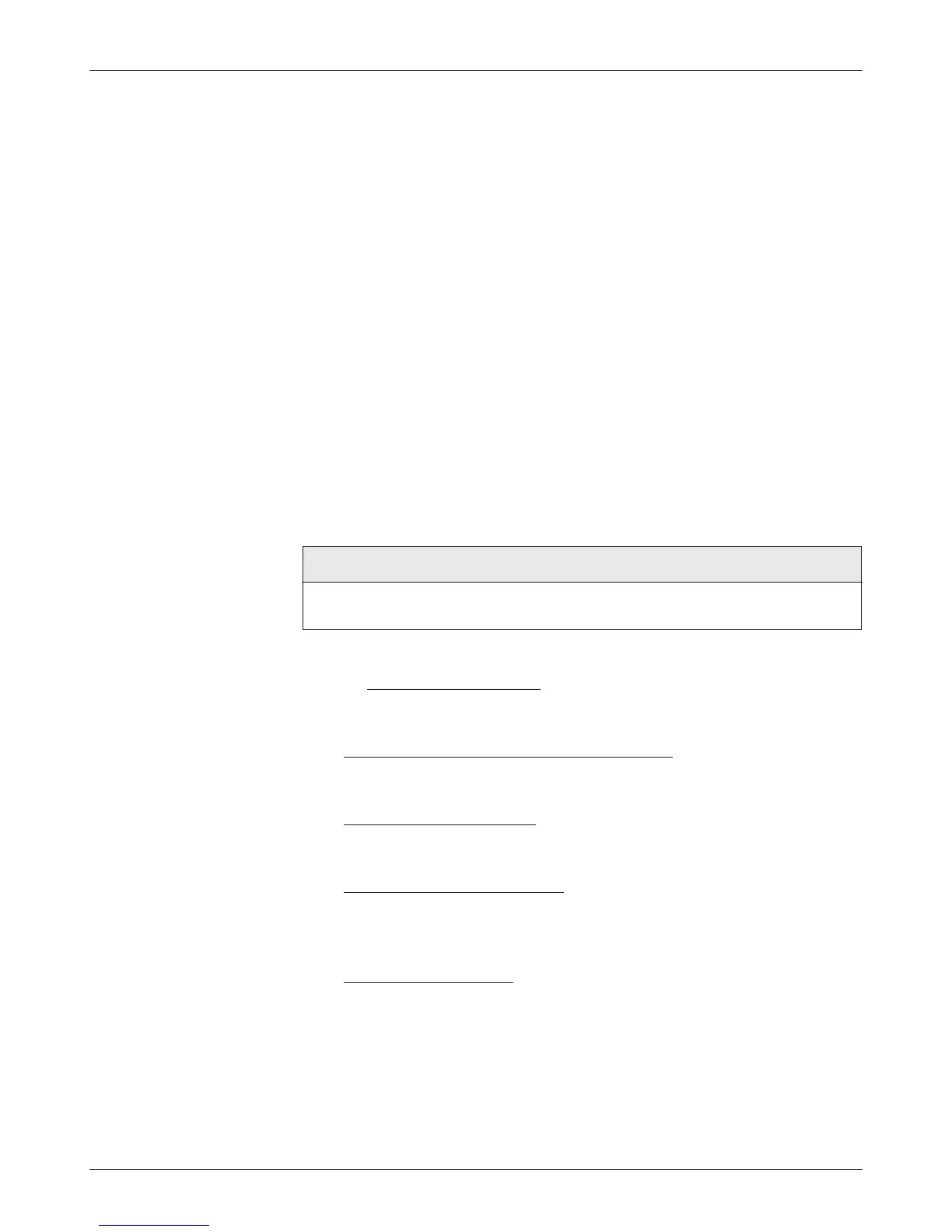
the 1232E controller is summarized as follows:
Safety Function
Designated
MTTFd DC CCF PL
Architecture
Uncommanded Powered Motion 2 >40 yrs >90% Pass d
Motor Braking Torque 2 >16 yrs >90% Pass c
EN1175 species that traction and hydraulic electronic control systems
must use Designated Architecture 2 or greater. is design employs input, logic,
and output circuits that are monitored and tested by independent circuits and
software to ensure a high level of safety performance (up to PL=d).
Mean Time To Dangerous Failure (MTTFd) is related to the expected
reliability of the safety related parts used in the controller. Only failures that
can result in a dangerous situation are included in the calculation.
Diagnostic Coverage (DC) is a measure of the eectiveness of the control
system’s self-test and monitoring measures to detect failures and provide a safe
shutdown.
Common Cause Faults (CCF) are so named because some faults within
a controller can aect several systems. EN13849 provides a checklist of design
techniques that should be followed to achieve sucient mitigation of CCFs.
e CCF value is a pass/fail criterion.
Performance Level (PL) categorizes the quality or eectiveness of a safety
channel to reduce the potential risk caused by dangerous faults within the system
with “a” being the lowest and “e” being the highest achievable performance.
 Loading...
Loading...