-- 1 8 --
bi09d1e2
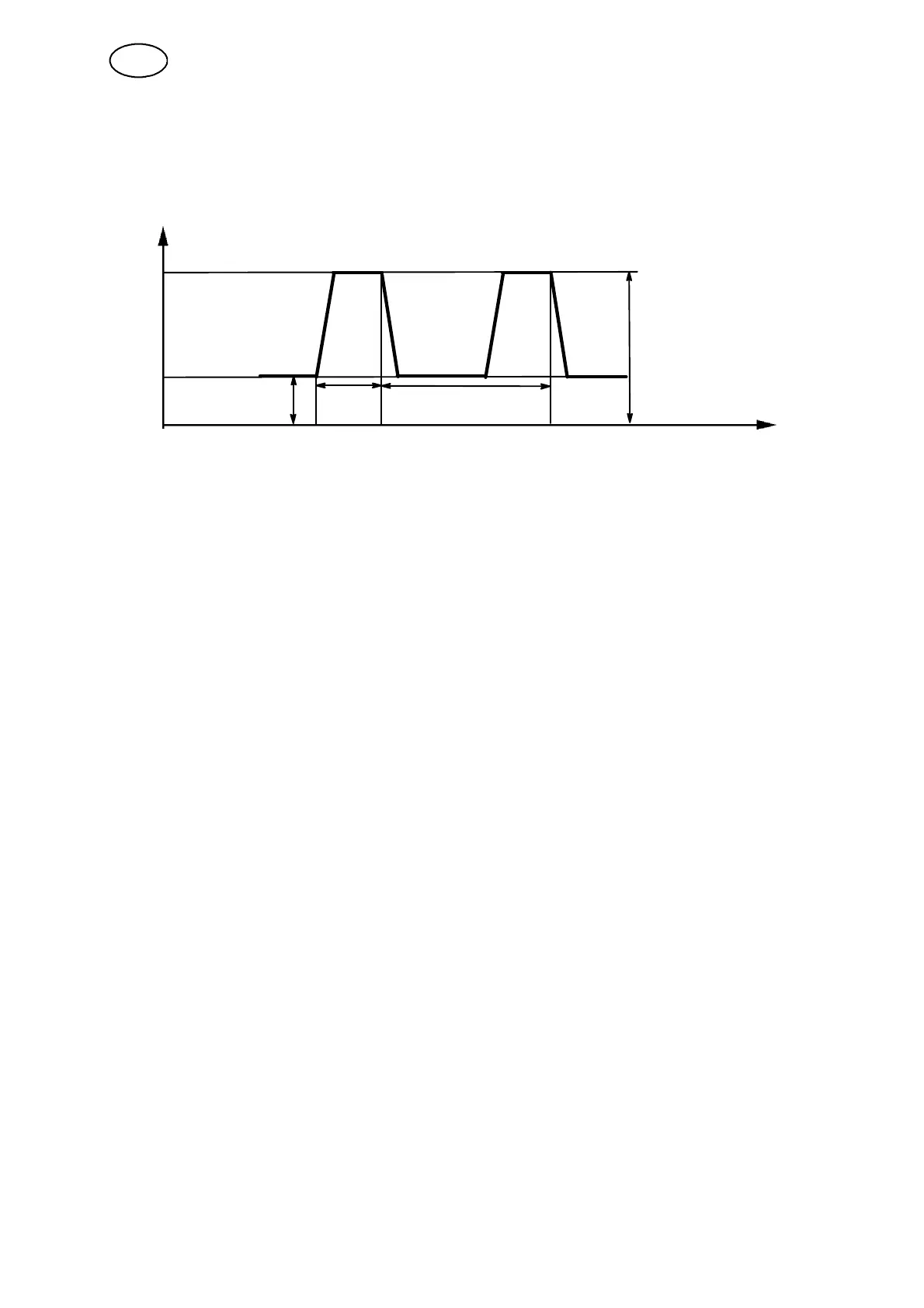
3.2.8 Background current
The lower of the two current values in the event of pulsed current.
Only applies for MIG/MAG welding with pulse.
Current
Pulse current
Background current Pulse
time
Pulse period time
Time
MIG/MAG welding with pulsing.
3.2.9 Slope
Slope means that the pulse current rises/falls slowly to the set value. The slope
parameter can be set in nine steps, with each step corresponding to 100 μs.
Slope is significant with r espect to sound. A steep slope generates a higher, sharper
sound. A slope that is too gentle can in the worst case, affect the pulse’s capacity to
cut off the droplet.
Only applies for MIG/MAG welding with pulse.
3.2.10 Ka
Ka is the proportional element and corresponds to the regulator’s amplification. A
low value means that the voltage is not maintained at a constant level as precisely.
Only applies for MIG/MAG welding with pulse.
3.2.11 Ki
Ki is the integrating element that attempts in the longer term to eliminate an error.
Here too, a low value will produce a weaker regulatory effect.
Only applies for MIG/MAG welding with pulse.
3.2.12 Synergy
Each combination of wire type, wire diameter and gas mixture requires a unique
relationship between wire feed speed and voltage (arc length) to obtain a stable
functioning arc. The voltage (arc length) automatically conforms in accordance with
the pre--programmed synergic line you have selected, which m akes it much easier to
find the correct welding parameters. The relationship between the wire feed speed
and the other parameters is called the synergic line.
It is also possible to order other packages of synergy lines, but these must be
installed by an authorised ESAB service engineer.
3.2.13 Gas pre--flow
Gas pre--flow controls the time during which shielding gas flows before the arc is
struck.
GB
 Loading...
Loading...