-- 3 0 --
bi09d1e2
Welding example B
In this exemple we will weld a 6mmplatewith 1.2 mm aluminium wire and argon
shielding gas.
Make the following settings with the controller:
Process MIG SUPERPULSE MIG SUPERPULSE
Phase Primary Secondary
Method Pulse Pulse
Wire type Al Mg Al Mg
Shielding gas Ar Ar
Wire dimension 1.2 mm 1.2 mm
Voltage (+ 1.0V) (+ 2.0V)
Wire feed speed 12.5 m/min 9.0 m/min
Phase weld time 0.15 s 0.15 s
The primary and secondary phase time is 0.15 s + 0.15 s = 0.3 s.
The difference in wire feed speed is 12.5 m/min -- 9.0 m/min = 3.5 m/min.
8 MEMORY MANAGEMENT
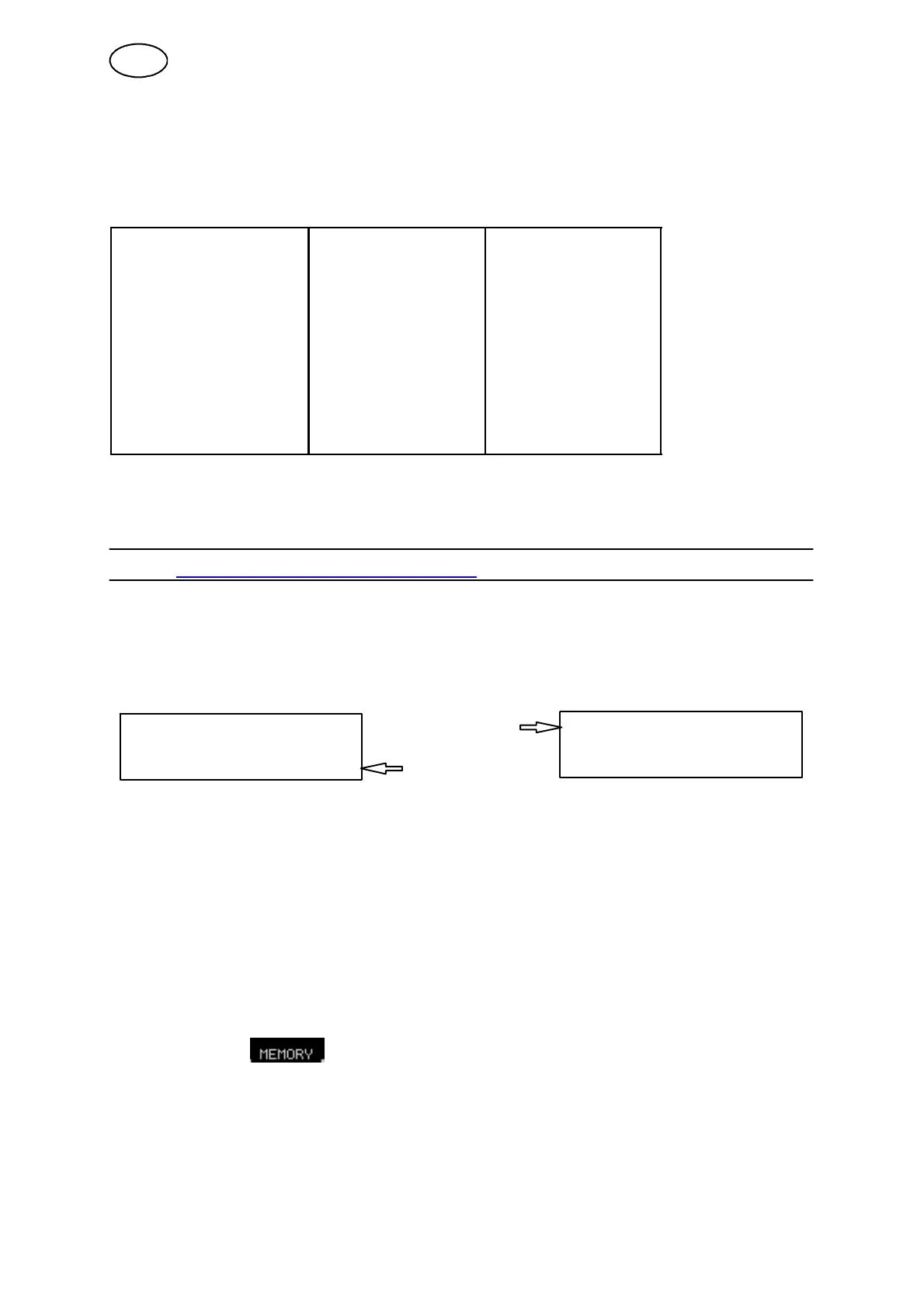
8.1 How the controller works
The controller consists in principle of two units: primary memory and weld data
memory.
Store
Primary memory Weld data memory
Recall
In the primary memory you create a complete set of weld data settings, which can be
saved in the weld data m emory.
During welding it is always the content of the working memory that controls the
process. It is therefore also possible to recall a weld data setting from the weld data
memory to the working memory.
Note that the working memory always contains the last weld data settings that were
defined. T hey may have been recalled from the weld data memory, or they can be
individually modified settings. In other words, the working memory is never empty or
”reset to zero”.
M a i n m e n u -- -- >
In the controller you can store up t o 255 sets of weld data. Each set is given a
number from 1 to 255.
You can also delete and copy data sets, and you can also recall a set of weld data
to the working memory.
Here are some examples to show how to store, recall, copy and delete.
GB
 Loading...
Loading...