Aisys
2-64 04/08 M1046983
2.13.7 Mechanical
Overpressure Valve
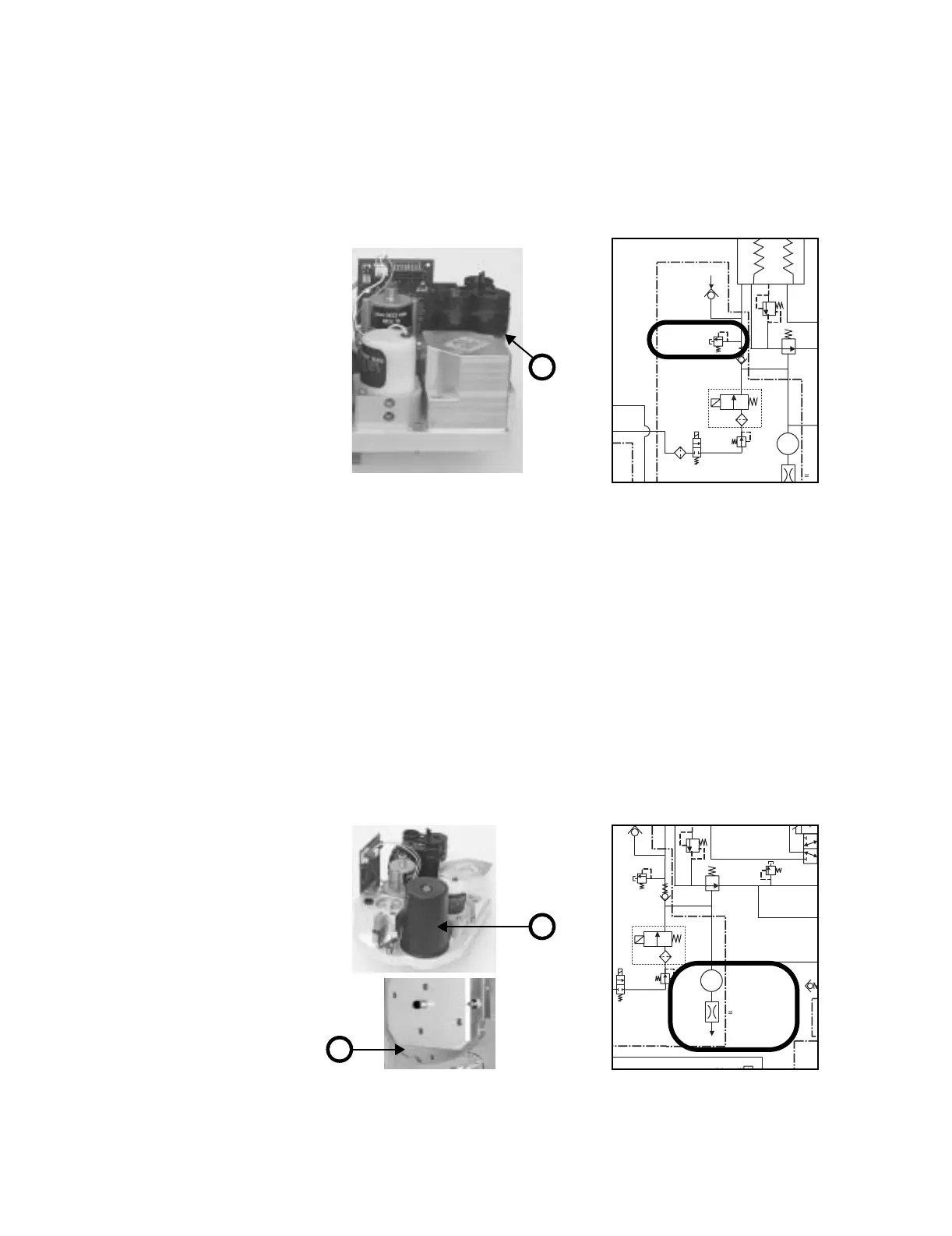
The Mechanical Overpressure Valve (MOPV) is a mechanical valve (14) that operates
regardless of electrical power. It functions as a third level of redundancy to the
ventilator's pressure limit control functions, supplying pressure relief at approximately
110 cm H
2
O.
Figure 2-53 • Mechanical overpressure valve
2.13.8 Reservoir
and bleed resistor
The reservoir (15) is a 200 ml chamber that dampens the manifold (pilot) pressure
pulses to the exhalation valve.
The bleed resistor (16) is a “controlled leak” from 0 to 12 l/min in response to circuit
pressures from 0 to 100 cm H
2
O. The small quantity of pneumatic flow exhausting
through the bleed resistor permits control of the exhalation valve's pilot pressure by
modulation of the valve output. The bleed resistor exhausts only clean drive gas and
must not be connected to a waste gas scavenging circuit. The output is routed away
from the electrical components to make sure that systems using oxygen drive gas meet
the 10VA limitation requirement for oxygen enrichment.
Figure 2-54 • Reservoir and bleed resistor
14
Exhalation V
(2.0 cm H2
Popoff
Valve
200
Atmosphere
25 psig @
15 LPM
Drive Gas Check Valve
(3.5 cm H2O bias)
Free Breathing
Check Valve
Mechanical Overpressure
Valve (110 cm H2O)
Inspiratory Flow
Control Valve
Gas Inlet
Valve
Contr
1.0
Vent Engine
15
Vent to Ambient
Bag/Ve
Exhalation Valve
(2.0 cm H2O bias)
0-10 LPM Drive Gas
0-10 LPM Patient and Fresh Gas
0-20 LPM Total Typical Flow
Popoff
Valve
200 mL Reservoir
Negative Press
relief valve
(10 cm H2O)
25 psig @
15 LPM
ve Gas Check Valve
5 cm H2O bias)
hing
ve
verpressure
H2O)
ory Flow
rol Valve
Gas Inlet
Valve
Control Bleed to Ambient
1.0 LPM @ 3.0 cm H2O
if continuous (rate dependent)
16
 Loading...
Loading...