1-13
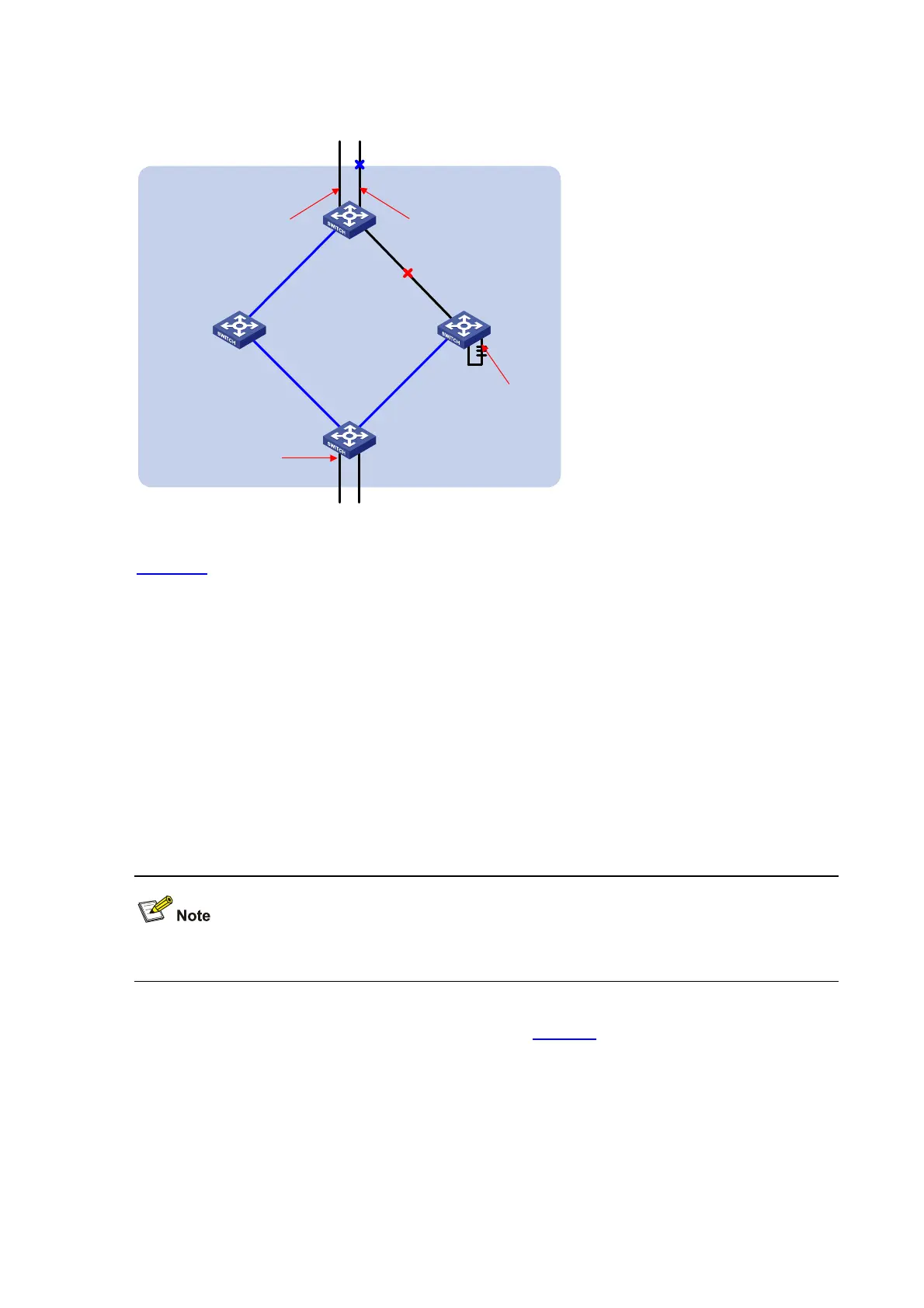
Figure 1-5 Port roles
Connecting to the
common root bridge
Port 1
Port 2
Master port Alternate port
Designated port
Port 3 Port 4
Port 5
A
B
C
D
Port 6
Backup port
MST region
Figure 1-5
helps understand these concepts. In this figure:
z Devices A, B, C, and D constitute an MST region.
z Port 1 and port 2 of device A connect to the common root bridge.
z Port 5 and port 6 of device C form a loop.
z Port 3 and port 4 of device D connect downstream to other MST regions.
Port states
In MSTP, port states fall into the following three:
z Forwarding: the port learns MAC addresses and forwards user traffic;
z Learning: the port learns MAC addresses but does not forward user traffic;
z Discarding: the port neither learns MAC addresses nor forwards user traffic.
When in different MSTIs, a port can be in different states.
A port state is not exclusively associated with a port role. Table 1-6
lists the port state(s) supported by
each port role (“√” indicates that the port supports this state, while “—“ indicates that the port does not
support this state).

 Loading...
Loading...















