HIMax System 5 Programming
HI 801 001 E Rev. 4.01 Page 77 of 122
i
Take the following point into account when reloading actions:
During the reload, actions are loaded with their corresponding data. All potential
consequences must be carefully analyzed prior to performing a reload.
Examples:
If a timer action qualifier is deleted due to the reload, the timer expires immediately.
Depending on the remaining settings, the Q outputs can therefore be set to TRUE.
If the status action qualifier (e.g., the S action qualifier) is deleted for a set element, the
element remains set.
Deleting a P0 action qualifier set to TRUE actuates the trigger.
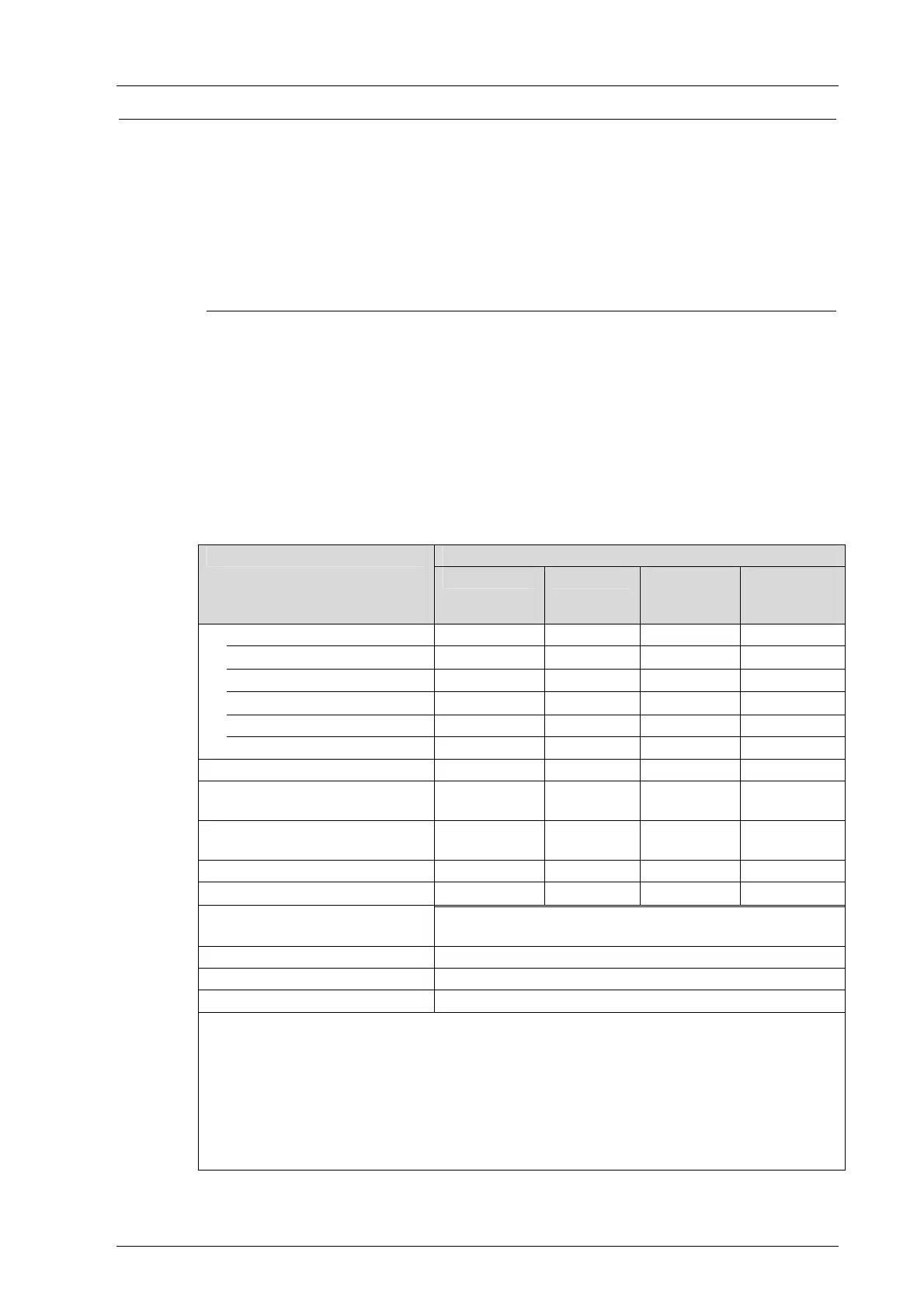
Conditions for Using the Reload Function
The following project modifications can be transferred to the controller by performing a
reload:
Changes to the user program parameters.
Changes to the logic of the program, function blocks and functions.
Changes that allows a reload in accordance with
Table 24.
Type of change Changes to
Add Delete
Change of
the initial
value
Assignment
of other
variables
Assigning global variables to
User programs
• • • •
System variables
• • • •
I/O channels
• • • •
Communication protocols - - - -
safeethernet - -
•
-
SOE - -
Base plate with system bus and
I/O modules
• •
n.a. n.a.
Modules (I/O, system bus, and
processor modules)
•
•*
n.a. n.a.
Communication protocols - - n.a. n.a.
User programs
•
•**
n.a. n.a.
Name of modules and base
plates
•
System ID, rack ID -
IP addresses -
User accounts and licenses
•
• Reload possible
- Reload impossible
* Reload possible, except for system bus modules in which the Responsible attribute is
activated
** Reload possible, but the controller must still contain at least one user program
n.a. non-applicable
Table 24: Reloading after Changes
 Loading...
Loading...