14
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1.3 Measurements and Working Systems
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
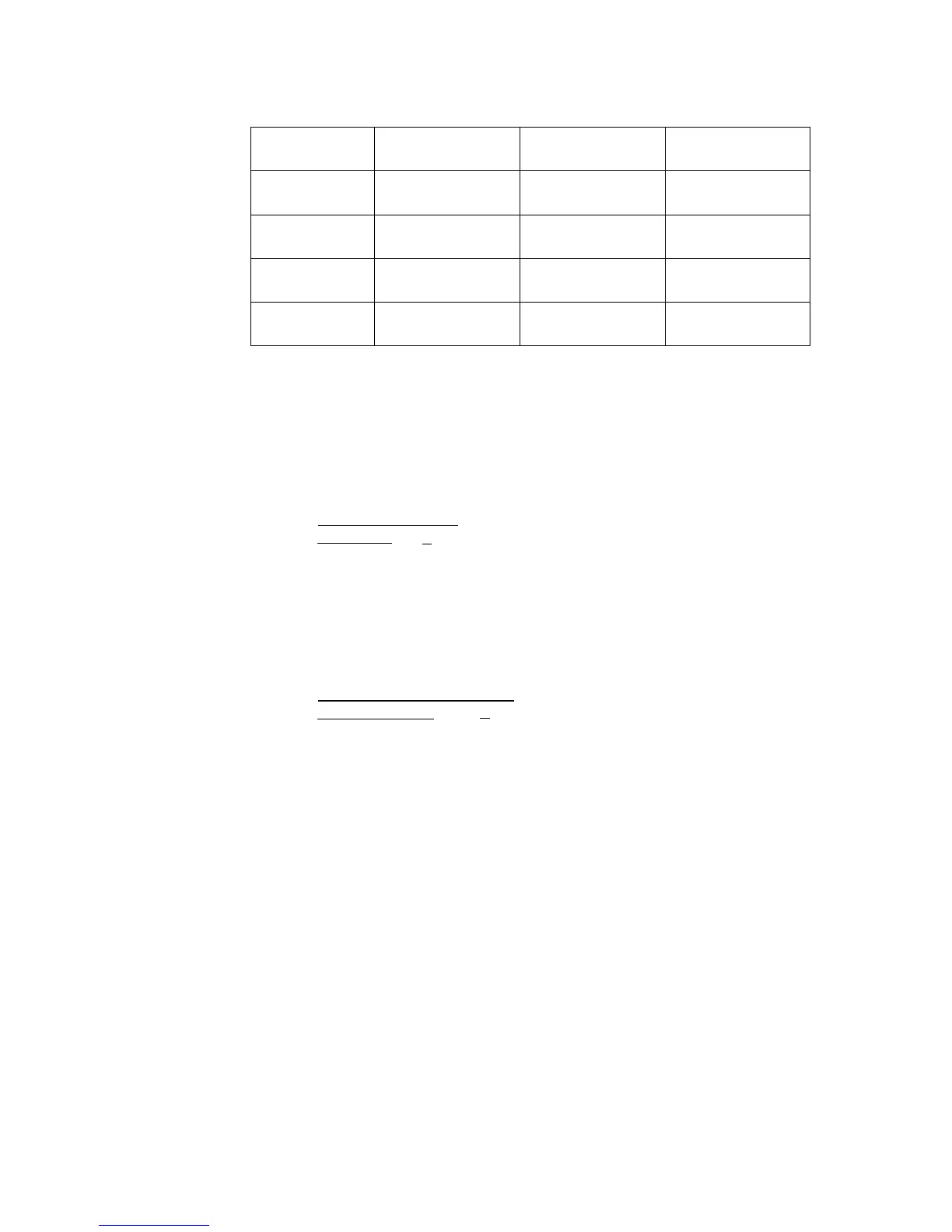
Diameter [mm]
Annealed copper
wire
Tin-plated annealed
copper wire
Hard drawn coppe
(1) Properties of metal and alloy conductive materials
(2) Conductivity of copper wire
The temperature coefficient changes in relation to temperature and
conductivity. Assume the temperature coefficient is α
20
at 20℃ and that the
temperature coefficient is α
Ct
at t (℃) with a conductivity of C. Then Ct at
around room temperature is represented as follows:
The temperature coefficient of international standard annealed copper is 3930
ppm at 20℃. For tin-plated annealed copper wire (not less than 0.10 but
below 0.26 in diameter), the temperature coefficient α
20
at 20℃ can be
calculated using the following formula:
 Loading...
Loading...