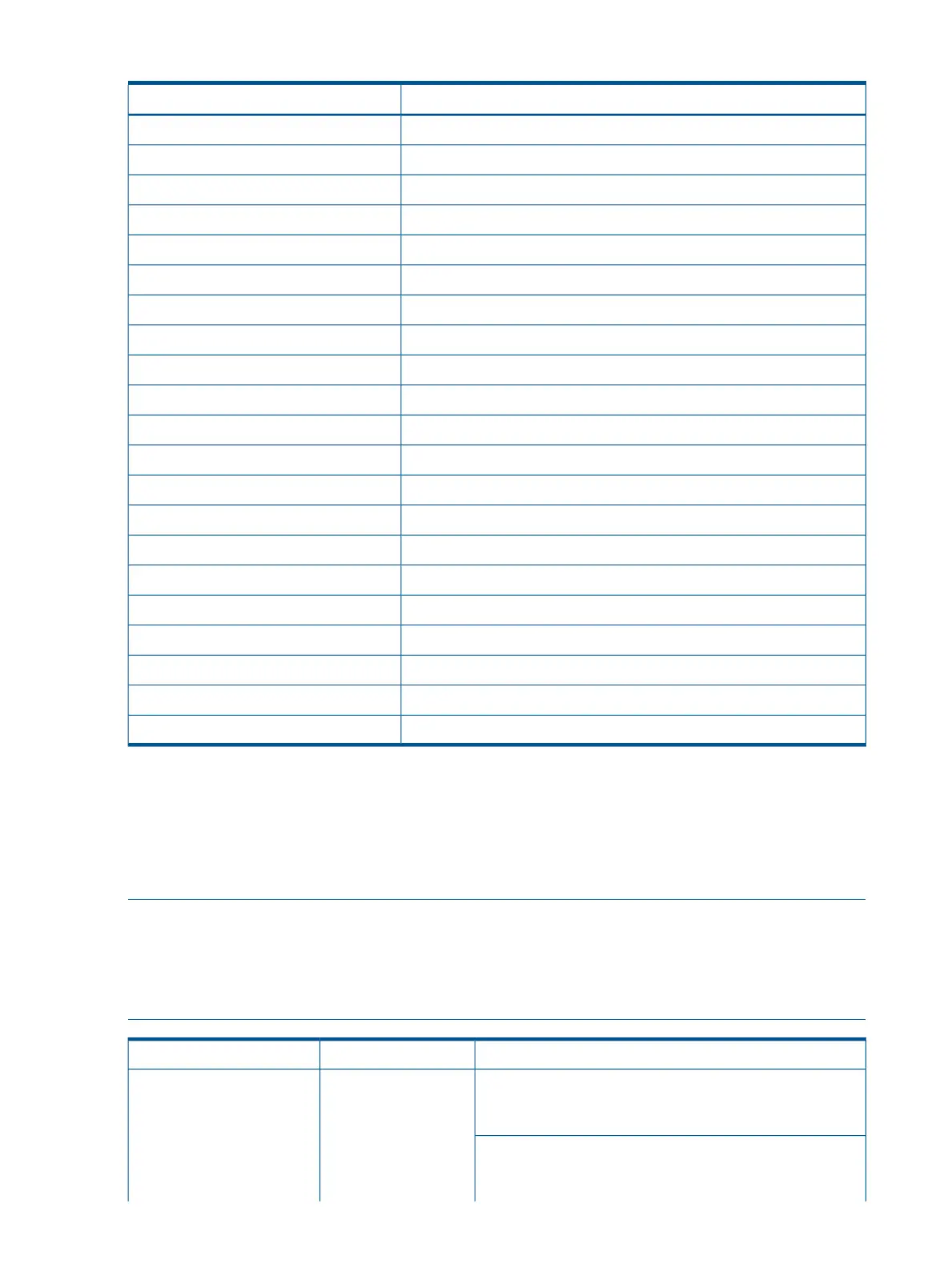
Table 45 UEFI shell commands (continued)
DefinitionUEFI shell command
Resets the systemreset
Deletes one or more files or directoriesrm
Make a SAL procedure callsalproc
Connect drivers for bootable devicessearch
View/configure system security featuressecconfig
Sets serial port attributessermode
Displays or modifies UEFI Shell environment variablesset
Set the size of a filesetsize
Shifts batch file input parameter positionsshift
Displays SMBIOS informationsmbiosview
Stalls the processor for the specified number of microsecondsstall
Boot from tapetapeboot
Perform TFTP operationtftp
Displays or changes the current system timetime
Displays or sets time zone informationtimezone
Updates filename timestamp with current system date and timetouch
Displays file contentstype
Unloads a UEFI driverunload
Displays UEFI Firmware version informationver
Displays or changes a file system volume labelvol
Turn on/off extended character featuresxchar
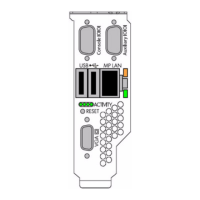
Drive paths in UEFI
Devices in the server are represented by device paths in the UEFI shell. Each internal SAS drive
could be configured either as:
• RAID mode
• HBA (raw) mode
NOTE: A SAS drive in RAID mode is identified by "Scsi" in the device path A SAS drive in HBA
mode is identified by "SAS" in the device path.
NOTE: Unlike parallel SCSI, you cannot correlate UEFI device paths to internal SAS disk drive
bays with SAS regardless of RAID/HBA mode. The UEFI device paths currently do not contain any
information that could be used to determine the physical location of the drives.
Path examplePath formatDevice
PcieRoot(0x30304352)/Pci(0x2,0x0)/
Pci(0x0,0x0)/Scsi(0x0,0x0)
UIDPCIe root bridge device path
node
(RAID mode)
PcieRoot(0x30304352)/Pci(0x2,0x0)/Pci(0x0,0x0)
/SAS(0x5000C500037688B9,0x0,0x1,NoTopology,
0,0,0,0x0)
HP Confidential144 Utilities

 Loading...
Loading...