176
Protocols and standards
RFC 6037, Cisco Systems' Solution for Multicast in BGP/MPLS IP VPNs
How MD-VPN works
This section describes how the MD-VPN technology is implemented, including the default-MDT
construction, multicast traffic delivery based on the default-MDT, and inter-AS MD-VPN implementation.
The VPN multicast data transmission on the public network is transparent to this VPN instance. The VPN
data is exchanged between the MTIs of the local PE and the remote PE. This implements the seamless
transmission of the VPN data over the public network. However, the multicast data transmission process
(the MDT transmission process) over the public network is complicated.
Default-MDT establishment
The multicast routing protocol running on the public network can be PIM-DM or PIM-SM. The process of
creating a default-MDT is different in these PIM modes.
Default-MDT establishment in a PIM-DM network
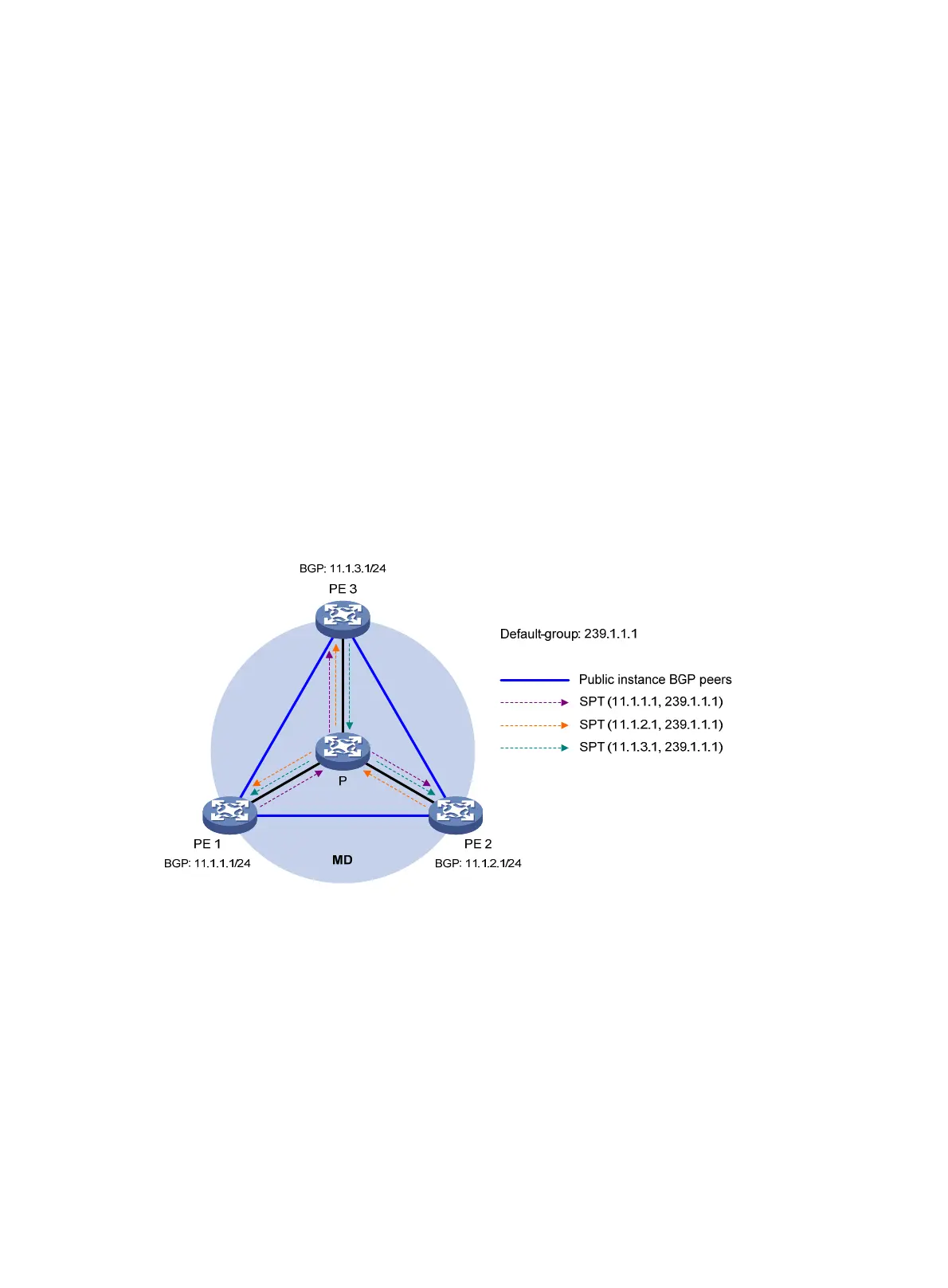
Figure 60 Default-MDT establishment in a PIM-DM network
As shown in Figure 60, PIM-DM is enabled in the network, and all the PE devices support VPN instance
A. The process of establishing a default-MDT is as follows:
1. To establish PIM neighboring relationships with PE 2 and PE 3 through the MTI in VPN instance A,
PE 1 does the following:
a. Encapsulates the PIM protocol packet of the private network into a public network multicast
data packet. PE 1 does this by specifying the source address as the IP address of the MD
source interface and the multicast group address as the default-group address.
b. Sends the multicast data packet to the public network.
For other PE devices that support VPN instance A as default-group members, PE 1 of VPN instance
A initiates a flood-prune process in the entire public network. A (11.1.1.1, 239.1.1.1) state entry
is created on each device along the path on the public network. This forms an SPT with PE 1 as the
root, and PE 2 and PE 3 as leaves.

 Loading...
Loading...