T
F
Friction torque [N·m] -
t
D
Time to deceleration [s] -
t
CYC
Time between decelerations cycles + t [s]
D
-
Calculated parameters
E
K
System kinetic energy before deceleration [J] -
E
L
Energy related to system loses during deceleration [J] -
E
D
Net deceleration energy [J] -
P
D(PK)
Deceleration peak power [W] -
P
D(AV)
Average deceleration power on a cyclic system [W] -
R
SH
Calculated shunt resistor [Ω] 5 to 200
P
R
Shunt resistor rated power [W] -
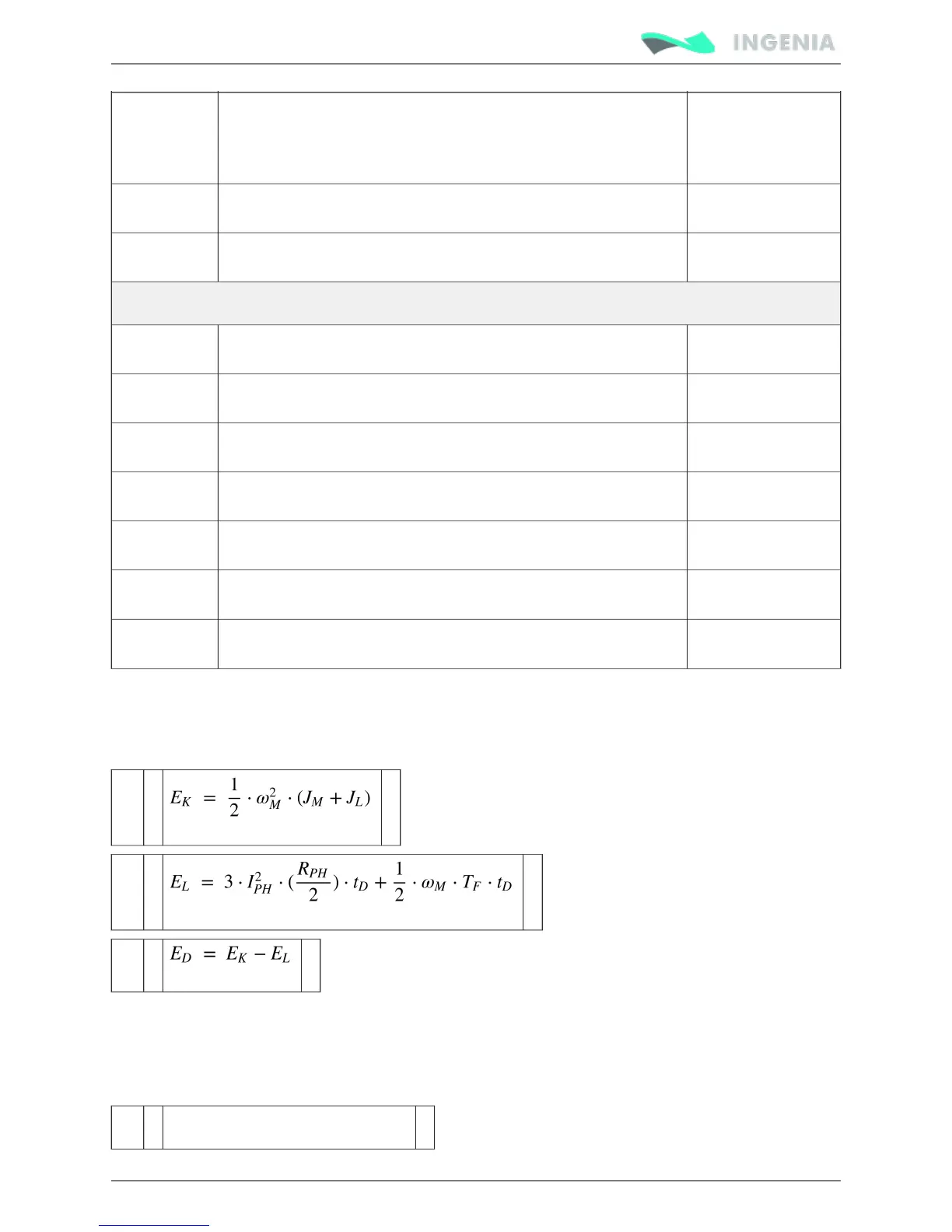
Use following equations to calculate the net deceleration energy (E ) (eqn. 1) by subtracting system loses
D
during deceleration (E ) (eqn. 2) from the kinetic energy (E ) (eqn. 3) of the system before deceleration. If
L K
some parameters regarding system loses are not known, some terms may be cancelled in the formula,
this may oversize the shunt resistor but is a safe approach.
(1)
(2)
(3)
If the calculated net deceleration energy (E ) exceeds the energy that bus capacitors can store a shunt
D
resistor is required, see eqn.4. Note that the minimum capacitance is the Pluto internal (600 µF); however
typical power supplies have large output capacitances that are parallel to the bus capacitance. Since
battery operated systems allow regenerative breaking this equation is not valid in this case. The worst
case is a diode protected system.
 Loading...
Loading...