Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guide 93
PECI Interface
7.1.7 Client Responses
7.1.7.1 Abort FCS
The Client responds with an Abort FCS under the following conditions:
• The decoded command is not understood or not supported on this processor (this
includes good command codes with bad Read Length or Write Length bytes).
• Assured Write FCS (AW FCS) failure. Note that under most circumstances, an
Assured Write failure will appear as a bad FCS. However, when an originator issues
a poorly formatted command with a miscalculated AW FCS, the client will
intentionally abort the FCS in order to guarantee originator notification.
7.1.7.2 Completion Codes
Some PECI commands respond with a completion code byte. These codes are designed
to communicate the pass/fail status of the command and may also provide more
detailed information regarding the class of pass or fail. For all commands listed in
Section 7.1.2 that support completion codes, the definition in the following table
applies. Throughout this document, a completion code reference may be abbreviated
with ‘CC’.
An originator that is decoding these commands can apply a simple mask as shown in
Ta b l e 7 - 2 2 to determine a pass or fail. Bit 7 is always set on a command that did not
complete successfully and is cleared on a passing command.
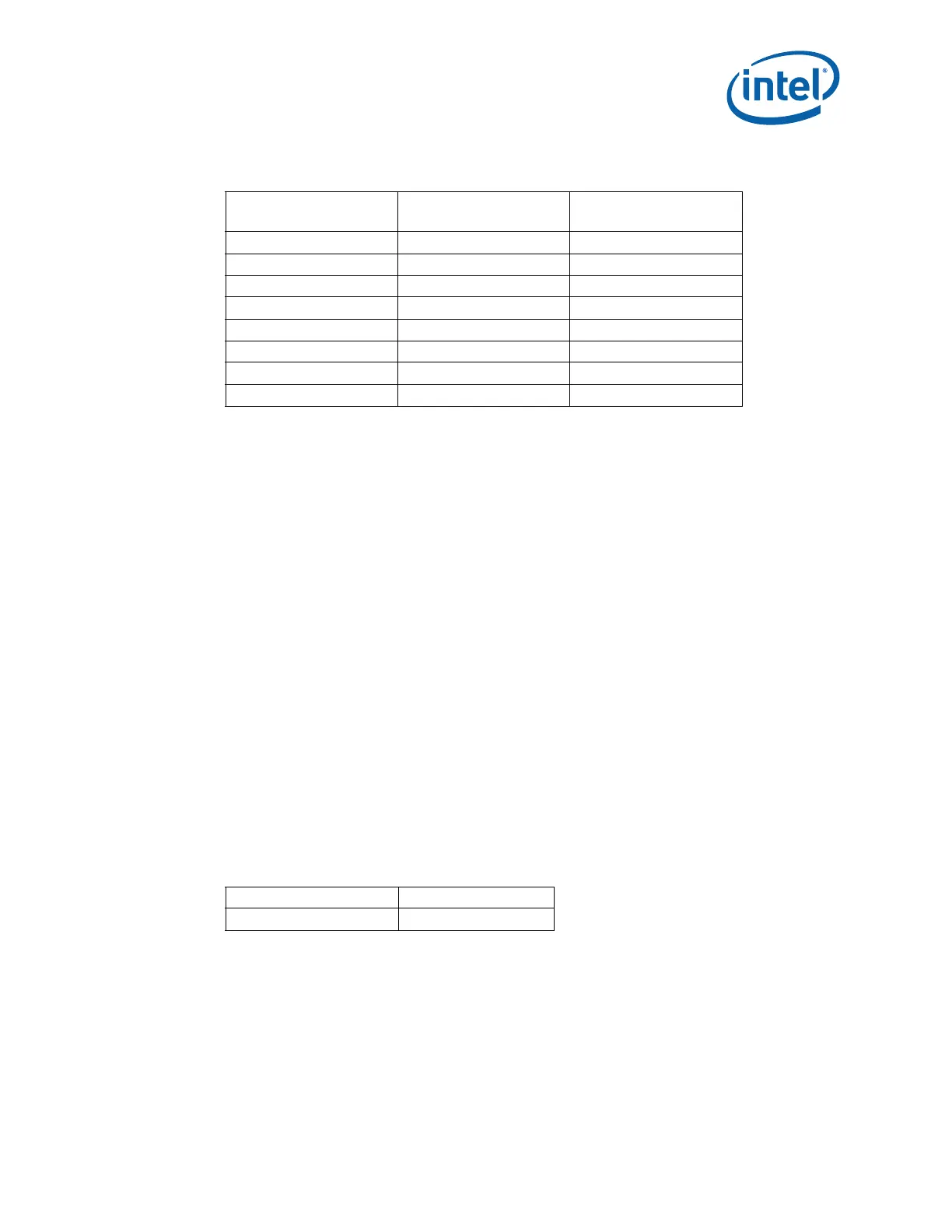
Table 7-21. Multi-Domain Command Code Reference
Command Name
Domain 0
Code
Domain 1
Code
GetTemp() 0x01 0x02
RdPkgConfig() 0xa1 0xa2
WrPkgConfig() 0xa5 0xa6
RdIAMSR() 0xb1 0xb2
RdPCIConfig() 0x61 0x62
WrPCIConfig() 0x65 0x66
RdPCIConfigLocal() 0xe1 0xe2
WrPCIConfigLocal() 0xe5 0xe6
Table 7-22. Completion Code Pass/Fail Mask
0xxx xxxxb Command passed
1xxx xxxxb Command failed

 Loading...
Loading...











