135
POWERHEAD
INSPECTION
7
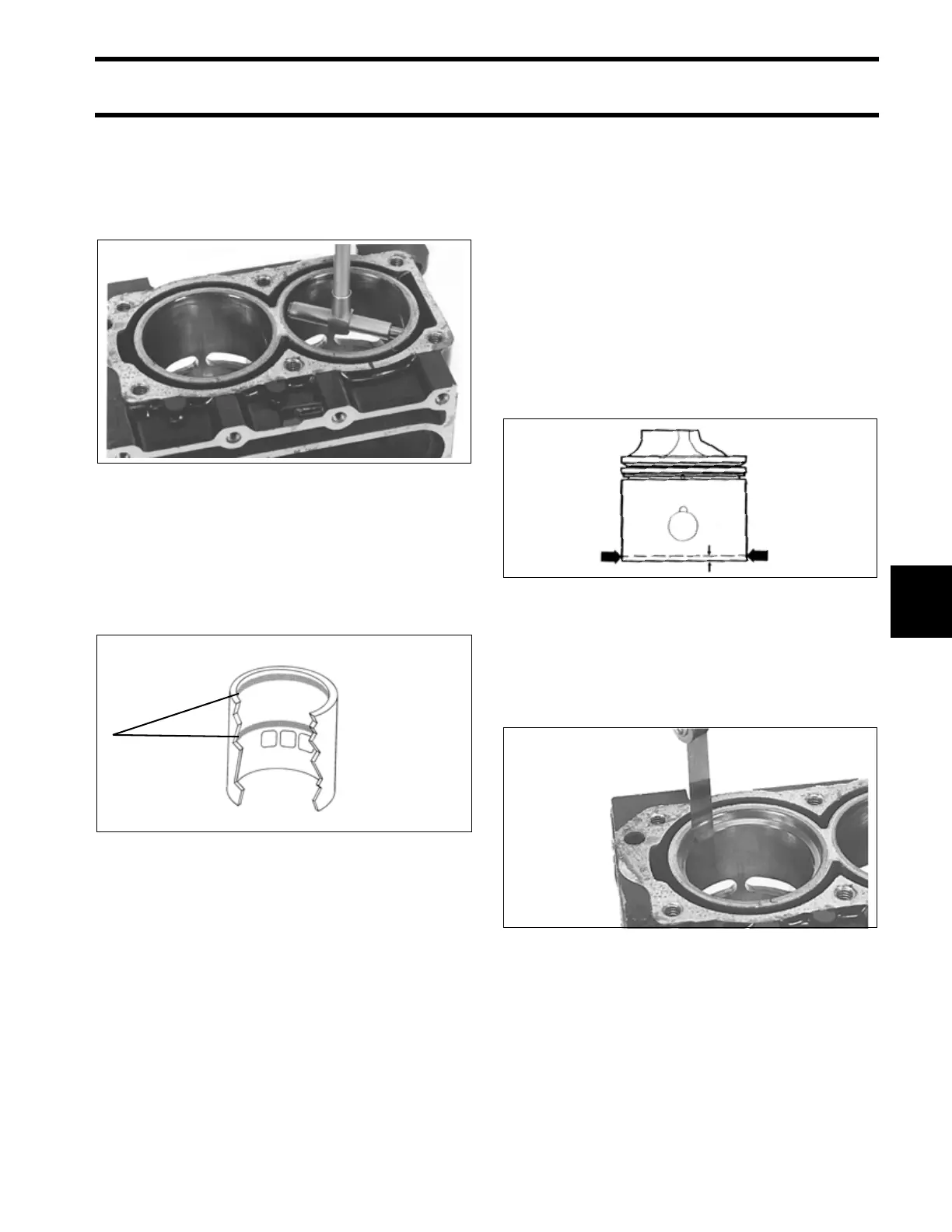
Use Cylinder Bore Gauge, P/N 771310, to inspect
each cylinder bore for an out-of-round, oversize,
or tapered condition. Make sure the gauge or
micrometer is perfectly square in the bore when
measuring.
Measure each cylinder in at least two areas as
shown. Each area should be measured twice. The
difference between the two measurements in
each area is the cylinder out-of-round dimension.
• The cylinder must not be out-of-round by more
than 0.003 in. (0.08 mm).
The dimensional difference between the two
areas is the cylinder taper.
• Cylinder taper must not exceed 0.002 in. (0.05
mm).
The difference between your measurements and
standard bore dimension is cylinder oversize.
Refer to TECHNICAL DATA on p. 18 for dimen-
sions.
• The cylinder must not be oversize by more than
0.002 in. (0.05 mm).
IMPORTANT: If any cylinder is outside these
tolerances, it must be bored oversize. One over-
size piston is available for this engine 0.020 in.
(0.508 mm). To determine oversize bore, add
0.020 in. (0.508 mm) to the standard bore. Refer
to TECHNICAL DATA on p. 18. It is permissible to
have one or more oversize pistons in an engine.
Measure the piston in two locations, 90° apart
from each other, 1/8 in. (3 mm) above the bottom
of the piston skirt.
• The difference between the two measurements
is the out-of-roundness and must be no more
than 0.002 in. (0.05 mm).
Place each ring, separately, in its respective bore.
Use a piston to square the ring in the cylinder.
Use a feeler gauge to measure the ring end gap.
The ring gap must be within 0.005 to 0.015 in.
(0.13 to 0.38 mm).
Use a feeler gauge to check groove side clear-
ance on the lower square rings. Install each
square ring on its piston. With the ring seated in
its groove, make several checks around the pis-
TYPICAL 32409
1. Measurement areas DR1119
1
CO3082
32408
 Loading...
Loading...











