Load Edge Series
24 Connections
2. Affect by Load current setting
As the nature of this product, slew rate may be decreased depending on the slew rate
and load current settings. Specifically, if the setting of load current is less than a certain
current, the slew rate won‟t exceed the min load response time which is 500ns.
Some examples are explained below with reference to the following figure.
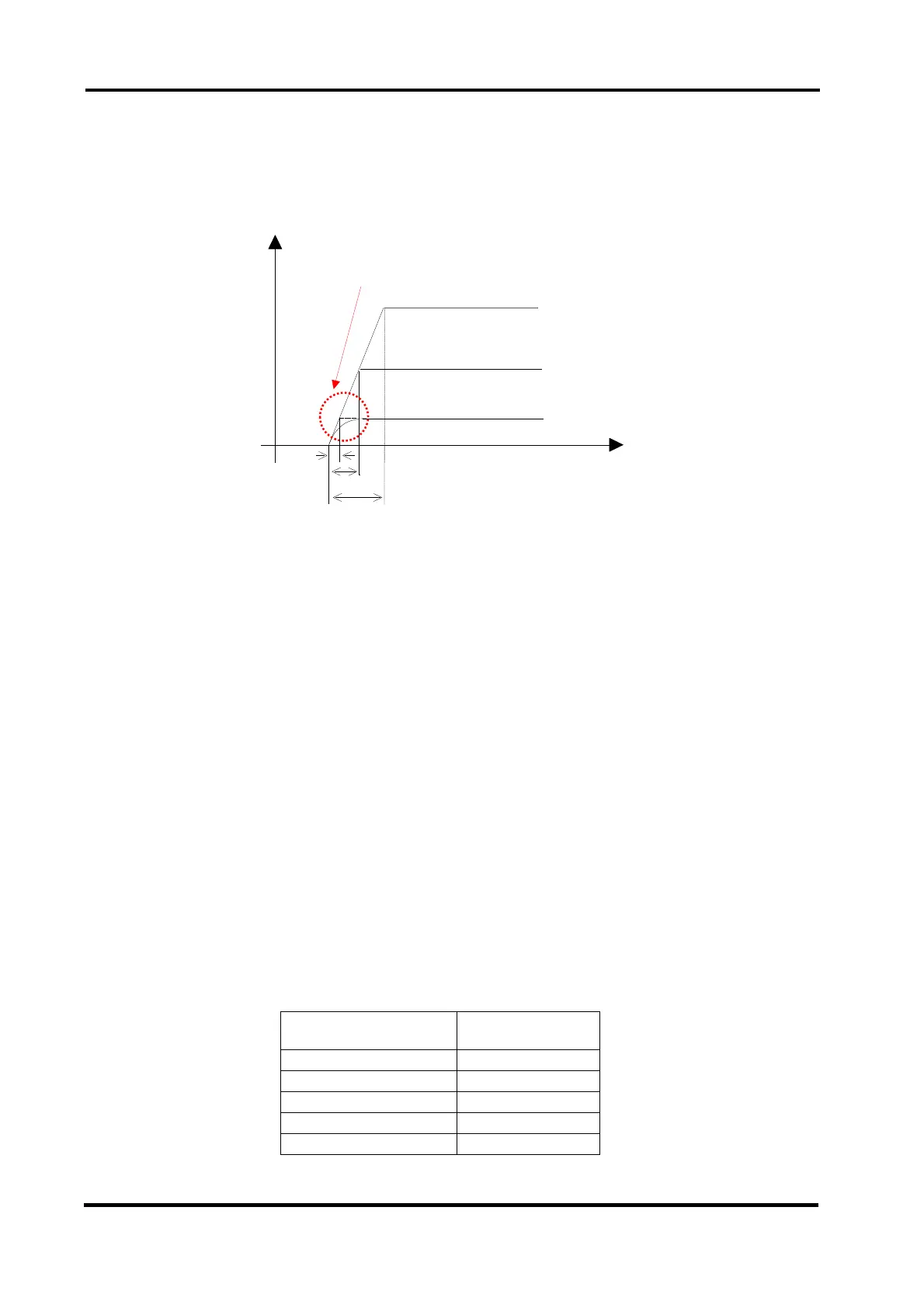
Fig. 2-3-1 Relation between slew rate and load current (ELZ-175)
When slew rate: 25A/μs and load current: 25A are set:
The Load response changes on the 25A line above. This slew rate is 25A per 1μs.
However, when slew rate: 25A/μs and load current: 5A are set:
The load response changes on the 5A line above. Theoretically, the load current should
have reached 5A in about 200ns, but it takes 500ns whose slew rate is about 10A/μs.
This slew rate is slower than 25A/μs.
This 500ns is called minimum load response time that is literally minimum load
response time specified in the specifications of this product. In other words, when a load
current and slew rate are set so as to reach the load current less than 500ns (min. load
response time), the load response time to reach the load current is automatically set for
500ns (min. load response time), and accordingly slower slew rate than setup slew rate is
automatically setup.
For example, when slew rate and load current are set for 25A/μs and 12.5A respectively,
the rise time is set 500ns which is equal to the min. load response time. But when the
load current is set for 5A, the theoretical rise time is 200ns but the actual rise time is set
500ns which is slower than theoretical value.
Table below shows the relation between setup slew rate you set and min load current
that can support the slew rate.
Note
Min. load current X (A) = slew rate Y (A)/2
Table 2-3-2 Minimum Setting of Load Current about slew rate(ELZ-175)
 Loading...
Loading...