Chapter 7 EtherCAT Communication
The process data object (PDO) consists of objects in the object dictionary that can be mapped to by PDO. The
contents of the PDO data are defined by the PDO map. While PDO data is read and written periodically and does
not need to look up an object dictionary, mailbox communication (SDO) is aperiodic and looks up an object
dictionary when reading and writing them.
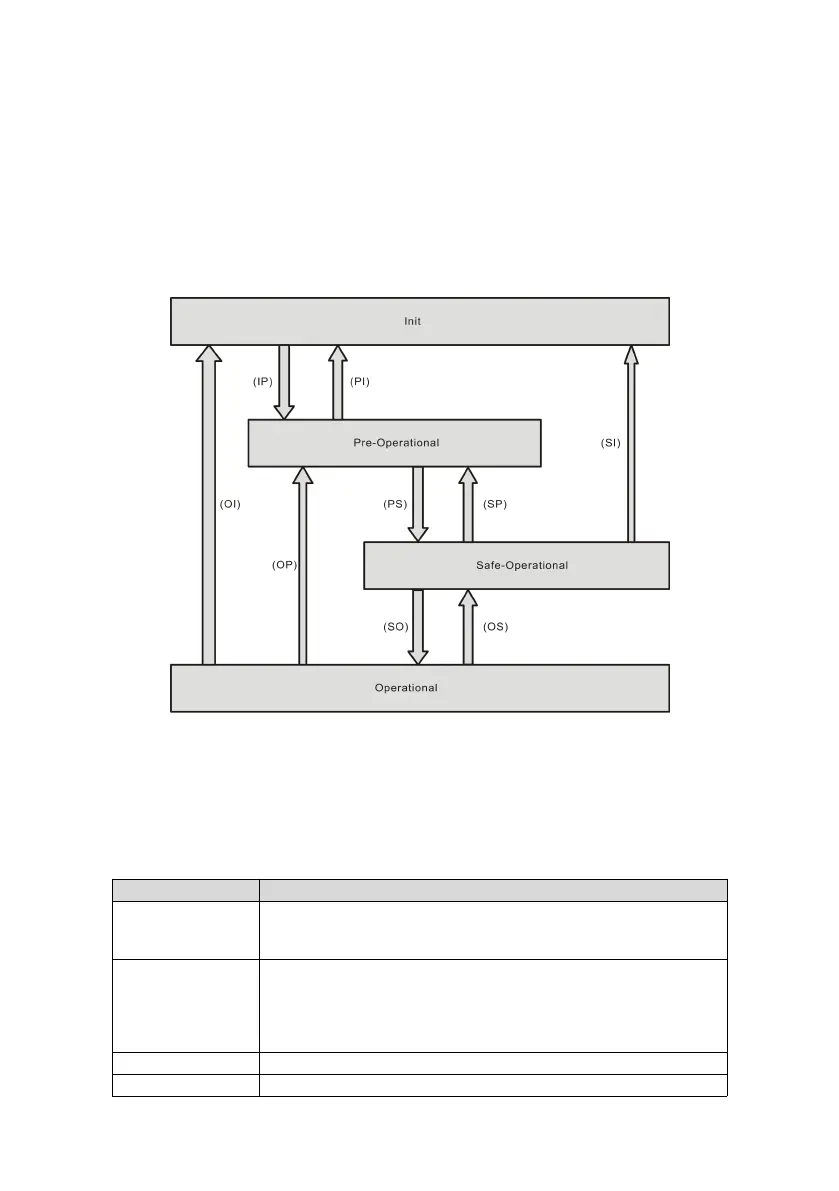
7.2.3 EtherCAT network state machine
EtherCAT state machine is used to describe the state and state changes of the slave application.
State change requests are usually initiated by the master station and responded to by the slave station.
The EtherCAT state machine must support the following four states and coordinate the states between the
master and slave application program during initialization and operation.
These four states are Init (I), Pre-Operational (P), Safe-Operational (S), and Operational (O).
Transition from "Init" to "Operational" must be in the sequence of "Init → Pre-Operational → Safe-Operational →
Operational". Transition from "Operational" to "Init" can be done with certain states skipped. The following table
lists the state transition and the initialization process.
Communication initialization;
No communication in the application layer, EtherCAT slave controller (ESC)
register can only be read/written by the master.
Slave address configured by the master;
Mailbox channel configured;
Distributed clock (DC) configured;
Check whether the mailbox is successfully initialized.
Request for Pre-Operational state.
Mailbox data communication in the application layer (SDO)
Mailbox initialization process data mapping used by the master;
 Loading...
Loading...