transformer nominal current several times over. It takes some time for the
current to assume its small stationary value. Since the high inrush current flows
on the connected side only, the tripping characteristic of the P631 differential
protection may give rise to a trip unless stabilizing action is taken. The fact that
the inrush current has a high proportion of harmonics having twice the system
frequency offers a possibility of stabilization against tripping by the inrush
current.
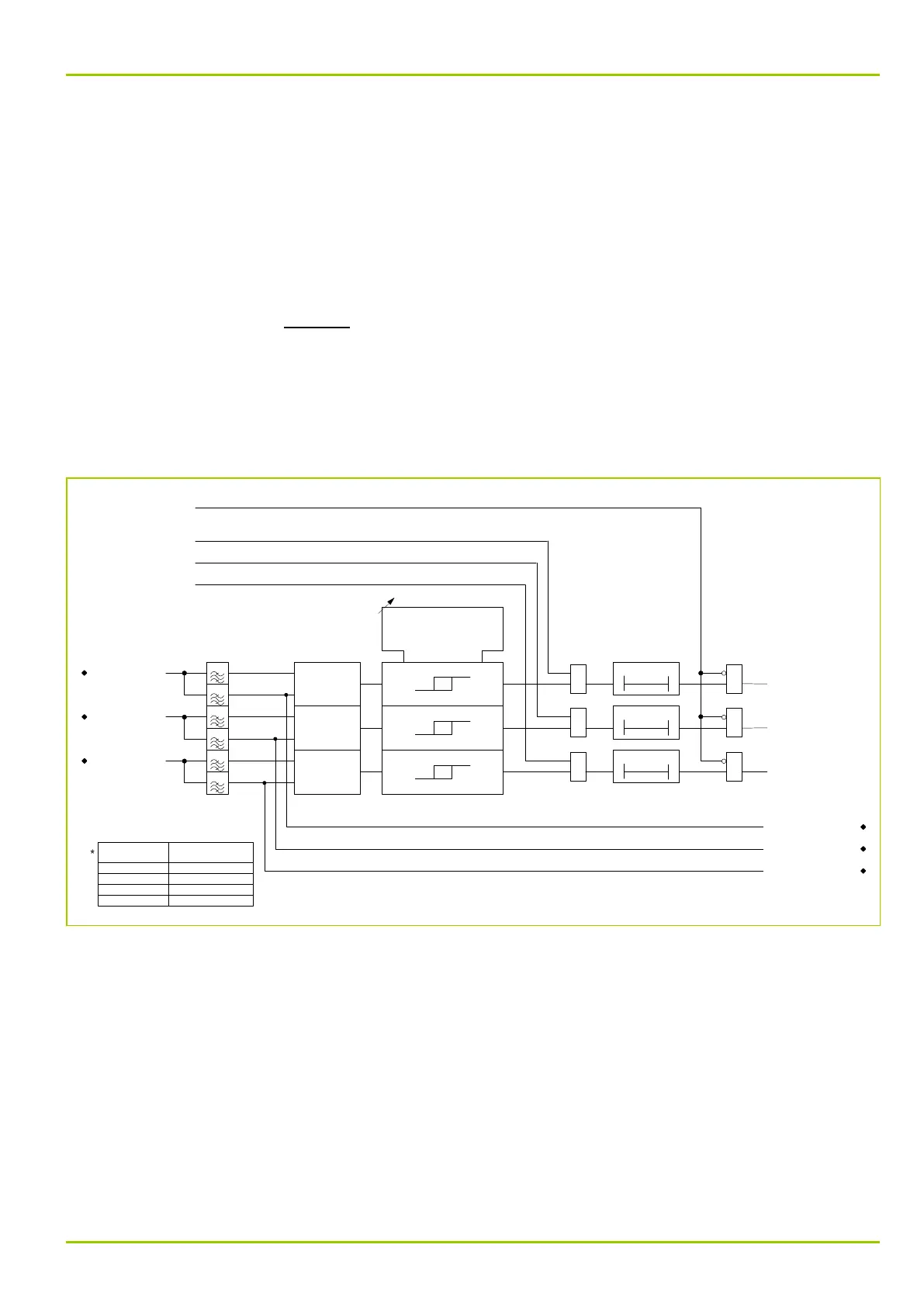
The P631 filters the differential current. The fundamental wave I
(
f
0
)
and second
harmonic components I
(
2 ⋅ f
0
)
of the differential current are determined. If the
ratio
I
(
2 ⋅ f
0
)
I
(
f
0
)
exceeds a specific adjustable value in at least one measuring
system, tripping is blocked optionally in one of the following modes:
●
across all three measuring systems
●
selectively for one measuring system (see Fig. 3-86, (p. 3-119)).
There will be no blocking if the differential current exceeds the set threshold
DIFF: Idiff>> PSx.
DIFF:
Id,1
303 303
f0
I(f0)
I(2⋅f0)
I(2⋅f0)/I(f0)
DIFF:
RushI(2f0)/I(f0) PSx
[ * ]
DIFF:
Meas.system 1 trigg.
[ 041 124 ]
DIFF:
Meas.system 2 trigg.
[ 041 125 ]
DIFF:
Meas.system 3 trigg.
[ 041 126 ]
0 30ms
&
DIFF:
Trip signal
[ 041 075 ]
DIFF:
Harm.block 1 trigg.
[ 041 118 ]
I(f0)
I(2⋅f0)
I(2⋅f0)/I(f0)
0 30ms
&
DIFF:
Harm.block 2 trigg.
[ 041 119 ]
I(f0)
I(2⋅f0)
I(2⋅f0)/I(f0)
0 30ms
&
DIFF:
Harm.block 3 trigg.
[ 041 120 ]
DIFF:
I(2⋅f0),1
303 301
DIFF:
I(2⋅f0),2
303 302
DIFF:
I(2⋅f0),3
303 309
Q6Z0110C
DIFF:
Id,2
303 304
DIFF:
Id,3
303 307
Parameter
set 1
set 2
set 3
set 4
DIFF:
RushI(2f0)/I(f0) PSx
072 159
073 159
074 159
075 159
f0
f0
2⋅f0
2⋅f0
2⋅f0
&
&
&
Fig. 3-86: Inrush stabilization (harmonic restraint)
3.21.8 Saturation Discriminator
Up to a certain limit, stability in the event of external faults is ensured by means
of the bias. Due to the triple-slope tripping characteristic, the stabilization is
particularly pronounced for high currents. However, as an additional safeguard
for through-currents with transformer saturation, the P631 is provided with a
saturation discriminator.
After each zero crossing of the restraining current, the saturation discriminator
monitors the occurrence of the differential current over time. For internal faults,
the differential current appears after a zero crossing together with the restraining
current. In the case of passing currents with transformer saturation, however, a
differential current will not appear until transformer saturation begins.
Accordingly, a locking signal is generated on the basis of level monitoring of the
3 Operation
P631
P631/EN M/R-11-C // P631-310-650 3-119
 Loading...
Loading...