1 - 10 1 - 10
MELSEC-Q
1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
1.3.5 Derivative action (D-action)
(1) The derivative action adds the manipulation value proportional to the change speed
to eliminate error when an deviation occurs.
The derivative control action can prevent the control target from changing
significantly due to disturbance.
(2) In the derivative action, the time from the deviation occurrence until the
manipulation value of the derivative action becomes that of the proportional action
is called the derivative time, and is indicated by T
D.
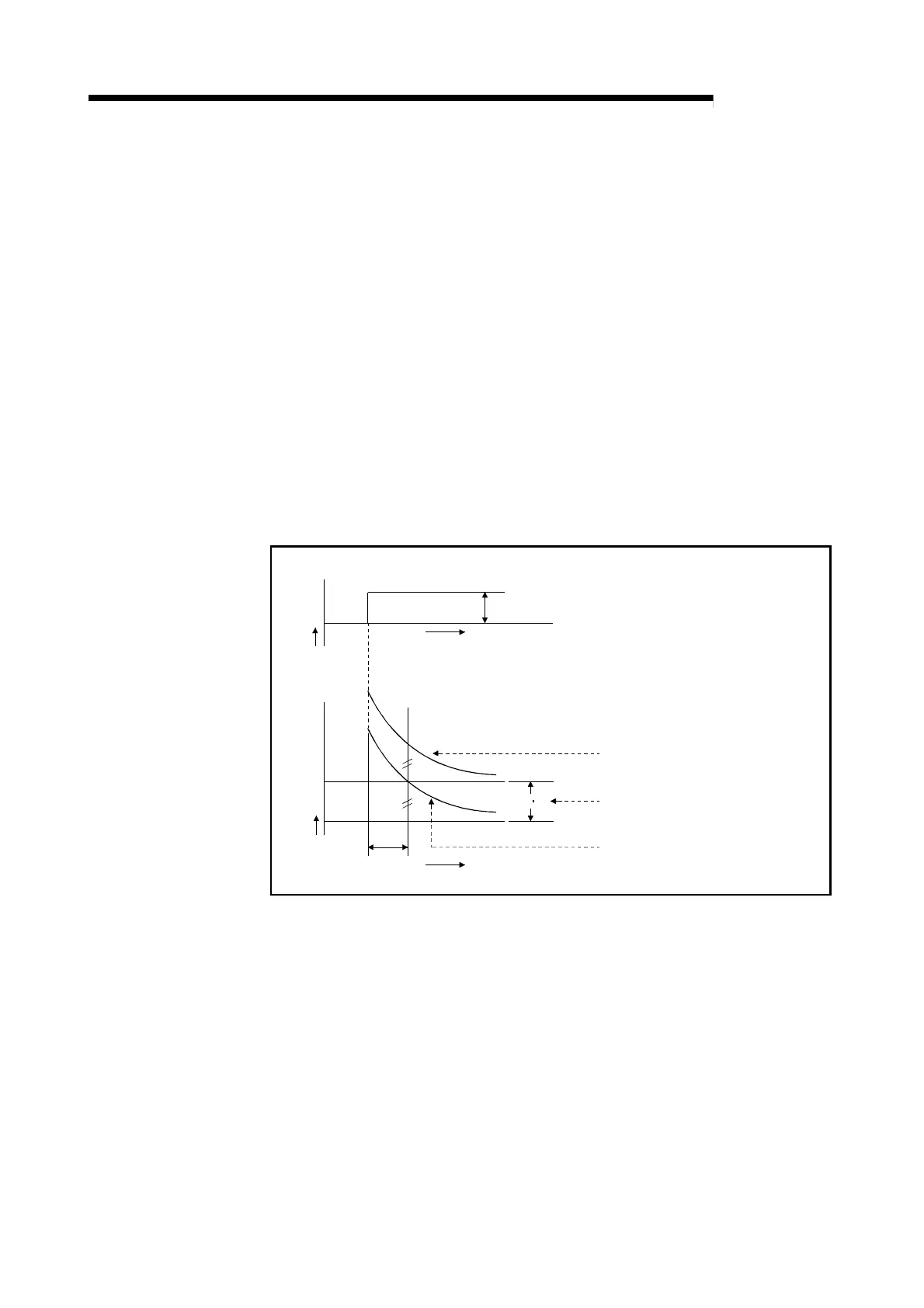
(3) The derivative action for the step response when the deviation is constant is shown
in Figure 1.9.
(4) The derivative action is used as a PD action in combination with the proportional
action, or PID action in combination with the proportional and integral actions.
The derivative action cannot be used alone.
Deviation
Manipulated
value
Time
Time
Manipulated value of the proportional
action
E
T
D
K
P
E
Manipulated value of the derivative
action
Manipulated value of the proportional
action + derivative action
Fig. 1.9 Derivative action for step response

 Loading...
Loading...











