3 - 34 3 - 34
MELSEC-Q
3 SPECIFICATIONS
3.2.14 Scaling function
The scaling function scales the measured value and stores it in the scaling value
(buffer memory address: 196, 212).
The conversion method differs depending on micro voltage, voltage, current input in
the case of thermocouple input.
The conversion method is automatically selected by the setting of input range (buffer
memory address: 32, 64).
(1) Thermocouple input
The measured value within the scaling range set by the scaling range upper
limit value (buffer memory address: 197, 213) and also scaling range lower limit
value (buffer memory address: 198, 214) is, by performing the scaling, set to
the scaring width set by the scaling width upper limit value (buffer memory
address: 199, 215) and also scaling width lower limit value (buffer memory
address: 200, 216).
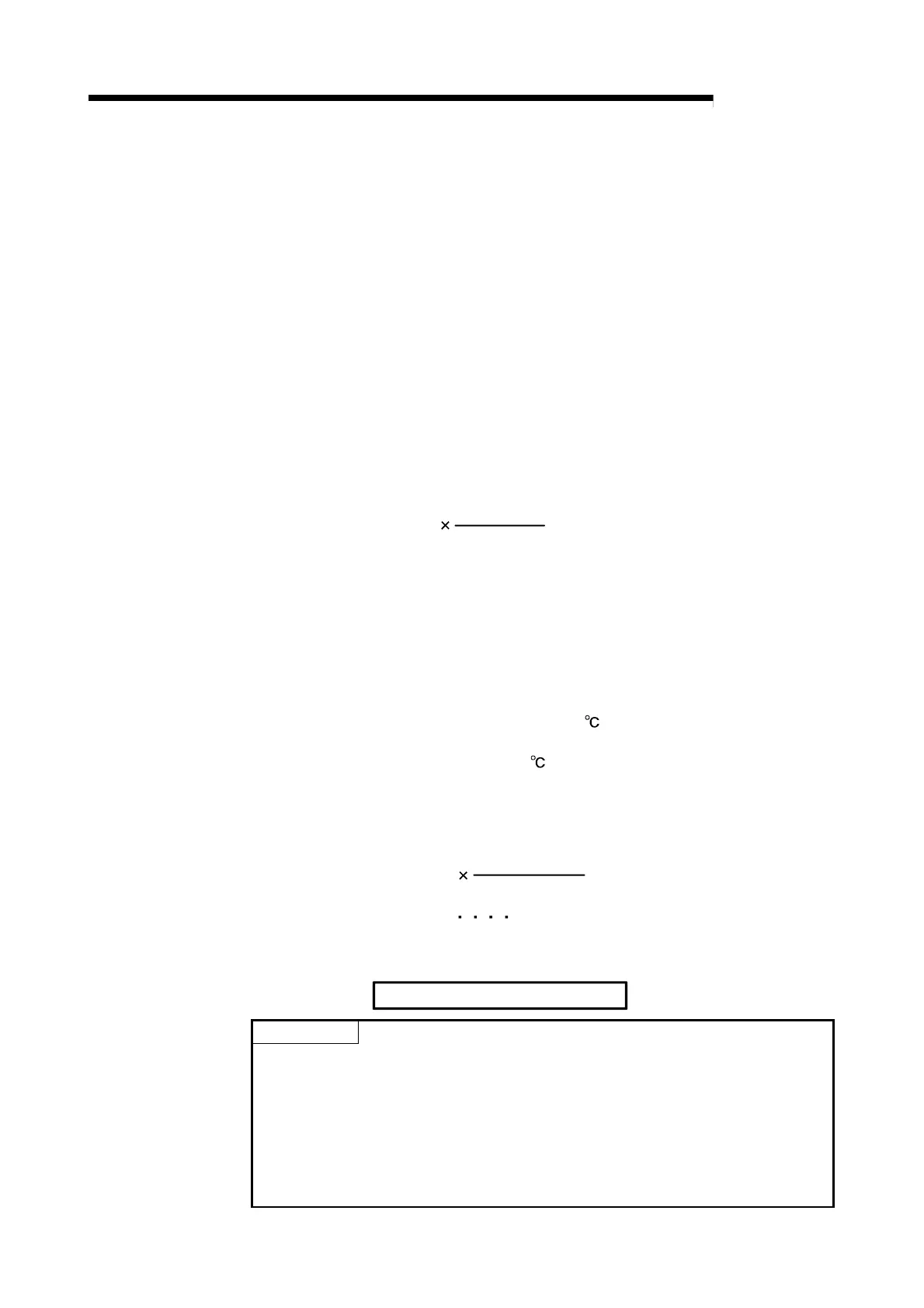
The following describes the calculation method of scaling value.
S
CV
= ( S
CWU
- S
CWL
)
+ S
CWL
T
EPV
- S
CRL
S
CRU
- S
CRL
S
CV : Scaling value
S
CWU : Scaling width upper limit value
S
CWL : Scaling width lower limit value
T
EPV : Set value
S
CRU : Scaling range upper limit value
S
CRL : Scaling range lower limit value
Example) When scaling the temperature to a percentage (%)
When scaling the temperature 360
(temperature conversion value:
3600) in the following setting.
Scaling range: -100 to 500
(lower limit value = -1000, upper limit
value = 5000)
Scaling width: 0 to 100% (lower limit value = 0, upper limit value =
100)
+ 0
3600 - (-1000)
5000 - (-1000)
= 76.6666
= 77 (%)
Scaling value = (100 - 0)
Rounded to the whole number.
POINT
The scaling is performed by the above method even if the upper limit value is set
smaller than the lower limit value for the scaling range upper/lower limit value and
scaling width upper/lower limit value.
When the upper limit value is set equal to the lower limit value, the scaling is not
performed.
When the measured values out of the range set with the scaling range upper/lower
limit value are measured, the values set with the scaling width upper/lower limit
value are stored.
 Loading...
Loading...











