8.21 EDH0162En1040 – 06/99
MM4005 Appendix D — Motion Program Examples
Example 3
The MM4005 does not offer true circular interpolation but in many cases
less demanding applications can be successfully implemented.
Take the example of dispensing glue on the pattern shown in Fig. D.2.
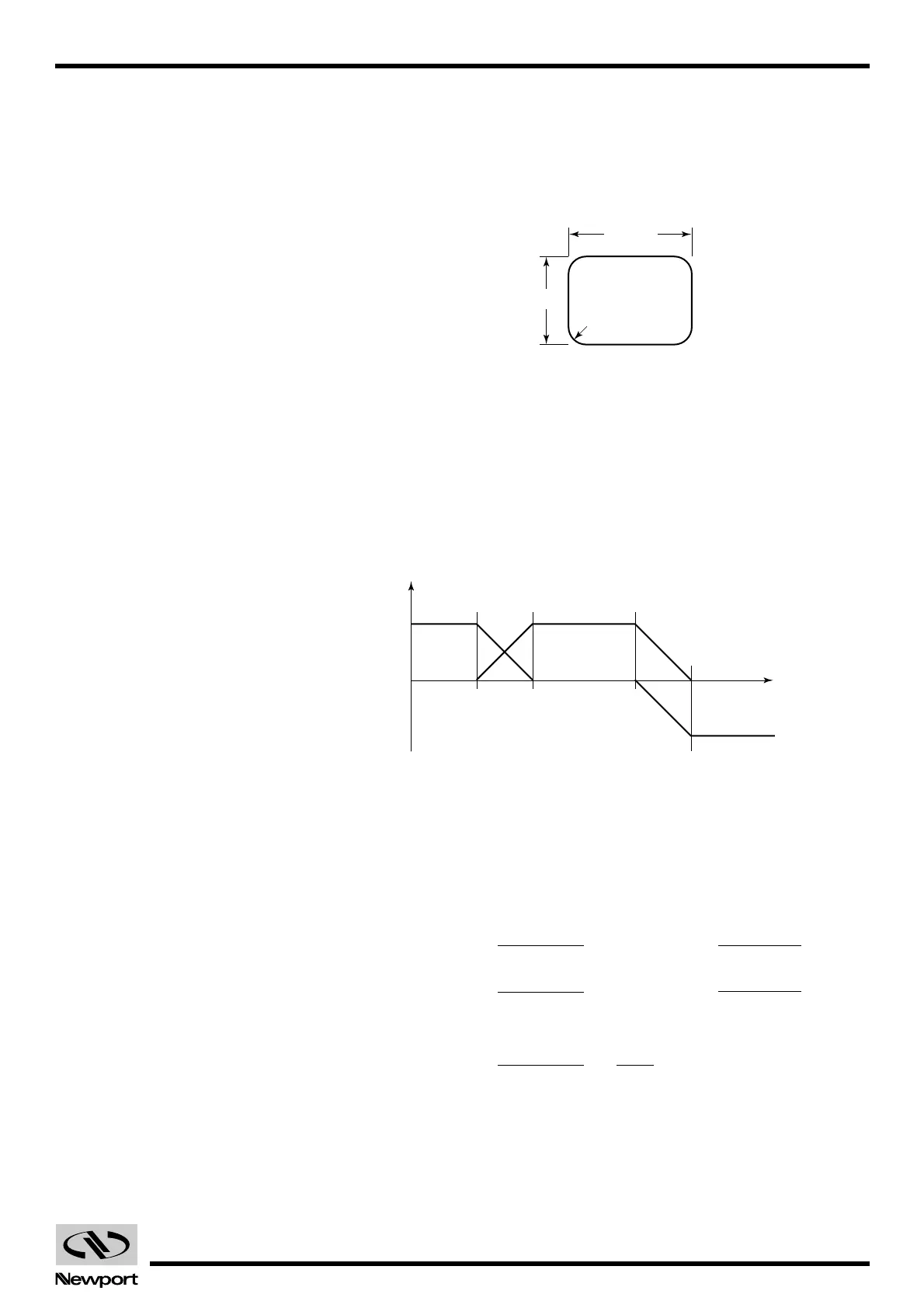
Fig. D.2 — Glue Dispensing Pattern.
Notice that there is no need to set the velocities before the synchronized
(interpolated) motion. The controller automatically calculates them to get
the best accuracy possible, without exceeding the pre-set individual veloci-
ties.
Also, when finished with an interpolated motion, always return the axes to
the non-synchronized mode.
Fig. D.3 — Overlapping Axis Acceleration/Deceleration.
Assuming that the desired velocity is 4 mm/sec, we need to calculate the
acceleration and the positions where one axis starts decelerating and the
other accelerating.
We know that an axis must travel 2 mm before reaching a velocity of
4 mm/sec.
Velocity =
∆ Distance
⇒ Time =
∆ Distance
Time Velocity
Acceleration =
∆ Velocity
= ∆ Velocity
•
Velocity
Time ∆ Distance
Since the velocity starts from zero, ∆ Velocity = Velocity.
Acceleration =
Velocity
2
= 42 = 8 mm/sec
2
∆ Distance 2
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...