SHAPING THE FUTURE OF SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS
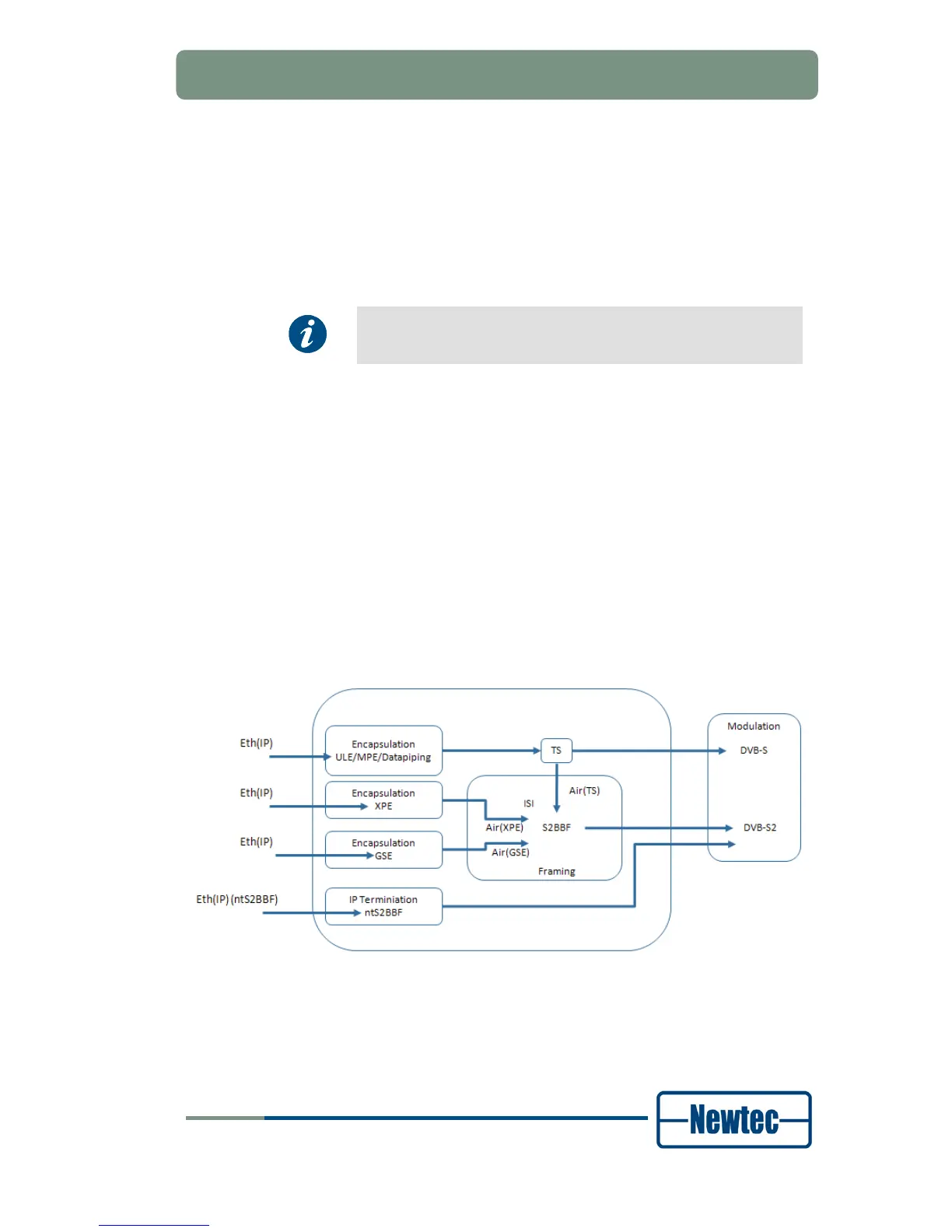
The possibilities for the incoming signal are:
• Eth(IP): The incoming signal is IP and is entering the modulator or leaving the
demodulator via an Ethernet interface (Eth).
Note that any regular Ethernet frame is acceptable, but most often it is used for
Internet Protocol (IP) traffic;
• Eth(ntS2BBF): The incoming signal enters the modulator via an Ethernet
interface (Eth). The incoming Ethernet frames must consist of encapsulated
DVB-S2 Baseband Frames.
In this manual the abbreviation for the Gigabit Ethernet interface is
GbE.
The signal can be modulated using:
• Air(TS): A Transport Stream is carried in a DVB-S or DVB-S2 carrier. The
transported data is first encapsulated in a Transport Stream in MPE, ULE or
data piping mode. The encapsulation/decapsulation is performed in the
modulator/demodulator;
• Air(XPE): IP data is encapsulated in XPE and carried directly in DVB-S2 Base
Band Frames. XPE encapsulation/decapsulation is performed in the
modulator/demodulator;
• Air (GSE): IP data is encapsulated in GSE and carried directly in DVB-S2 Base
Band Frames. GSE encapsulation/decapsulation is performed in the
modulator/demodulator;
• Air(S2BBF): Incoming baseband frames are modulated directly on the DVB-S2
carrier without additional processing.
Figure 63- GbE Processing
 Loading...
Loading...