31
Using FINS Commands Section 3-2
3-2-1 Issuing and using any command (CMND (490) instruction)
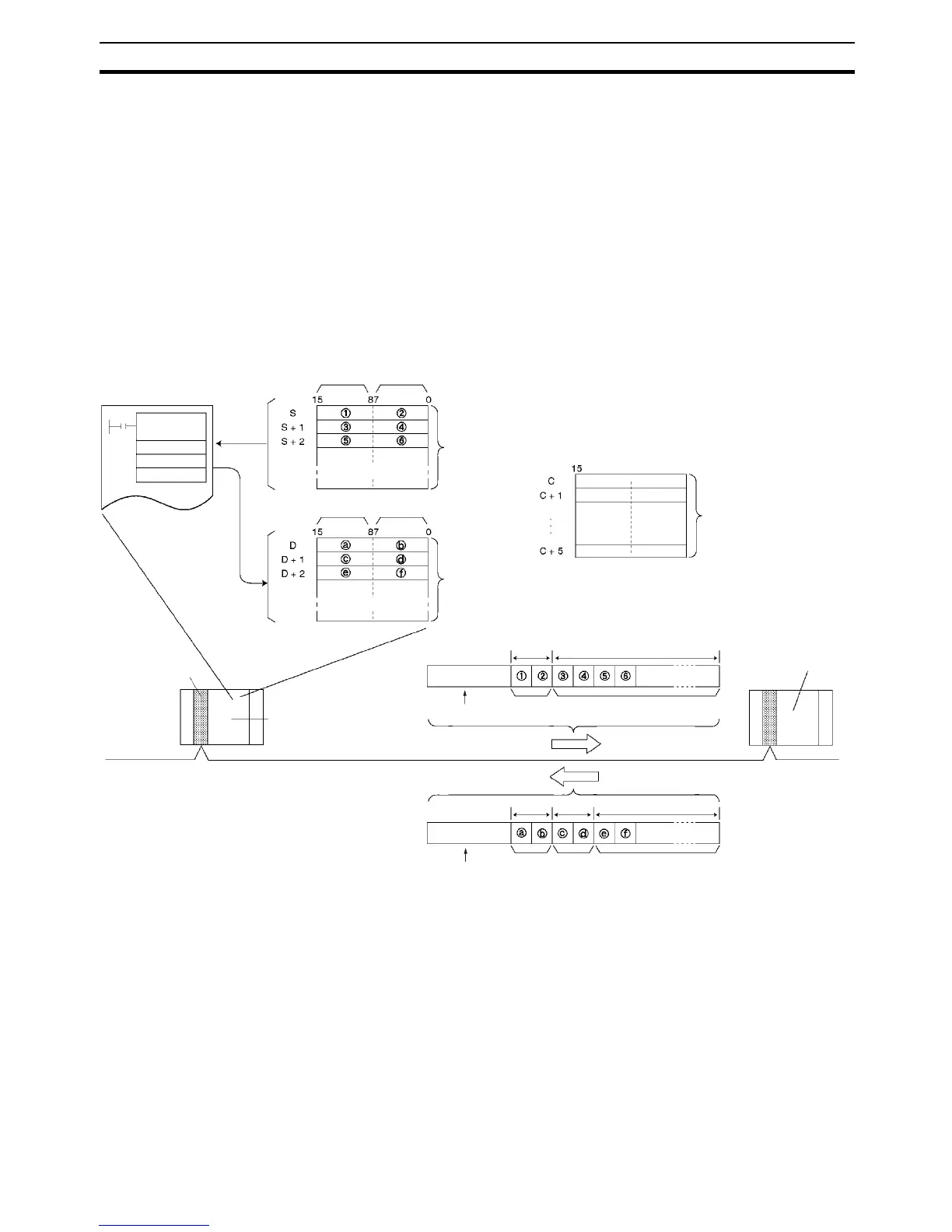
The procedure for execution by CMND instruction is described below.
1,2,3... 1. Store the command format of the FINS command (i.e., the command data)
in an I/O memory area, such as the DM area.
2. In the same way, store the control data (number of bytes of transmission
data, destination address, etc.) in an I/O memory area, such as the DM ar-
ea.
3. Designate S (first command word), D (first response word), and C (first
control word) for the CMND(490) operands, and execute the instruction.
4. When the FINS response is returned from the destination node (a CS/CJ/
CP-series CPU Unit or an NSJ Controller), the data will be stored accord-
ing to the response format beginning at the first response word.
Note FINS commands and responses are handled as binary data, and data is sent
and received in binary format. (Host Link communications, however, are basi-
cally in ASCII.)
3-2-2 Using with respect to a host computer connected by Host Link
With Host Link communications, a FINS command frame with a Host Link
header and a terminator is sent from a host computer to a CS/CJ/CP-series
CPU Unit or NSJ Controller. The basic frame formats are shown below.
Note Host Link communications handle ASCII data, so data is sent and received in
ASCII. For that reason, FINS command and response frames must also be
sent and received in ASCII when they are handled using Host Link communi-
cations.
CMND(490) execution
Command
Word
1 byte
1 byte
Command format data
1 byte 1 byte
Control data
Designates where to send, etc.
Communications Unit
(Controller Link Unit,
etc.)
CS/CJ-series CPU Unit
CS/CJ-series
CPU Unit
Response frame
2 bytes
2,000 bytes max.
FINS header
2 bytes 1,998 bytes max.2 bytes
Automatically attached.
Command
code
End
code
Tex t
Word
Response format data
FINS header
Automatically attached.
Command
code
Tex t
@CMND
S
D
C
Command frame
Response

 Loading...
Loading...











