139
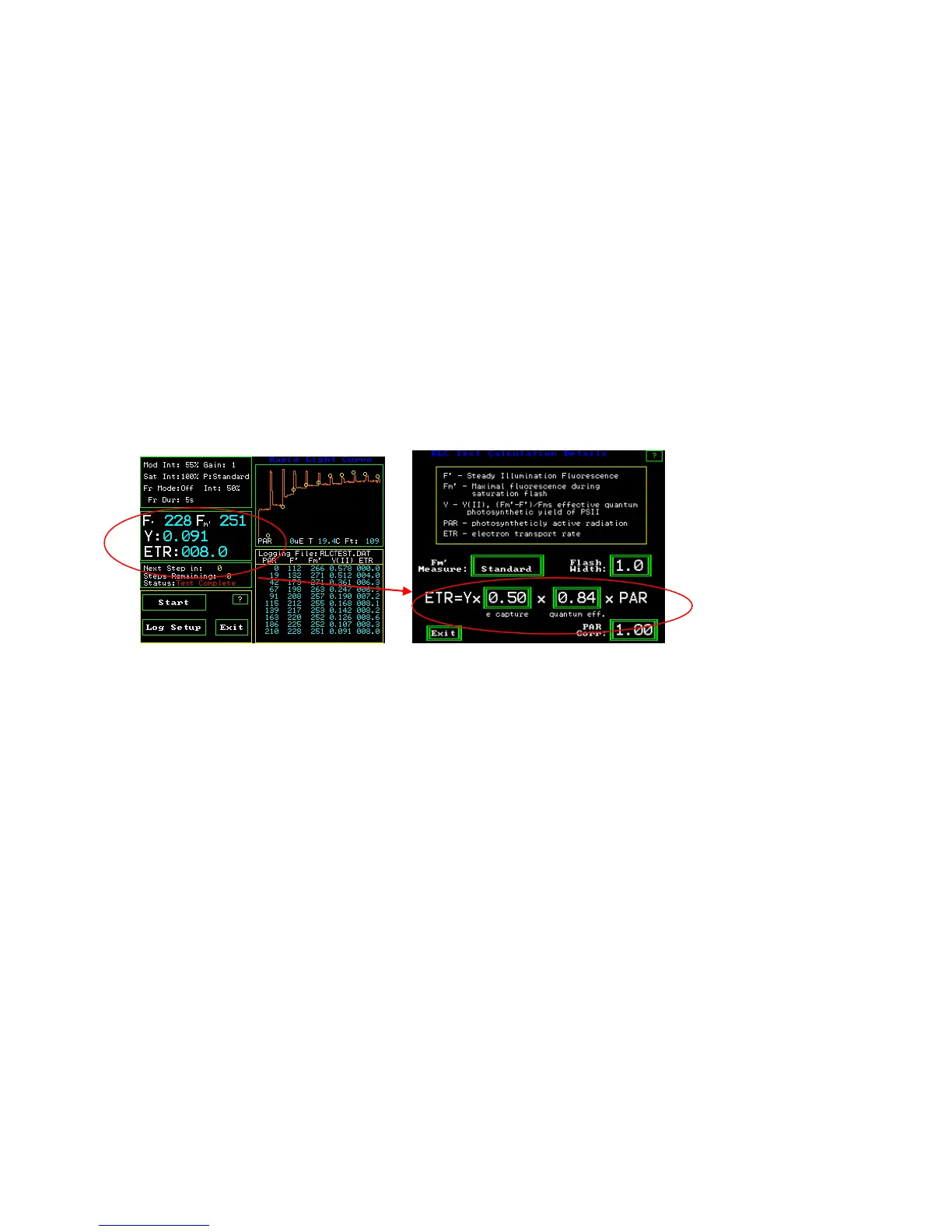
Relative Electron Transport Rate
Relative Electron Transport Rate - ETR :mols = (Yield of PSII) (PAR) (.84) (.5)
(quantum photosynthetic yield of PSII) (measured Photosynthetically Active Radiation
measured in :mols quanta m
-2
s
-1
.)( leaf absorption coefficient)(fraction of absorbed light
by PSII antennae)
Average plant values are used in the standard equation. 0.84 is a good average value for
many species of plants (Bjorkman and Demming, 1987). Research has shown that the
leaf absorption coefficient can vary between 0.7 and 0.9 (Eichelman H. 2004), with
species, chlorophyll content, and water content. Research has also shown that the fraction
of light that is absorbed by PSII varies by species and can range from at least .40 to .60
(Laisk and Loreto,1996). Even if the default average values are used, ETR can provide
useful relative comparative information between different samples and the same sample
under different conditions.
RLC Measuring Screen RLC ETR Calculation Details Screen
For more exact ETR values, the user can refer to papers by (Eichelman H. 2004) (Laisk
and Loreto,1996) ( Edwards & Baker 2002). The ratio of PSII reaction centers to PSI
reaction centers change with plant species and type. The number of PSII reaction centers
tends to be lower in C
4
plants than in C
3
plants (Laisk and Loreto,1996).
The ratio of PSII reaction centers can be changed in the equation, on the OS1p, by
pressing “e capture” and using the key board screen. Similarly, the over all leaf
absorption can be changed by pressing “quantum eff”. This correction is not needed for
most relative comparison ETR applications, however, it has been made available for
more exacting work when necessary.
“PAR Corr” is for correcting PAR sensor location error according to Rascher (2000).
When some artificial light sources are used, Rascher found that the location the PAR
sensor relative to the leaf surface can cause an error of up to 10%. This error is
insignificant if sun light is used due to the much greater distance from the light source.
Rascher used an independent PAR sensor and measured the intensity at the leaf plane. He
then made corrections due to PAR Clip sensor location, by comparing the differences
between the PAR clip values, and the leaf plane values. This correction may not be
needed for most relative comparison ETR applications, however it has been made
available for more exacting work when necessary.
 Loading...
Loading...