31
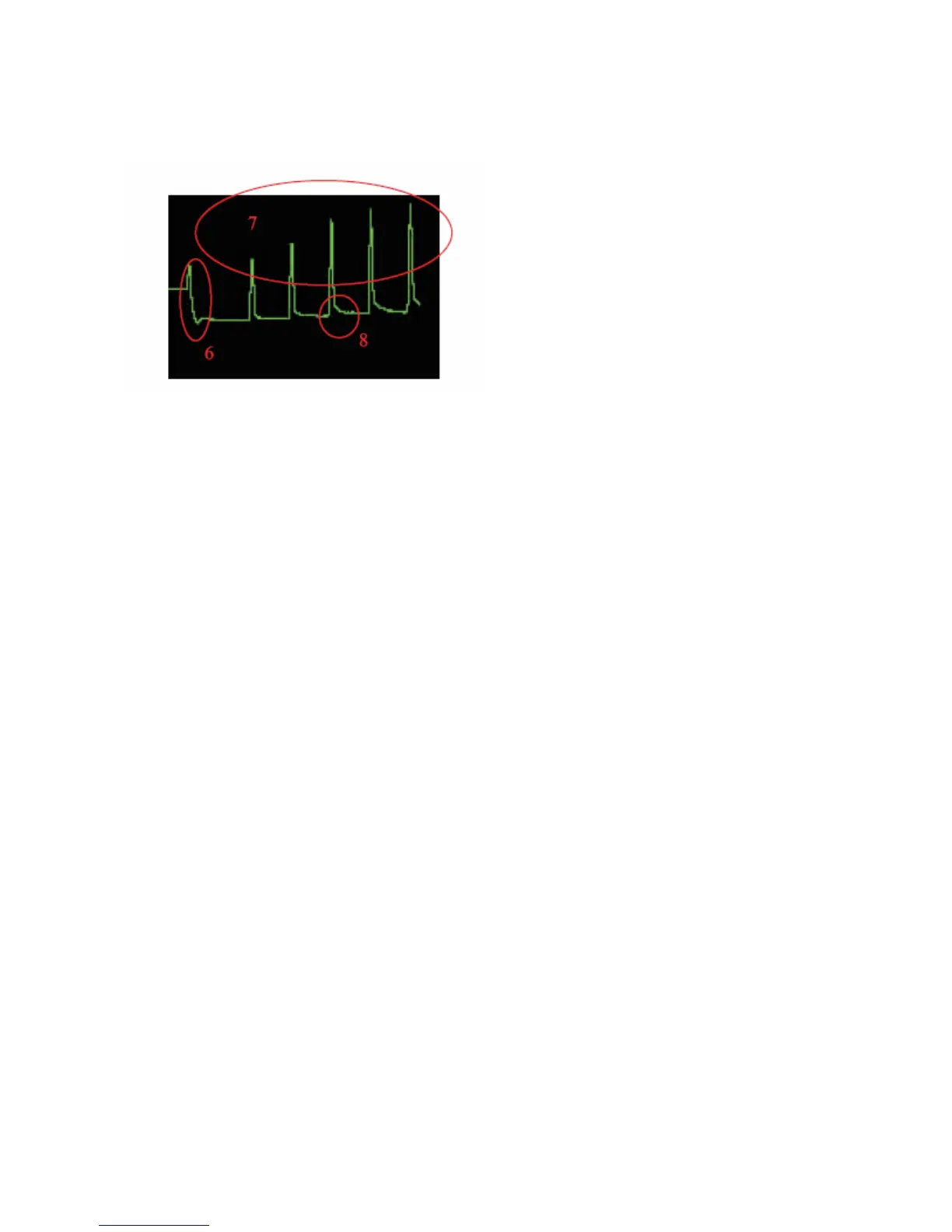
# 6
At this point the actinic light source is turned off, and a far red light is turned on for several
seconds to activate PSI and drain all remaining electrons from PSII. This results in a
quenched measurement of Fo called Fo’ or Fod, the minimum value measured. Fod is used in
the quenching parameters q
P
, q
L
, q
N
, and Kramer’s Y(NPQ), and Y(NO). It has also been used
in q
E
, q
T
, and q
I
when q
N
is used in place of NPQ. After five to ten seconds, the far red light
is turned off. The Far red light at 735 nm is too long to drive PSII, but it will drive PSI.
# 7
This section of the graph is used for non-photochemical quenching relaxation measurements
required in the puddle model for separation of qE, qT, and qI. During this phase of the graph,
the actinic light is automatically turned off and the sample is in the dark. Only the modulated
light and saturation pulses are used here. The increase in the peak height is a result of the
relaxation of non- photochemical mechanism including; photo-protective mechanisms, state
transitions, and eventually photoinhibition. Lichtenthaler found that the relaxation of photo
protective mechanisms that involve )ph of the thylakoid lumen and the xanthophyll cycle
takes between two and four minutes. A saturation pulse at the end of this period can be used
to measure qE (puddle model) photoprotective mechanisms (Lichtenthaler 1999). The
relaxation characteristics of field plants can vary with changing environmental conditions
(Baker 2008).
The relaxation of state transitions takes between fifteen and twenty minutes, so a saturation
pulse after twenty minutes in the dark can provide a measurement of qT. qI or photoinhibition
can also be determined with this peak, because Fm is known from the dark adapted first pulse
and the difference is considered to be photo inhibition. Chronic photoinhibition starts to relax
at about forty minutes in the dark and Lichtenthaler (1999, 2004) found that it could take up
to 60 hours for complete relaxation of photoinhibition.
 Loading...
Loading...