6 Commissioning
6.1 Adapting the direction of control action to the controlled system
Manual
SIPART DR21
C73000-B7476-C143-08
181
6 Commissioning
6.1 Adapting the direction of control action to the controlled
system
D Definitions
Normal control action system
Rising y causes rising x; e.g. an increasing energy supply or mass flow causes a rising
temperature.
Normal effecting actuator (valve):
Increasing current or positioning command +y cause the actuating element (increasing y)
to open, e.g. more energy or greater mass flow. y
displ.
is the displayed manipulated variable.
The direction of control action is referred to the controlled variable x1. The following state-
ments apply for transmitters with normal control action (increasing physical variable causes
increasing transmitter current), increasing process display (dE > dA) and no falling charac-
teristic in the linearizers.
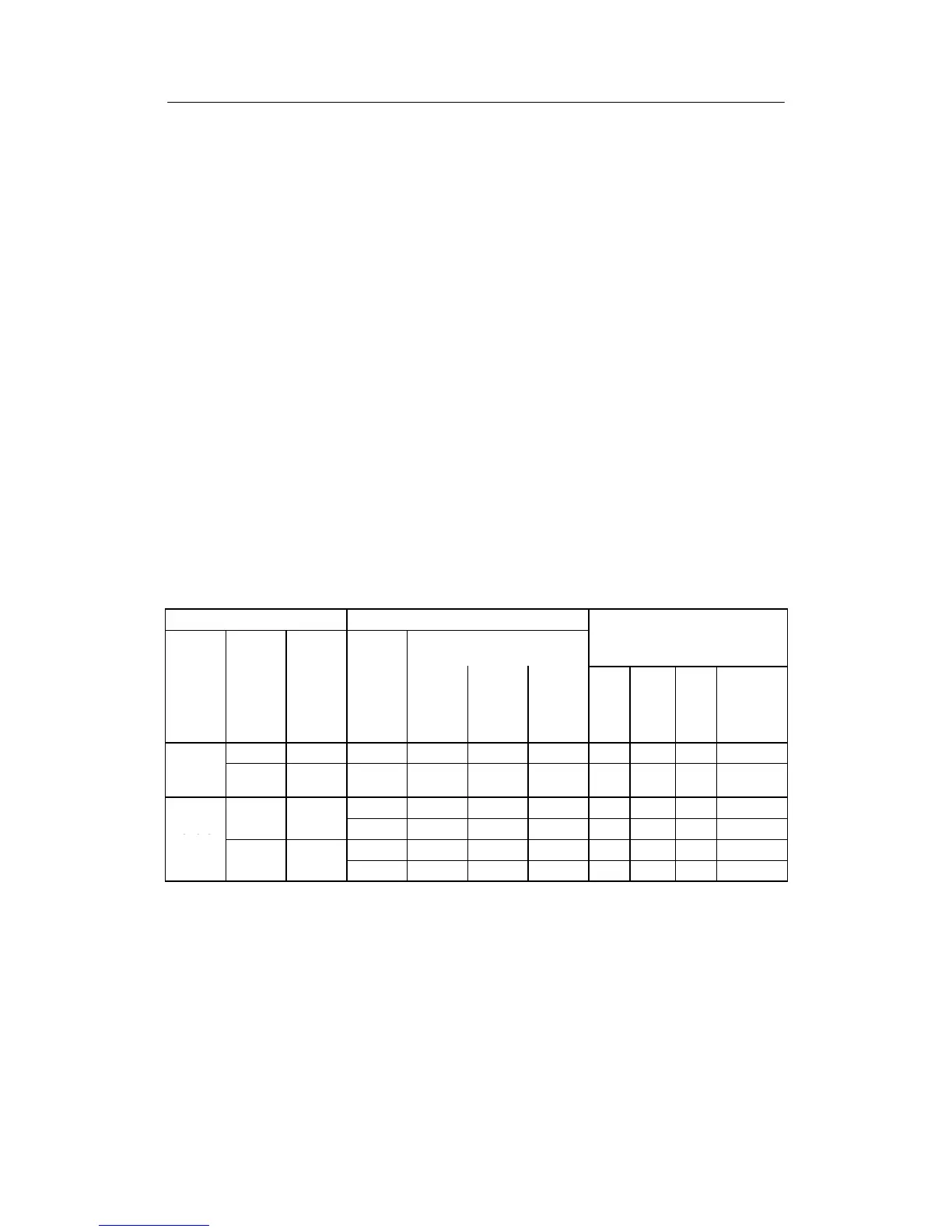
D Direction of control action of system and final control element known
K-controller
The following is prescribed: Select the desired control action here:
normal 100 % rises closes rises 0 pos. 0 y
ing
0% falls opens falls 0 pos. 1 100 % -y
Two more lines could be added to the table which are useless in practice: normal action system in which the actual values
falls with a rising change in the manipulated variable.
Table 6-1 Direction of control action and y-display direction of control action of the system- and final
control element direction of control action in K-controllers

 Loading...
Loading...











