2.24 Motor Starting Time Supervision (ANSI 48)
147
7UM61 Manual
C53000-G1176-C127-3
Example: Motor with the following data:
Rated voltage U
N
= 6600 V
Rated current I
Mot.nom
= 126 A
Starting current I
StartCurr.
= 624 A
Long-Term Current Rating I
max
= 135 A
Startup Duration for I
StartCurr.
T
Startmax
= 8.5 s
CT Ratio I
N CTprim
/I
N CTsec
200 A / 1 A
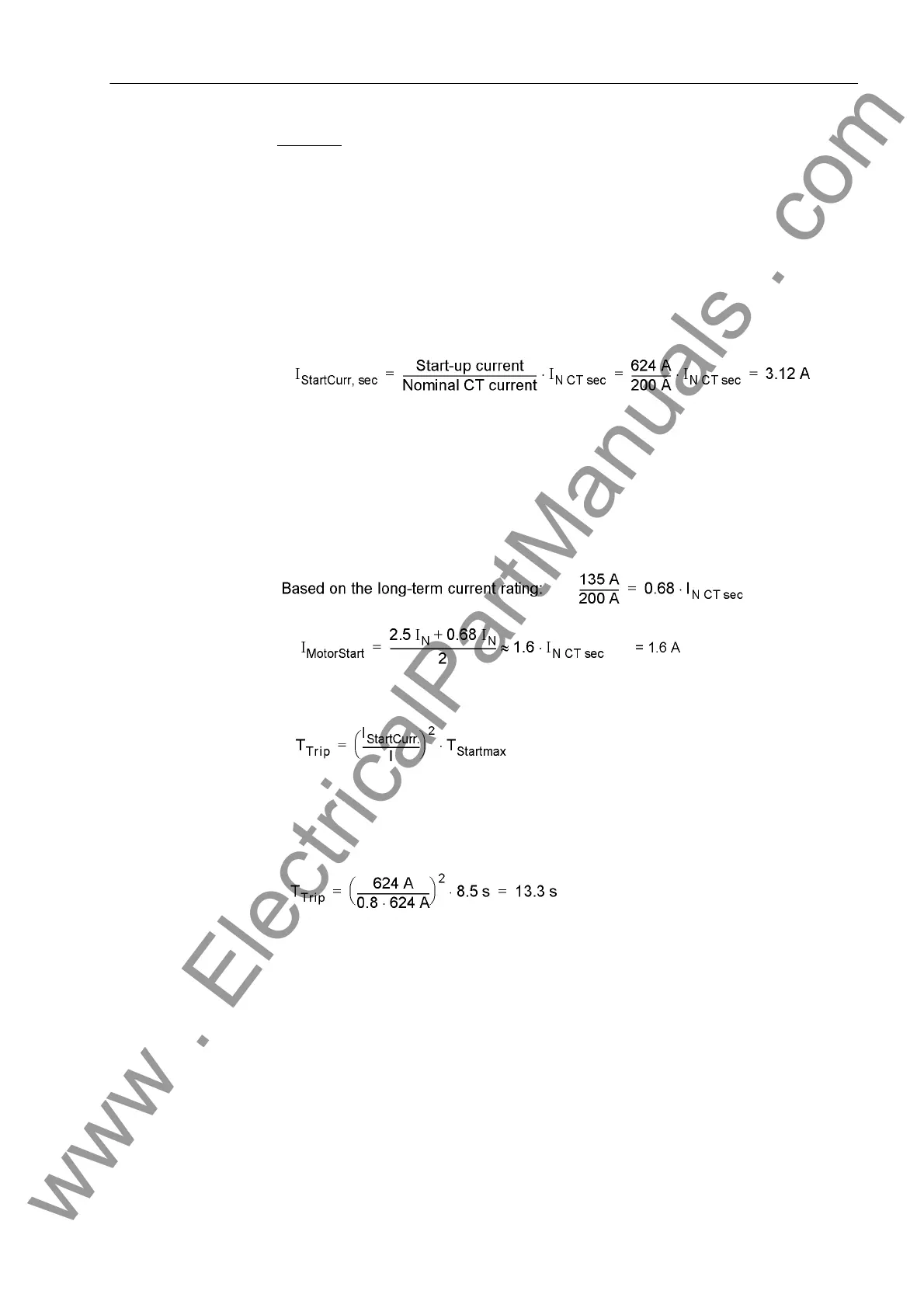
The setting for address START. CURRENT is calculated as follows:
For reduced voltage, the startup current is also reduced almost linearly. At 80%
nominal voltage, the startup current in this example is reduced to 0.8 · I
Startcurr.
= 2.5 · I
N
CTsec
The setting for detection of a motor startup must lie above the maximum load current
and below the minimum startup current. If no other influencing factors are present
(peak loads), the value for motor startup I MOTOR START set at address 6505 may
be set to an average value:
The tripping time of the starting time monitoring is calculated as follows:
Under nominal conditions, the tripping time is the maximum starting time T
Max.STARTUP
.
For ratios deviating from nominal conditions, the motor tripping time changes. At 80%
of nominal voltage (which corresponds to 80% of nominal starting current), the tripping
time is for example:
After the delay time LOCK ROTOR TIME has expired, the binary input becomes effec-
tive and initiates a tripping signal. If the blocked rotor time is set to a value that the
binary input “>Rotor locked” (No. 6805) is reliably reset during the delay time
LOCK ROTOR TIME, faster tripping will be available during motor starting under locked
rotor conditions.
www . ElectricalPartManuals . com

 Loading...
Loading...











