2.29 Trip Circuit Supervision
181
7UM61 Manual
C53000-G1176-C127-3
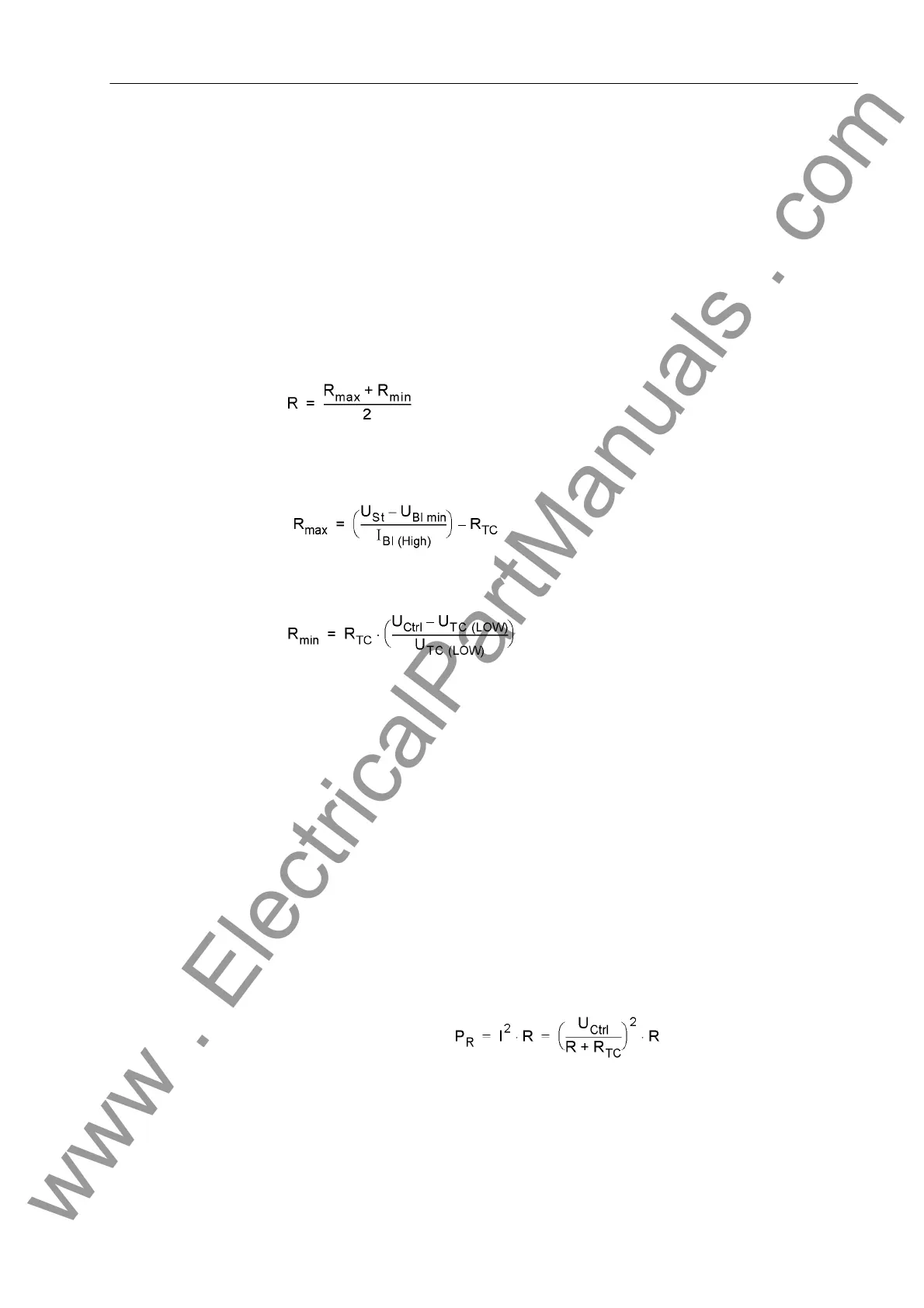
When using only one binary input, a resistor R is inserted into the circuit on the system
side, instead of the missing second binary input. Through appropriate sizing of the re-
sistor and depending on the system conditions, a lower control voltage can often be
sufficient. The resistor R is inserted into the circuit of the second circuit breaker auxil-
iary contact (AuxCont2) to detect a malfunction also when the circuit breaker auxiliary
contact (AuxCont1) is open, and the trip contact has dropped out (see Principle of Trip
Circuit Monitoring with One Binary Input figure). This resistor must be sized such that
the circuit breaker trip coil (CBTC) is no longer energized when the circuit breaker is
open (which means AuxCont1 is open and AuxCont2 is closed). Binary input (BI1)
should still be picked up when the trip contact is simultaneously opened.
This results in an upper limit for the resistance R
max
, and a lower limit R
min
, from which
the optimal value of the arithmetic mean R should be selected:
In order that the minimum voltage for controlling the binary input is ensured, the result
for R
max
is:
So the circuit breaker trip coil does not remain energized in the above case, R
min
is
derived as:
with
I
BI (HIGH)
Constant current with activated BI ( = 1.8 mA)
U
BI min
minimum control voltage for BI (19 V for delivery setting for nominal
voltages 24/48/60 V; 88 V for delivery setting for nominal voltages
110/125/220/250 V)
U
Ctrl
Control Voltage for Trip Circuit
R
CBTC
DC Resistance of circuit breaker trip coil
U
CBTC (LOW)
Maximum voltage on the circuit breaker trip coil that does not lead to
tripping
If the calculation results that R
max
< R
min
, then the calculation must be repeated, with
the next lowest switching threshold UBE min, and this threshold must be implemented
in the device using jumper(s).
For power consumption of the resistance:
www . ElectricalPartManuals . com

 Loading...
Loading...











