Version 5.2 Sourcefire 3D System Installation Guide 44
Understanding Deployment
Deployment Options
Chapter 2
The sample deployment illustrates common network segments. Deploying your
managed devices in each of these locations serves different purposes. The
following sections describe typical location recommendations:
• Inside the Firewall on page 44 explains how access control functions on
traffic that passes through the firewall.
• On the DMZ on page 45 explains how access control within the DMZ can
protect outward-facing servers.
• On the Internal Network on page 46 explains how access control can
protect your internal network from intentional or accidental attack.
• On the Core Network on page 46 explains how an access control policy
with strict rules can protect your critical assets.
• On a Remote or Mobile Network on page 47 explains how access control
can monitor and protect the network from traffic at remote locations or on
mobile devices.
Inside the Firewall
Managed devices inside the firewall monitor inbound traffic allowed by the
firewall or traffic that passes the firewall due to misconfiguration. Common
network segments include the DMZ, the internal network, the core, mobile
access, and remote networks.
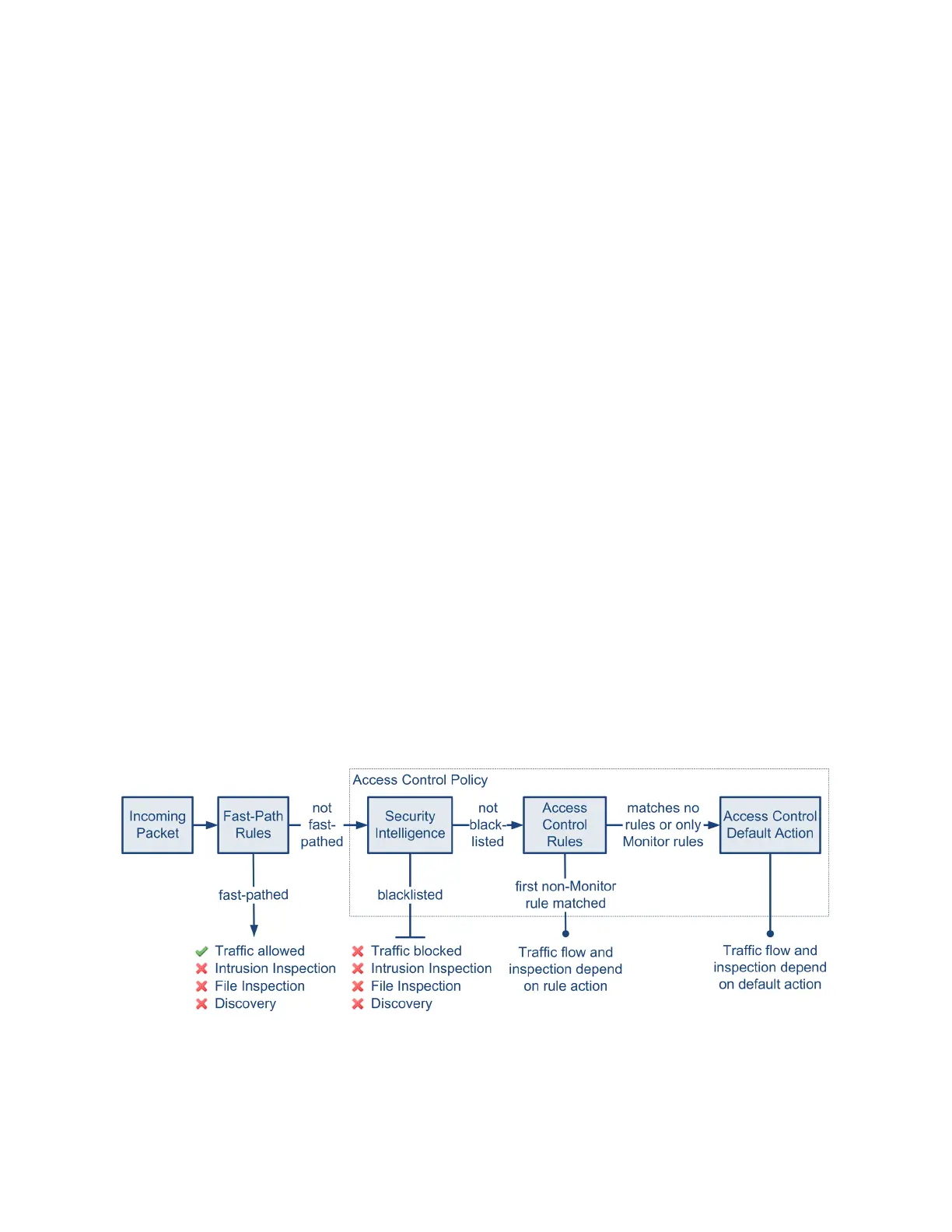
The diagram below illustrates traffic flow through the Sourcefire 3D System, and
provide some details on the types of inspection performed on that traffic. Note
that the system does not inspect fast-pathed or blacklisted traffic. For traffic
handled by an access control rule or default action, flow and inspection depend on
the rule action. Although rule actions are not shown in the diagram for simplicity,
the system does not perform any kind of inspection on trusted or blocked traffic.
Additionally, file inspection is not supported with the default action.
An incoming packet is first checked against any fast-path rules. If there is a match,
the traffic is fast-pathed. If there is no match, Security Intelligence-based filtering
determines if the packet is blacklisted. If not, any access control rules are applied.
 Loading...
Loading...