1-9
IM MV1000-01E
Feature Overview
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
App
Index
1.4 Display
Common Display functions
• LCD Display and Its Layout
The MV1000 has a 5.5-inch (240 × 320 dot resolution) TFT color LCD. The MV2000
has a 10.4-inch (480 × 640 dot resolution) TFT color LCD. The display consists of a
status display section and a data display section.
The MV1000 D
isplay
Status display section
Data display section
• Status Display Section
The status display section indicates the display name, date/time, batch name
(when using the batch function), user name (when using the login function), internal
memory and CF card usage, alarm occurrence, computation status (/M1 or /PM1
option), key lock status, and e-mail transmission.
• Data Display Section
The data display section shows measured data using numbers, waveforms, and
bar graphs. It displays a conguration screen when you are conguring a function.
• Group Display
On the trend, digital, and bar graph displays, channel data is displayed in preset
groups. With the MV1000, you can register up to 10 groups, each with up to 6
channels. With the MV2000, you can register up to 36 groups, each with up to 10
channels. The same groups are used for the trend, digital, and bar graph displays.
Displayed groups can be switched automatically at specied in
tervals (5 s to 1 min).
For conguration instructions, see section 6.1.
• Channel Number Display and Tag Name Display
You can choose to label displayed channels according to their tag names or according
to their channel numbers. This setting applies to all channels.
For conguration instructions, see section 6.2.
• Update Interval of Measured Values
Measured values are updated every second. However, if the scan interval is longer
than 1 s, measured values are updated at the scan interval.
For conguration instructions, see section 6.3.
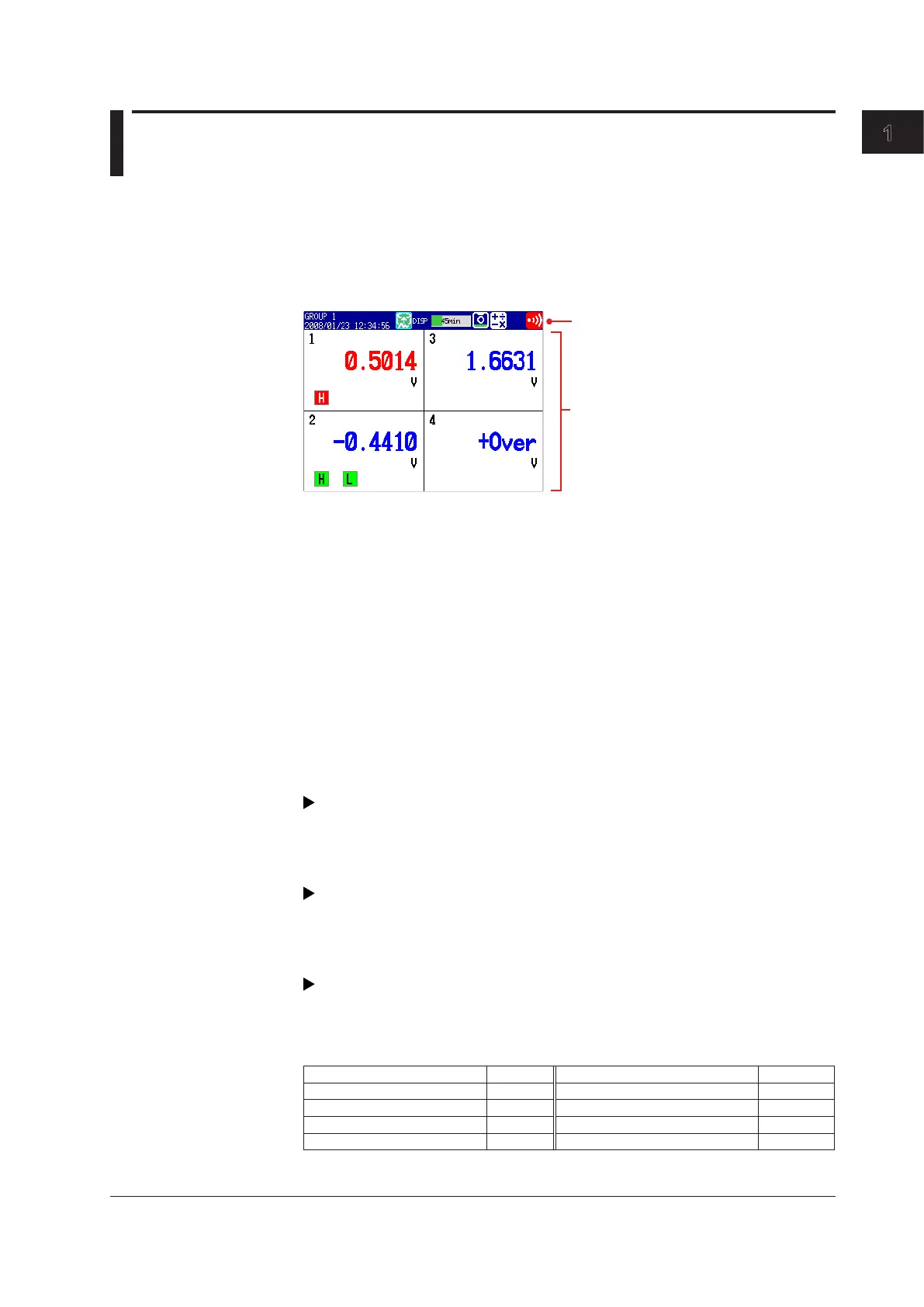
• Alarm Indication
The MV regularly checks for the alarms set to each channel and indicates alarms with
the following symbols:
Alarm Type Symbol Alarm Type Symbol
High limit alarm H High limit on rate-of-change alarm R
Low limit alarm L Low limit on rate-of-change alarm r
Difference high limit alarm h Delay high limit alarm T
Difference low limit alarm l Delay low limit alarm t

 Loading...
Loading...