Display and Event Data Recording Methods
For configuration instructions, see section 4.1. For operating instructions, see section
4.4.
• Types of Recorded Data
You can choose to record display data only, event and display data, or event data
only.
Choosing What Type of Data to Record
Record the type of data that meets your needs. Use the following examples for
reference.
Example 1 To record continuous waveform data only
, just like conventional chart
recorders:
Record display data.
Example 2 To record waveform data continuously and record more detailed data
before and after an alarm event:
Record display data continuously and use an alarm to trigger the
recording of event data.
Example 3 T
o continuously record data that is as detailed as possible:
Set the sampling interval and record event data.
Example 4 If there is no need to record data continuously but you want to record
data when an alarm occurs:
Use an alarm to trigger the recording of event data.
• Internal Memory
Measured data is partitioned and saved to les at set intervals. If the internal memory
is full or if the number of display data les and event data les exceeds 400, les are
overwritten from the oldest le.
• Display Data Recording Conditions
Item Description
Channel type You can set the channel type to measurement, computation, or
(only with the MV2000) external input.
Sampling interval Determined by setting the Trend/Storage interval. Choices are
available in the range of 5 s to 10 h. You cannot choose an
interval that is faster than the scan interval.
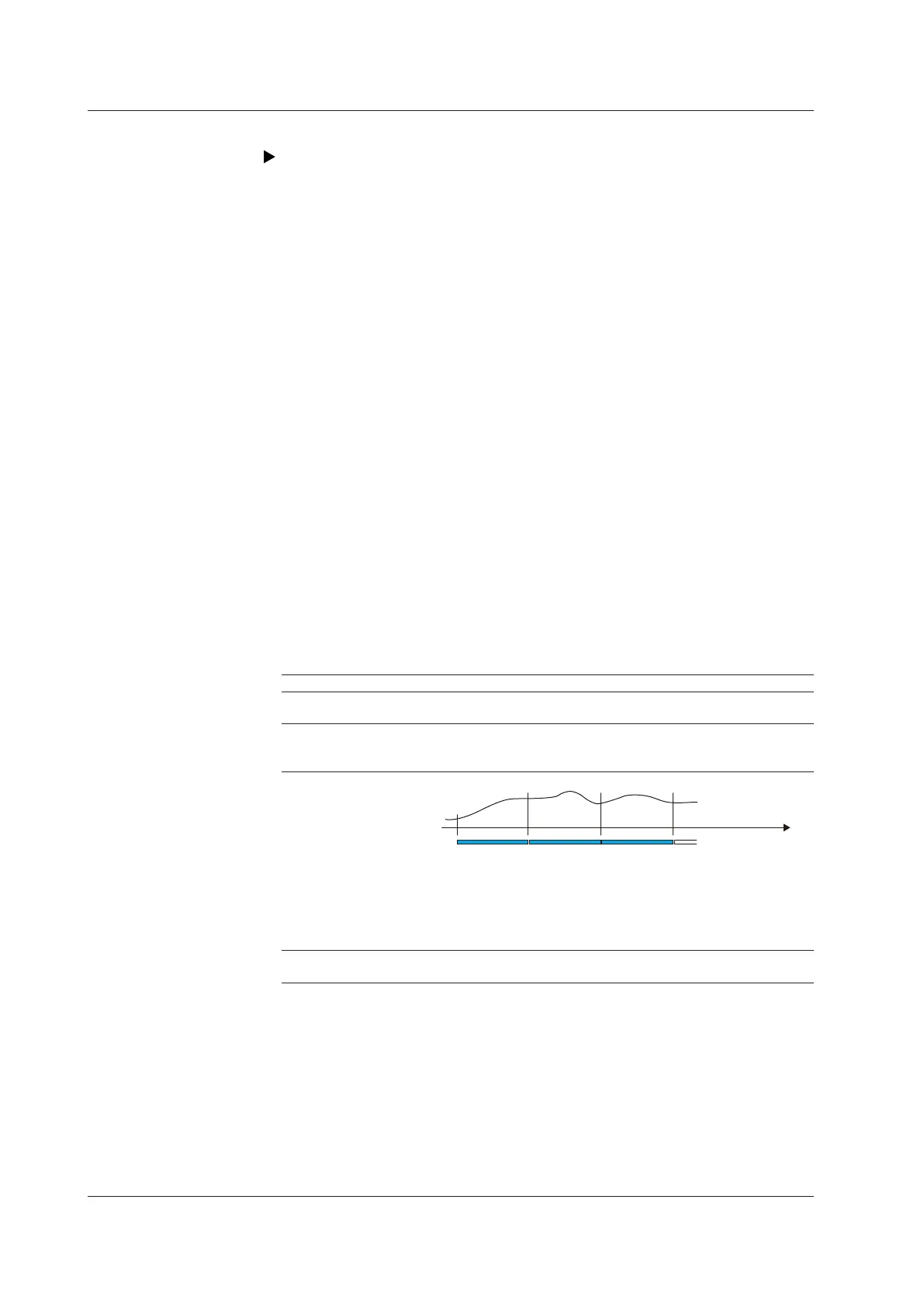
File generation Files are generated at the set file save interval.
Time
File File File Adding data
Files are also generated in these cases:
• When you generate a file manually.
• When there is a memory stop.
• When a file is generated using the event action function.
• After recovering from a power failure.
Memory start/stop Pressing START/STOP starts recording (memory start). Pressing
START/STOP again stops recording (memory stop).
1.5 Data Storage Functions

 Loading...
Loading...