2-8
Making Mixer Measurements
Measurement Considerations
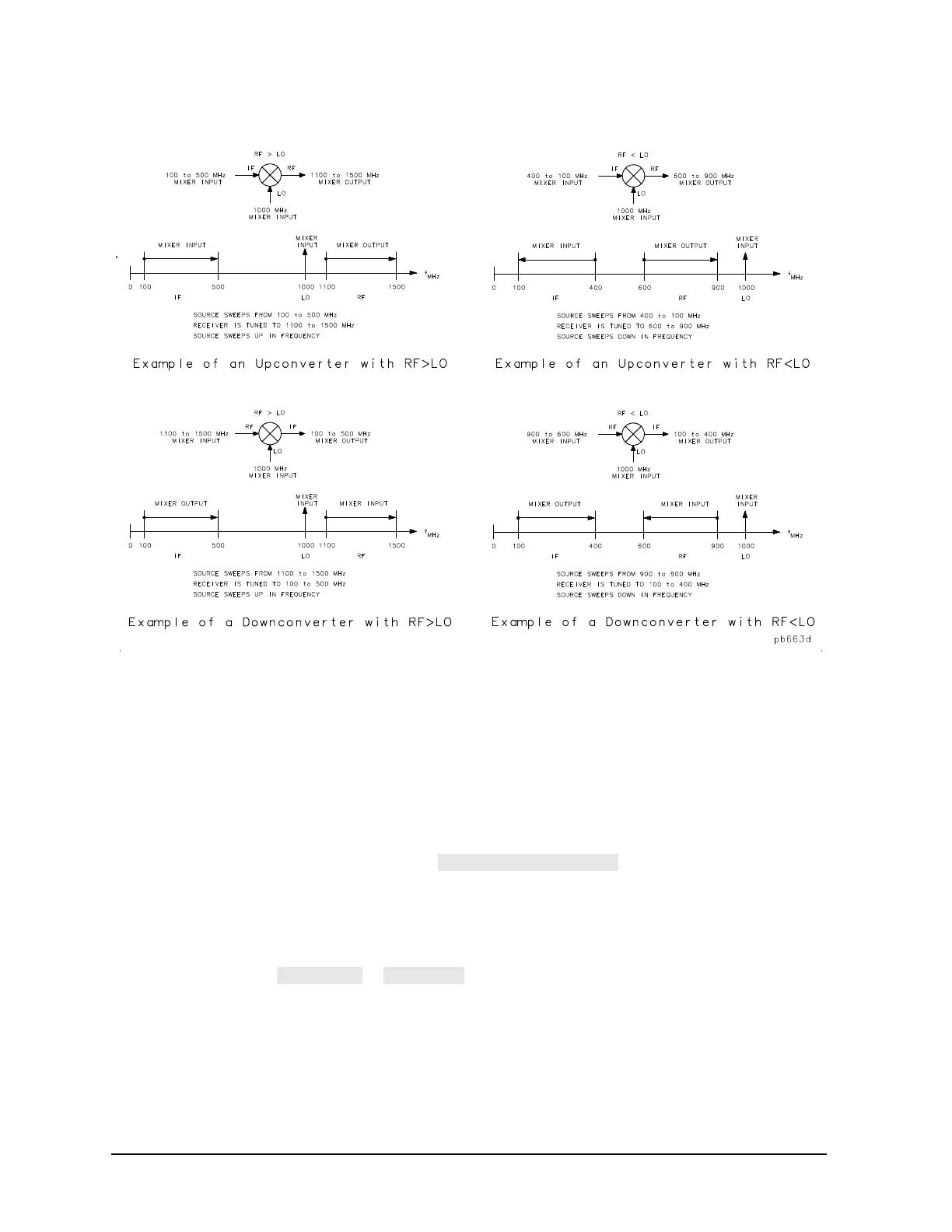
Figure 2-6 Examples of Up Converters and Down Converters
In standard mixer measurements, the input of the mixer is always connected to the analyzer's RF source,
and the output of the mixer always produces the IF frequencies that are received by the analyzer's receiver.
However, the ports labeled RF and IF on most mixers are not consistently connected to the analyzer's source
and receiver ports, respectively. These mixer ports are switched, depending on whether a down converter or
an up converter measurement is being performed.
It is important to keep in mind that in the setup diagrams of the frequency offset mode, the analyzer's source
and receiver ports are labeled according to the mixer port to which they are connected.
• In a down converter measurement where the softkey is selected, the
notation on the analyzer's setup diagram indicates that the analyzer's source frequency is labeled RF,
connecting to the mixer RF port, and the analyzer's receiver frequency is labeled IF, connecting to the
mixer IF port.
Because the RF frequency can be greater or less than the set LO frequency in this type of measurement,
you can select either
or .

 Loading...
Loading...















