2- 49
Making Mixer Measurements
Isolation Example Measurements
SWR / Return Loss
Reflection coefficient () is defined as the ratio between the reflected voltage (V
r
) and incident voltage (V
i
).
Standing wave ratio (SWR) is defined as the ratio of maximum standing wave voltage to the minimum
standing wave voltage and can be derived from the reflection coefficient () using the following equation.
Return loss can be derived from the reflection coefficient as well.
NOTE Mixers are three-port devices, and the reflection from any one port depends on the
conditions of the other two ports. You should replicate the operating conditions the mixer
will experience as closely as possible for the measurement. For all mixer SWR
measurements, use the same power level that the mixer will use during normal operation.
When you measure the RF port SWR, you should have the LO drive level present and set to the expected
frequency and power levels. Different LO drives and frequencies may yield different values for SWR at the
same RF frequencies. The IF port should be terminated in a condition as close to its operating state as
possible.
The measurements of LO port SWR and IF port SWR are very similar. For IF port SWR, you should terminate
the RF port in a matched condition and apply the LO signal at its normal operating level. For the LO port
SWR, the RF and IF ports should both be terminated in conditions similar to what will be present during
normal operation.
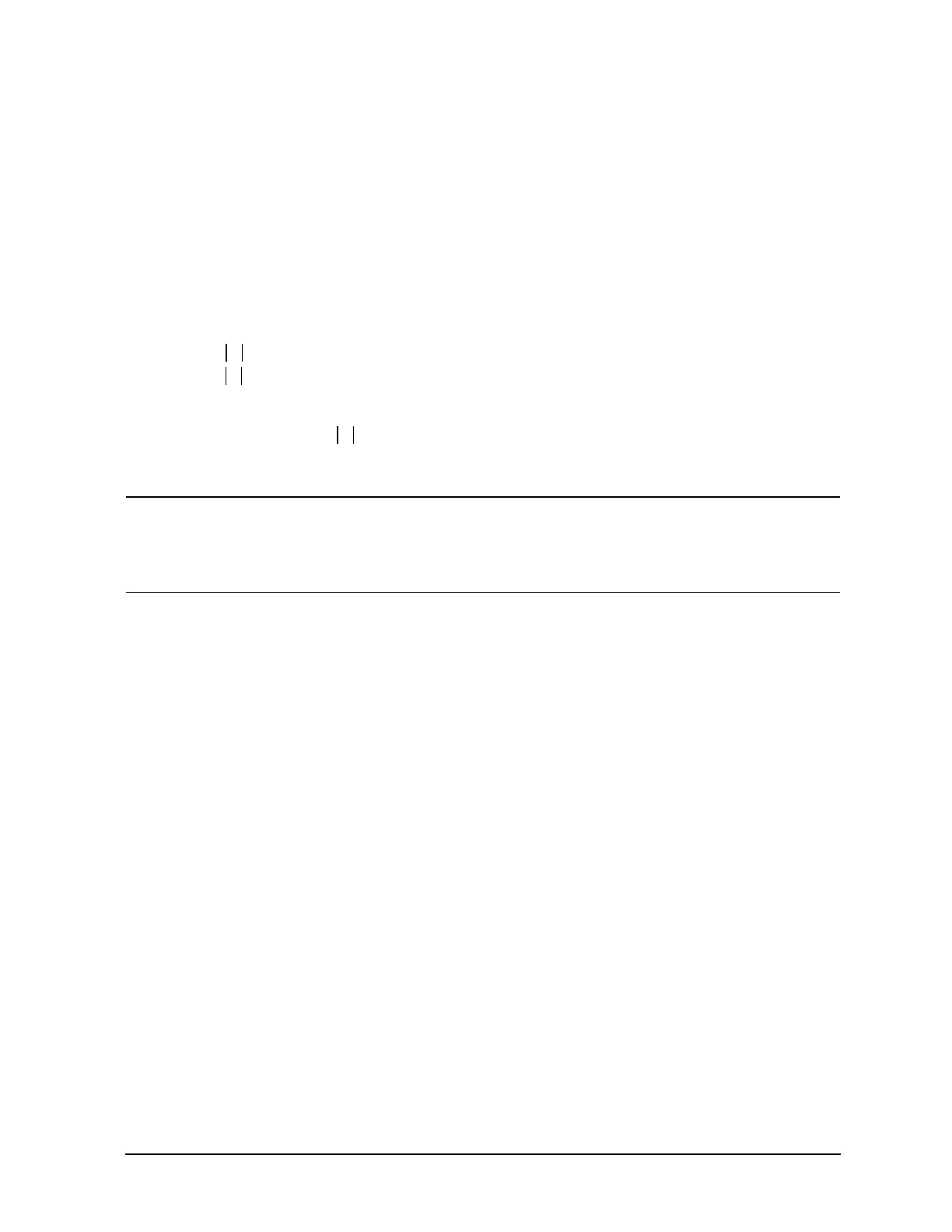
SWR
1 +
1 –
---------------=

 Loading...
Loading...















