xvii
Cutting flammable materials
C
hips of titanium or magnesium violently burn when they catch fire.
Once these chips burn, the resultant fire may explosively propagate
through surrounding chips. When an oil-based cutting fluid is used on
the machine, it may also be ignited and spread the fire.
When cutting such flammable materials, be sure to clean the machine
of accumulated chips at the start and end of every operation. During
automatic operation, stop the machine as required to remove the chips.
Take care so that the cutting fluid is discharged in a sufficient amount
during the cutting operation.
When cutting a flammable material, be sure to prohibit any use of fire in
the shop, install a fire extinguisher or other fire control device near the
machine. Never leave the machine unattended during the cutting
operation.
When carrying or disposing of chips, take due care so that they do not
catch fire. Be sure to prohibit any use of fire where the chips are
stored.
Cutting unknown materials
Before cutting an unknown material, consult the supplier of the material,
burn a small amount of chips from the material in a safe place, or follow
any other procedure to check to see if the material is flammable or not.
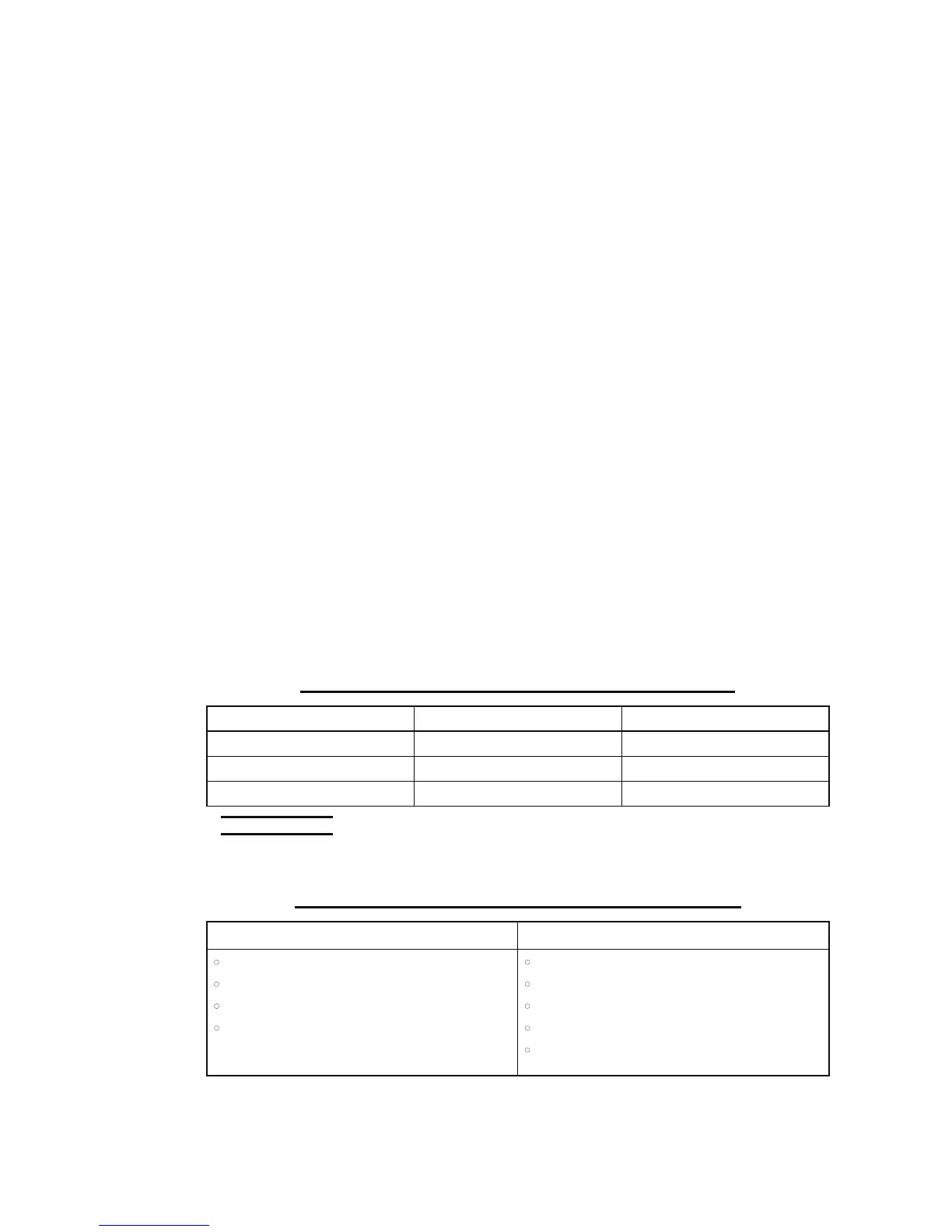
Appendix 1: Classification of water-soluble cutting fluids
Color when diluted Main composition
Soluble Milky white or clear Mineral oil
Semi-synthetic Clear Mineral oil
Synthetic Clear Polymer
NOTE
O Dilute each product to the specified ratio.
Appendix 2: Characteristics of water-soluble cutting fluids
Advantage Disadvantage
x Have high cooling effect
x Not flammable
x Economical
x Do not require cleaning of cut products
(especially when soluble)
x Remove paint
x Lose rust protection effect when deteriorated
x Foam
x Putrefy
x
Decline in performance, depending on quality of
water used for dilution
 Loading...
Loading...