Section 8. Working with Data Files on the PC
To process these files using the C option, the parameter file would be set up as
follows (assuming the name of our data file is Data_1.DAT):
First Input File = Data_1.DAT:1
Stop condition = C,1[200]
Copy = 1[100]
Select = 1,2,3,4
Second Input File = Data_1.DAT:2
Stop condition = C,1[200]
Copy = 1[101]
Select = 1,2,3
Third Input File = Data_1.DAT:3
Stop condition = C,1[200]
Copy = 1[102]
Select = 1,2,3,4,5
Fourth (“end of test”) Input File = Data_1.DAT:4
Stop condition = C,1[200]
Copy = 1[200]
Select = (leave blank)
The :(number) after the data file name is inserted automatically
by Split.
NOTE
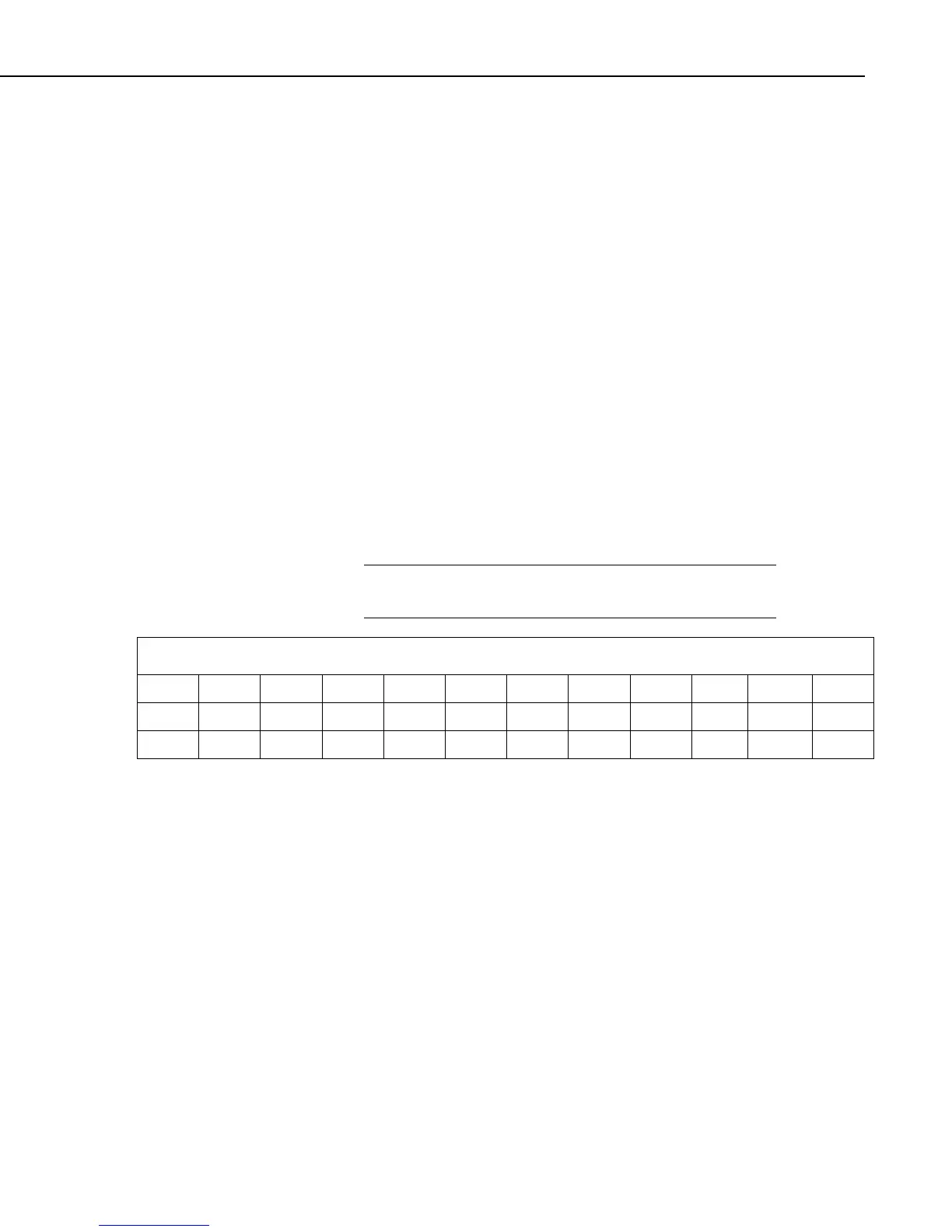
TABLE 8-3. Processed Data File Using Option C
100 12.1 10 32.6 101 92.7 67.7 102 56.1 48.7 98 220.1
100 12.5 9.89 30.1 102 56.2 50 100.5 210.6
100 13.1 10.1 33.1 101 94.1 69
When Split is run, the resulting data file will look similar to TABLE 8-3. Each
line of data represents one test. Notice that blanks were inserted if the data set
(conditional array) did not exist.
8.2.3.1.4.2 Trigger on Stop Condition (F Option) Output of Time Series
The Trigger on Stop Condition, or F option, changes the function of the Stop
Condition when one or more Time Series functions (Section 8.2.3.1.11, Time
Series Functions, Details, and Examples) are contained in the Select field.
When a Stop Condition is met, the time series data is calculated and written to
the output file. However, instead of stopping at this point, processing resumes
and time series data is output the next time the Stop Condition is met. This
continues until the end of file or until the user stops Split manually.
The Trigger on Stop Condition is enabled by clicking Other… on the Output
Tab and checking the box next to the Trigger on Stop Condition field. When
the Trigger on Stop Condition is enabled, the function affects all files being
processed that have a Stop Condition specified. If multiple files are being
8-51
 Loading...
Loading...