Section 8. Working with Data Files on the PC
8.2.3.1.10 Mathematical Functions, Details, and Examples
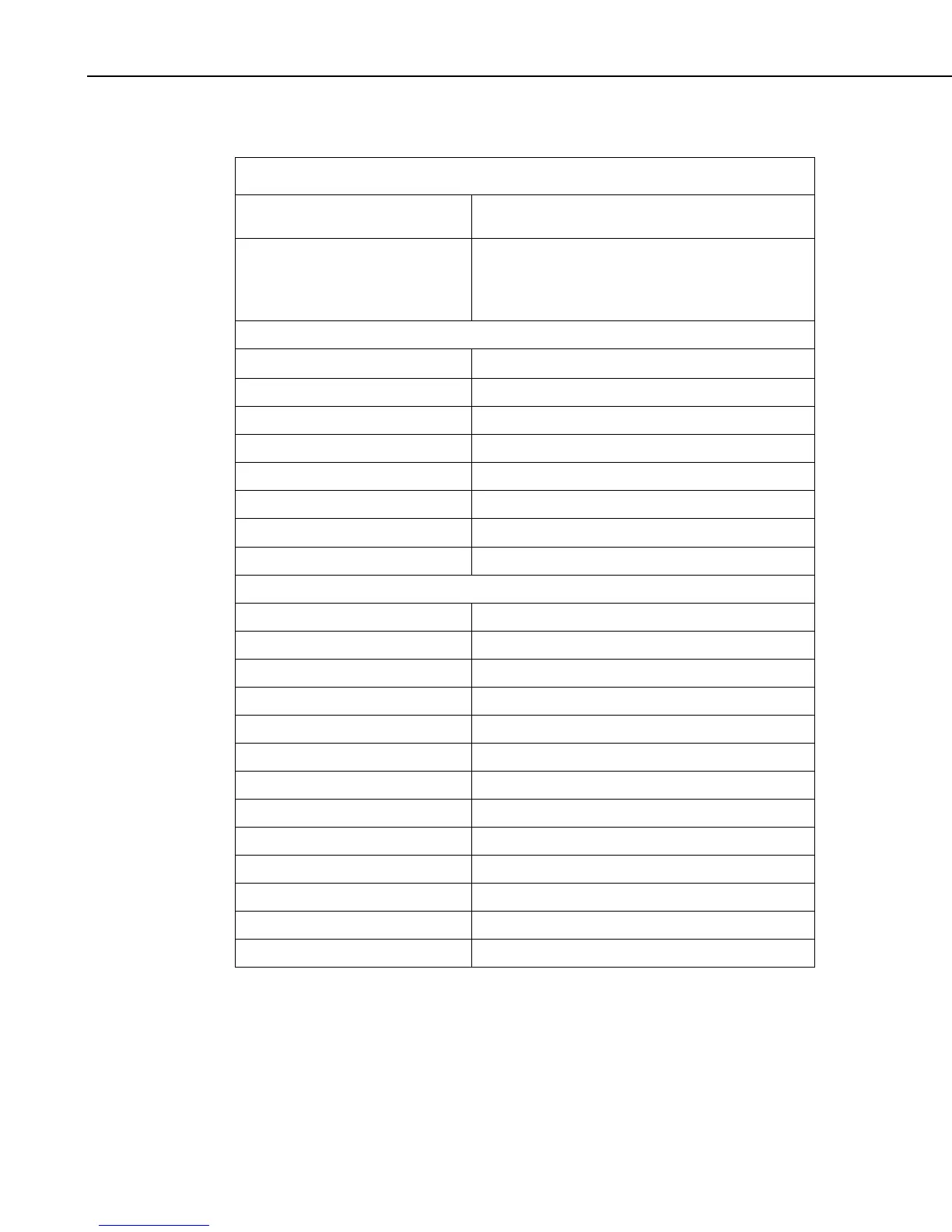
TABLE 8-6. Split Operators and Math Functions
OPERATORS
OPERATOR PRECEDENCE ORDER
(3 = high, 1 = low)
^ = raise to the power
x Mod y = Modulo divide of x by y
∗ / = multiplication, division
+ – = addition, subtraction
3
2
2
1
EXAMPLES OF SYNTAX FOR MATHEMATICAL OPERATORS
3∗5
multiply element 3 by element 5
3/5 divide element 3 by element 5
(3..5)/(8..10) same as 3/8, 4/9, 5/10
3+5 add element 3 to element 5
3–5 subtract element 5 from element 3
(3,9,5)–(8,7,10) same as 3–8, 9–7, 5–10
3∗2.0
multiply element 3 by a fixed number 2
2^3.0 raise element 2 to the third power
MATH FUNCTIONS
Abs(x) = Absolute value of x
Arctan(x) = Arc tangent of x (in degrees)
Cos(x) = Cosine of x (in degrees)
Exp(x) = Natural Exponent function (e
x
)
Frac(x) = Fractional portion of x
Int(x) = Integer portion of x
Ln(x) = Natural logarithm of x
Sin(x) = Sine of x (in degrees)
SpaAvg(x..y) = Spatial average of elements x through y
SpaMax(x..y) = Spatial maximum of elements x through y
SpaMin(x..y) = Spatial minimum of elements x through y
SpaSd(x..y) = Spatial standard deviation of elements x through y
Sqrt(x) = Square root of x
8-56
 Loading...
Loading...