Section 8. Working with Data Files on the PC
8.2.3.1.12 Special Functions, Details, and Examples
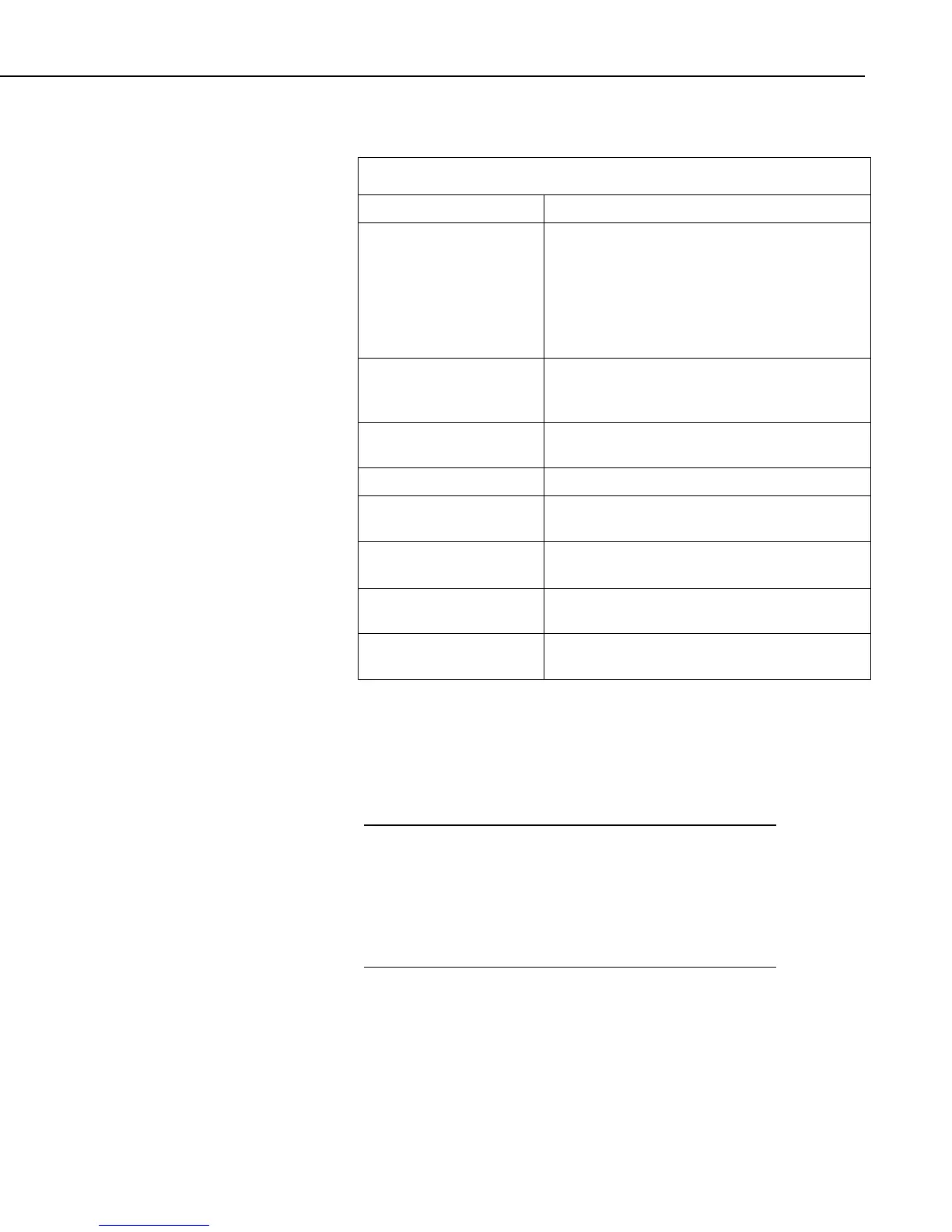
TABLE 8-8. Split SPECIAL FUNCTIONS
Crlf
= Insert carriage return line feed in Output File.
Date(“format”S;H;D;Y)
= Convert day of year and time to a timestamp
with calendar date and time, where format uses
Windows conventions to specify output format.
S=seconds, H = HoursMinutes, D = Day, Y =
year. The output timestamp is quoted text. Date
can be used to create monthly time series
summaries.
Edate(“format”S;H;D;Y)
= The same as the Date function except that the
output text is not quoted. EDate can be used to
create monthly time series summaries.
“Label”
= Insert Comment in Output file. (Label is
anything within the quote marks.)
Line
= Number of lines written to Output file.
smpl(.pa;n)
= Page break such that n is the number of lines
per page for the printer or the .RPT file.
PCdate or PCEdate
= Used in a report header to print the current
date.
WDQ(n)
= Outputs the wind direction using an
alphabetical abbreviation, based on 8 quadrants.
WDQS(n)
= Outputs the wind direction using an
alphabetical abbreviation, based on 16 quadrants.
The Mt. Logan data set is used for the Special Function examples. These
functions are helpful in converting time fields to formatted timestamps and
formatting the output. Since one of the main differences between mixed-array
data files and table based data files is the time format, these functions can be
used to convert between file types.
If you are processing the data file in multiple passes including
formatting of the date and time fields, you should put the date
processing in the final pass. Split cannot read all of the
timestamp formats that it can produce. For example, the quoted
timestamp in table based data files has a specific structure. Any
changes to the structure will make the timestamp unreadable for
Split.
NOTE
Crlf returns a carriage return and line feed where the Crlf is
placed in the parameter file.
Examples:
Smpl(“Max Temp”;24),Max(3;24),
Smpl(Crlf;24),Smpl(“Max RH”;24),Max(4;24)
= Max Temp 67.33
Max RH 38.8
8-63
 Loading...
Loading...