20060301
14-3-1
Graphing a Second Order Differential Equation
14-3 Graphing a Second Order Differential
Equation
This section explains how to input a second order differential equation and draw a slope
field, and how to graph the solution curve(s) for a second order differential equation based
on given initial conditions.
With this application, a second order differential equation is input in the form of a set of two
first order differential equations.
Drawing the Phase Plane of a Second Order Differential Equation
A phase plane is the family of solutions of either a second order differential equation or two
first order differential equations of the form
x
’
=
dx
/
dt
=
f
(
x
,
y
) and
y
’
=
dy
/
dt
=
g
(
x
,
y
). A single
second order differential equation can also be graphed, but it must be written as two first
order differential equations.
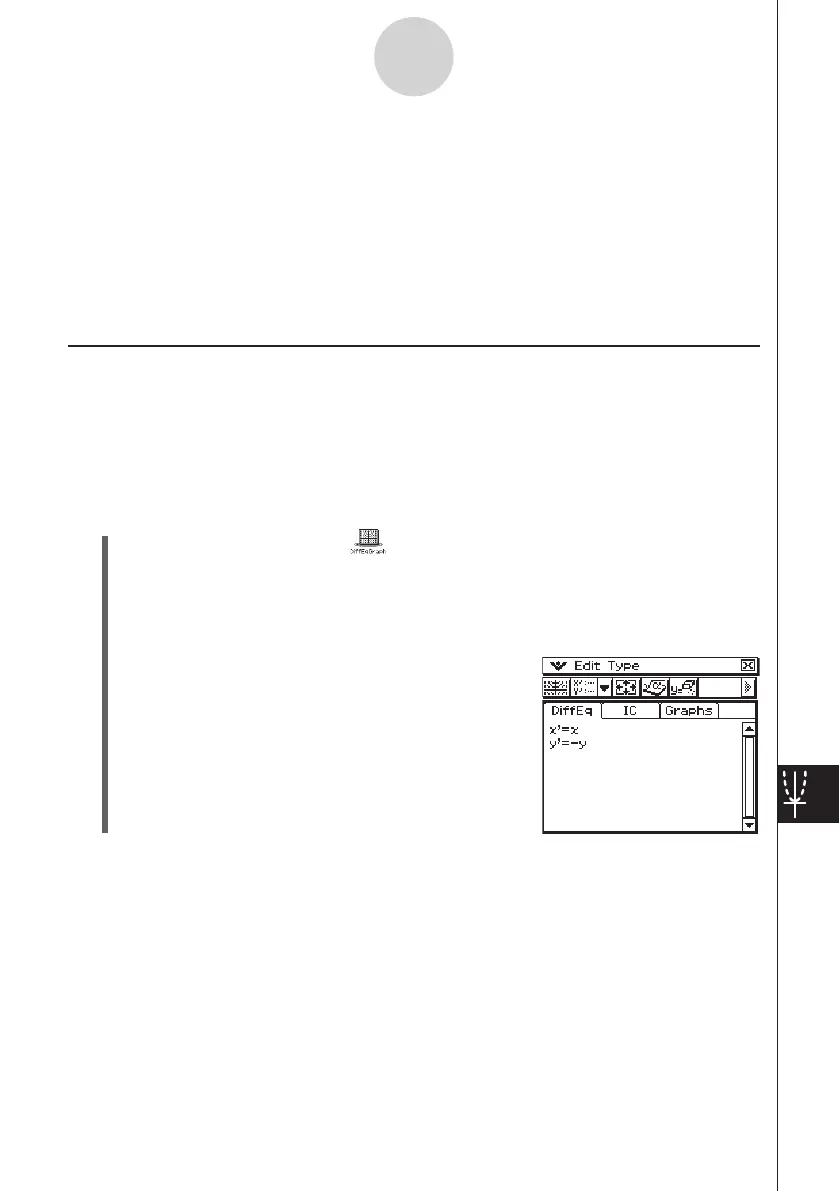
Example: To input {
x
’ =
x
,
y
’ = −
y
} and draw its phase plane
u
ClassPad Operation
(1) On the application menu, tap .
• This starts up the Differential Equation Graph application and activates the differential
equation editor ([DiffEq] tab).
(2) Tap [Type] - [2nd (Phase Plane)] or the
B
toolbar button.
(3) Use the differential equation editor to input
x
’ =
x
,
y
’ = −
y
.
9X
w
-
Y
w

 Loading...
Loading...











