The same is true for traffic in the opposite direction, that is, going into a GRE tunnel. Furthermore
a Route has to be defined so NetDefendOS knows what IP addresses should be accepted and
sent through the tunnel.
An Example of GRE Usage
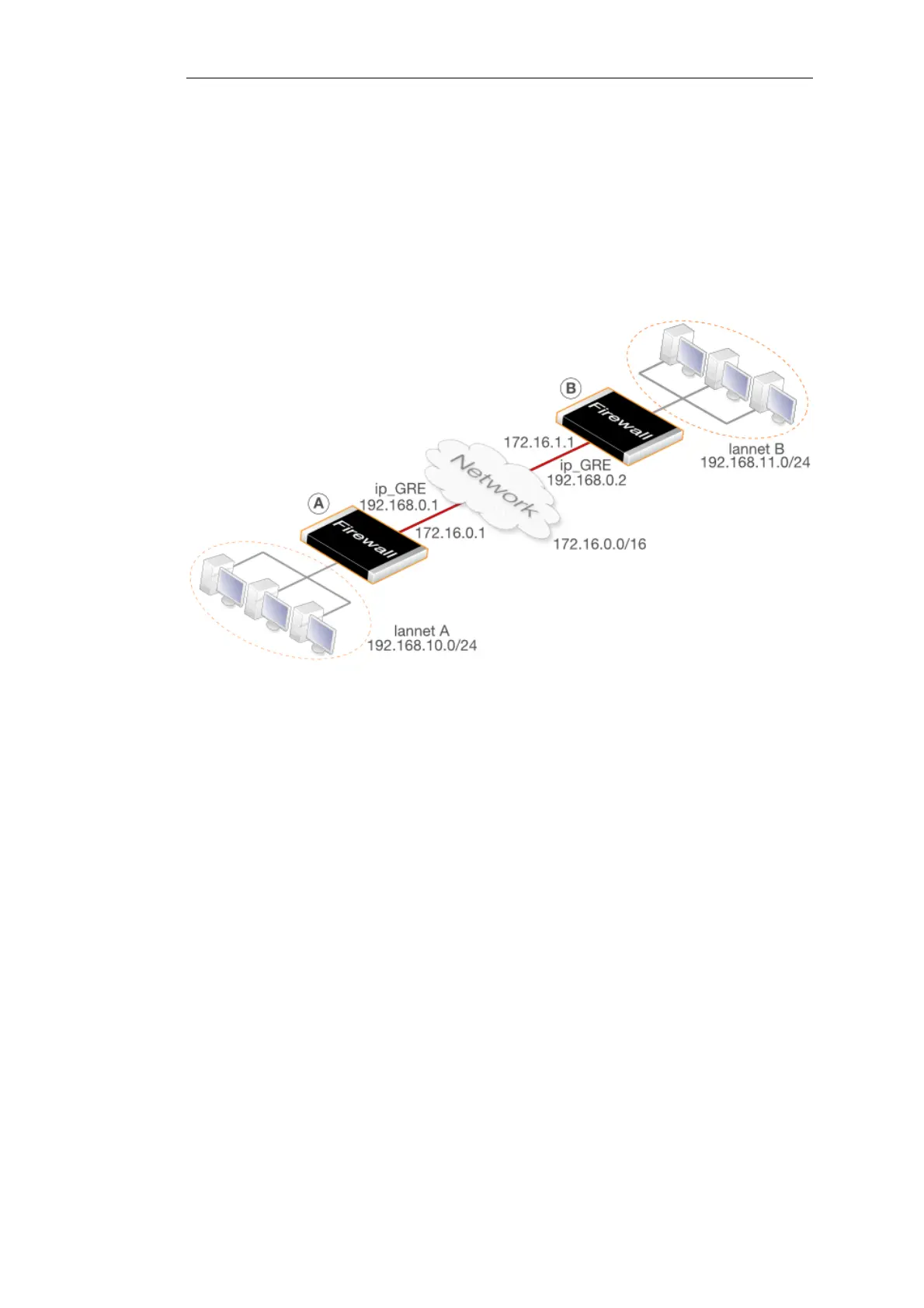
The diagram below shows a typical GRE scenario, where two NetDefend Firewalls labeled A and
B must communicate with each other through the intervening internal network 172.16.0.0/16.
The setup for the two firewalls are described next.
Figure 3.5. An Example of GRE Usage
Any traffic passing between A and B is tunneled through the intervening network using a GRE
tunnel. Since the network is internal and not passing through the public Internet, there is no
need for encryption.
Part 1. Setup for NetDefend Firewall A
Assuming that the network 192.168.10.0/24 is lannet on the lan interface, the steps for setting up
NetDefendOS on A are:
1. In the address book set up the following IP objects:
• remote_net_B: 192.168.11.0/24
• remote_gw: 172.16.1.1
• ip_GRE: 192.168.0.1
2. Create a GRE Tunnel object called GRE_to_B with the following parameters:
• IP Address: ip_GRE
• Remote Network: remote_net_B
• Remote Endpoint: remote_gw
Chapter 3: Fundamentals
207
 Loading...
Loading...