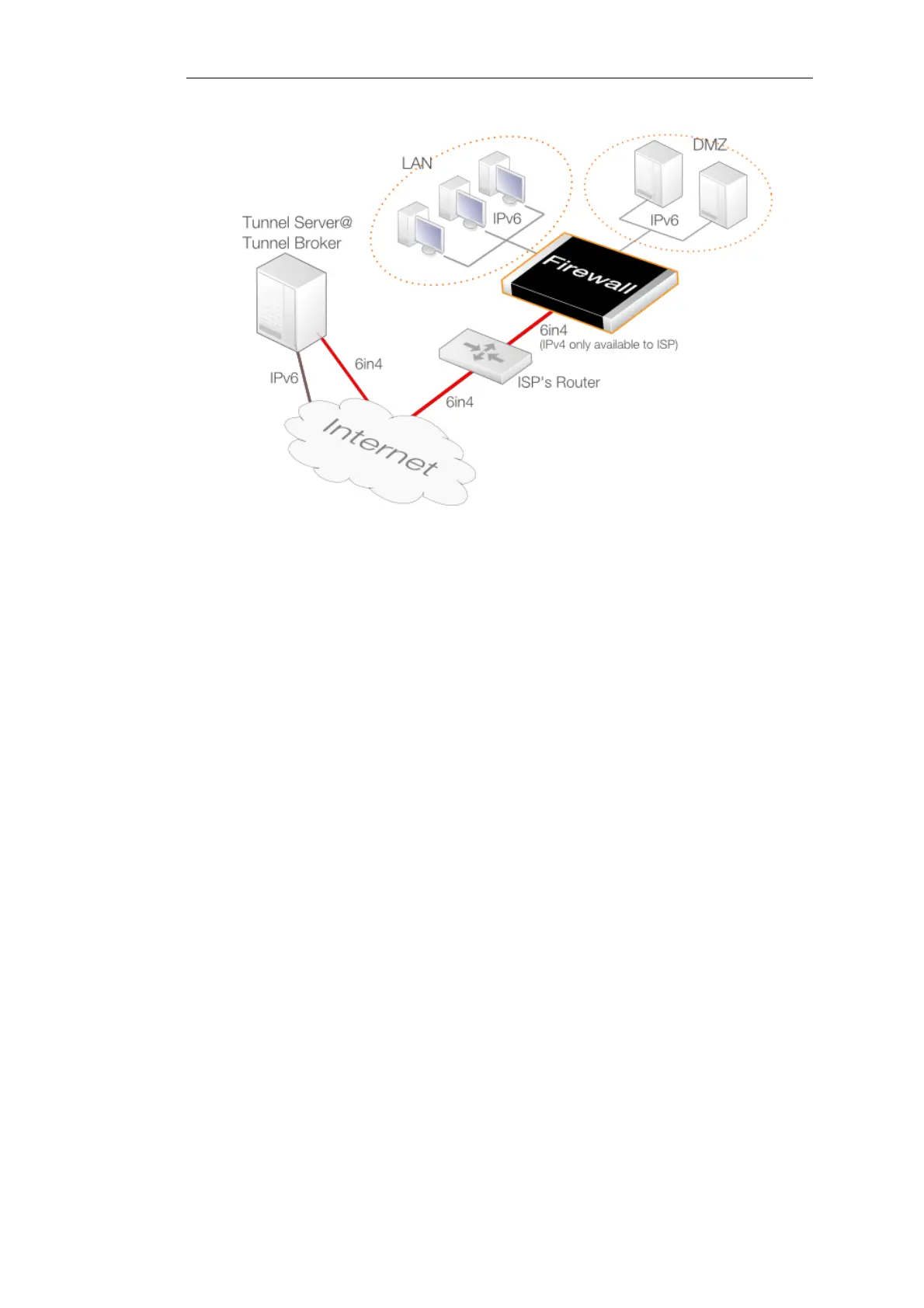
Figure 3.6. IP6in4 Tunnel Usage
Configuring a 6in4 Tunnel Object
Apart from the name of the object, there are three key properties which must be assigned values:
• Remote Network
This specifies the network for the route that is added automatically by NetDefendOS when
the tunnel object is defined. For the typical client scenario described here, this will usually be
all-nets6 indicating the IPv6 gateway to the public Internet.
If the option to add a route automatically is disabled, this property has no relevance since the
network is specified in a manually added route.
The interface which is the local endpoint for the tunnel will be derived from a route lookup of
this property. In most cases the default route to the public Internet will be looked up and the
interface will be the Ethernet interface connected to an ISP.
• IP Address
This is the local IPv6 address inside the tunnel. It may be provided by the tunnel broker in
which case it can be pinged to establish if the tunnel is alive. If this is the case then the
appropriate NetDefendOS IP rule or policy needs to be set up so that the ICMP ping is
answered.
If the broker does not require a specific address then this should be set to any IPv6 address
which belongs to the prefix handed out by the broker.
• Remote Endpoint
This is the IPv4 address for the tunnel server so NetDefendOS knows how to contact it across
the public Internet. It is assumed that NetDefendOS has access to the public Internet via an
ISP for IPv4 traffic only.
Chapter 3: Fundamentals
210
 Loading...
Loading...