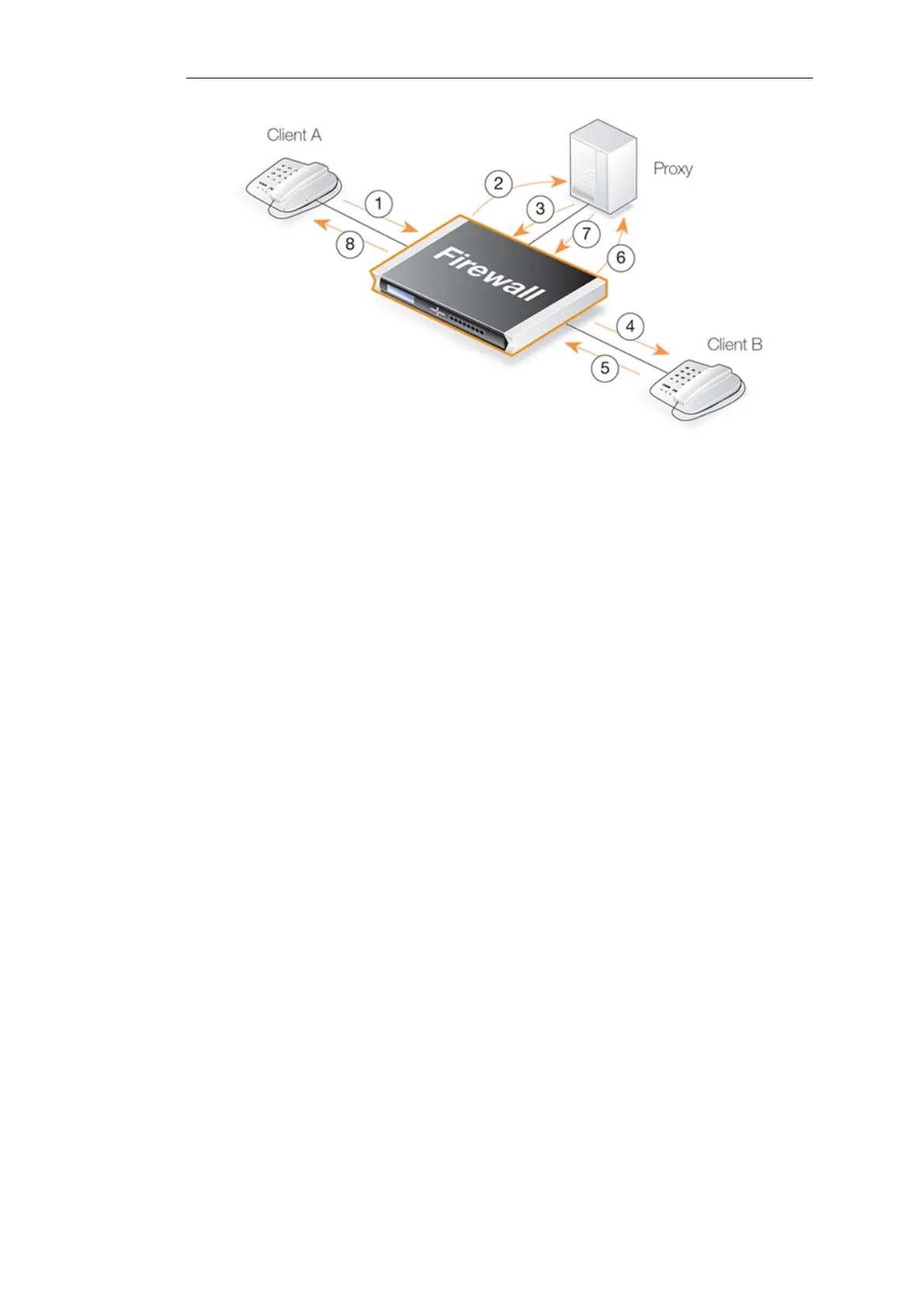
The exchanges illustrated in the above diagram are as follows:
• 1,2 - An initial INVITE is sent to the outbound local proxy server on the DMZ.
• 3,4 - The proxy server sends the SIP messages towards the destination on the Internet.
• 5,6 - A remote client or proxy server replies to the local proxy server.
• 7,8 - The local proxy forwards the reply to the local client.
This scenario can be implemented in a topology hiding setup with DMZ (Solution A below) as
well as a setup without NAT (Solution B below).
Solution A - Using NAT
The following should be noted about this setup:
• The IP address of the SIP proxy must be a globally routable IP address. The NetDefend
Firewall does not support hiding of the proxy on the DMZ.
• The IP address of the DMZ interface must be a globally routable IP address. This address can
be the same address as the one used on the external interface.
The setup steps are as follows:
1. Define a single SIP ALG object using the options described above.
2. Define a Service object and associate it with the SIP ALG object. The service should have:
• Destination Port set to 5060 (the default SIP signaling port)
• Type set to TCP/UDP
3. Define four rules/policies in the IP rule set:
• A NAT rule/policy for outbound traffic from the clients on the internal network to the
proxy located on the DMZ interface. The SIP ALG will take care of all address translation
needed by the NAT rule. This translation will occur both at the IP level and at the
application level.
Chapter 6: Security Mechanisms
476
 Loading...
Loading...