• Priority 6 - VoIP (500 Kbps)
• Priority 4 - Citrix (250 Kbps)
• Priority 2 - Other traffic (1000 Kpbs)
• Priority 0 - Web plus remaining from other levels
To implement this scheme, we can use the in-pipe and out-pipe. We first enter the Pipe Limits for
each pipe. These limits correspond to the list above and are:
• Priority 6 - 500
• Priority 4 - 250
• Priority 2 - 1000
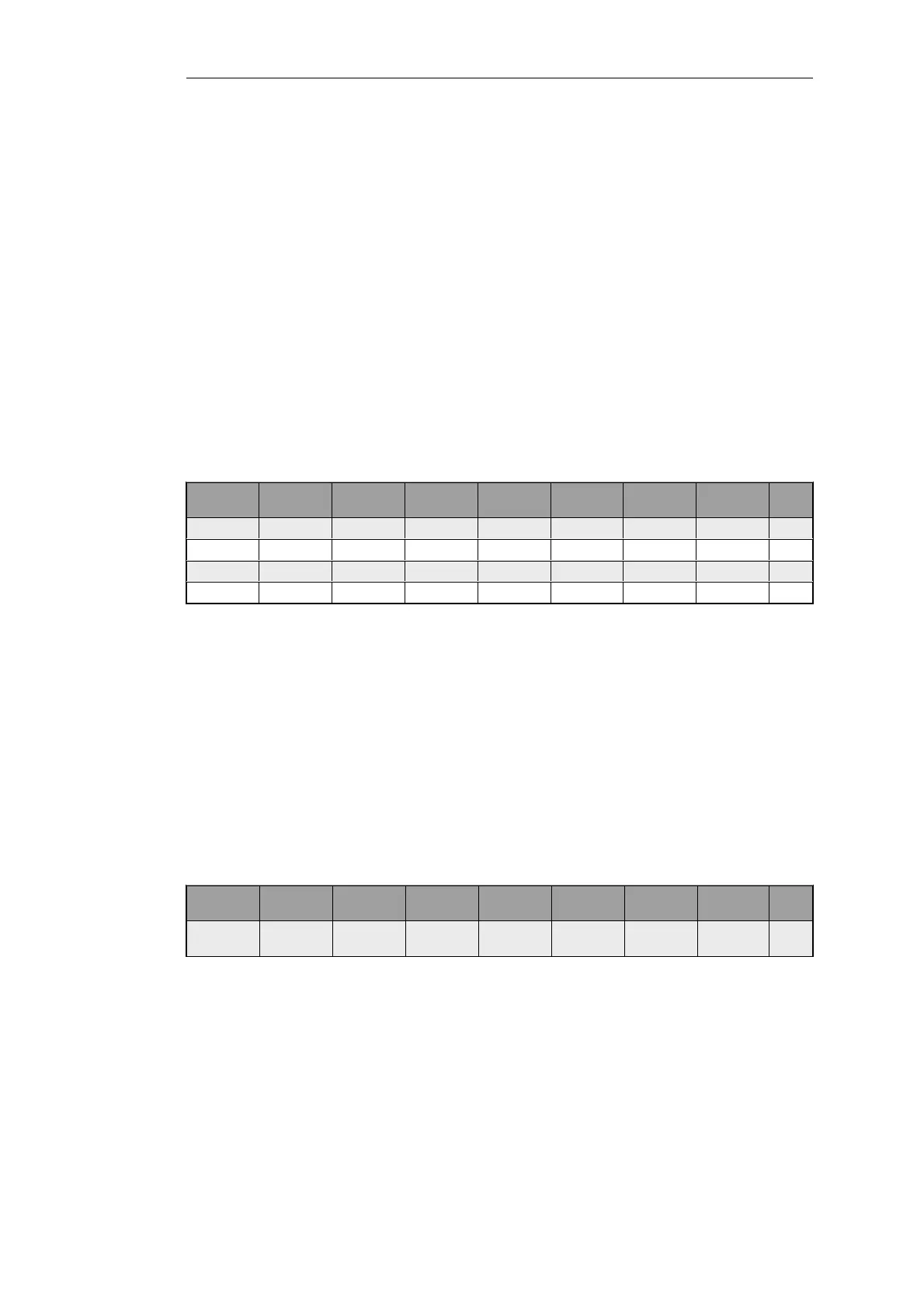
Now create the Pipe Rules:
Rule
Name
Forward
Pipes
Return
Pipes
Source
Interface
Source
Network
Dest
Interface
Dest
Network
Selected
Service
Prece
dence
web_surf out-pipe in-pipe lan lannet wan all-nets http-all 0
voip out-pipe in-pipe lan lannet wan all-nets H323 6
citrix out-pipe in-pipe lan lannet wan all-nets citrix 4
other out-pipe in-pipe lan lannet wan all-nets all_services 2
These rules are processed from top to bottom and force different kinds of traffic into
precedences based on the Service. Customized service objects may need to be first created in
order to identify particular types of traffic. The all service at the end, catches anything that falls
through from earlier rules since it is important that no traffic bypasses the pipe rule set otherwise
using pipes will not work.
Pipe Chaining
Suppose the requirement now is to limit the precedence 2 capacity (other traffic) to 1000 Kbps so
that it does not spill over into precedence 0. This is done with pipe chaining where we create new
pipes called in-other and out-other both with a Pipe Limit of 1000. The other pipe rule is then
modified to use these:
Rule
Name
Forward
Pipes
Return
Pipes
Source
Interface
Source
Network
Dest
Interface
Dest
Network
Selected
Service
Prece
dence
other out-other
out-pipe
in-other
in-pipe
lan lannet wan all-nets all_services 2
Note that in-other and out-other are first in the pipe chain in both directions. This is because we
want to limit the traffic immediately, before it enters the in-pipe and out-pipe and competes with
VoIP, Citrix and Web-surfing traffic.
A VPN Scenario
In the cases discussed so far, all traffic shaping is occurring inside a single NetDefend Firewall.
VPN is typically used for communication between a headquarters and branch offices in which
case pipes can control traffic flow in both directions. With VPN it is the tunnel which is the source
and destination interface for the pipe rules.
Chapter 10: Traffic Management
795
 Loading...
Loading...