8-32
HOW TO DIAGNOSE
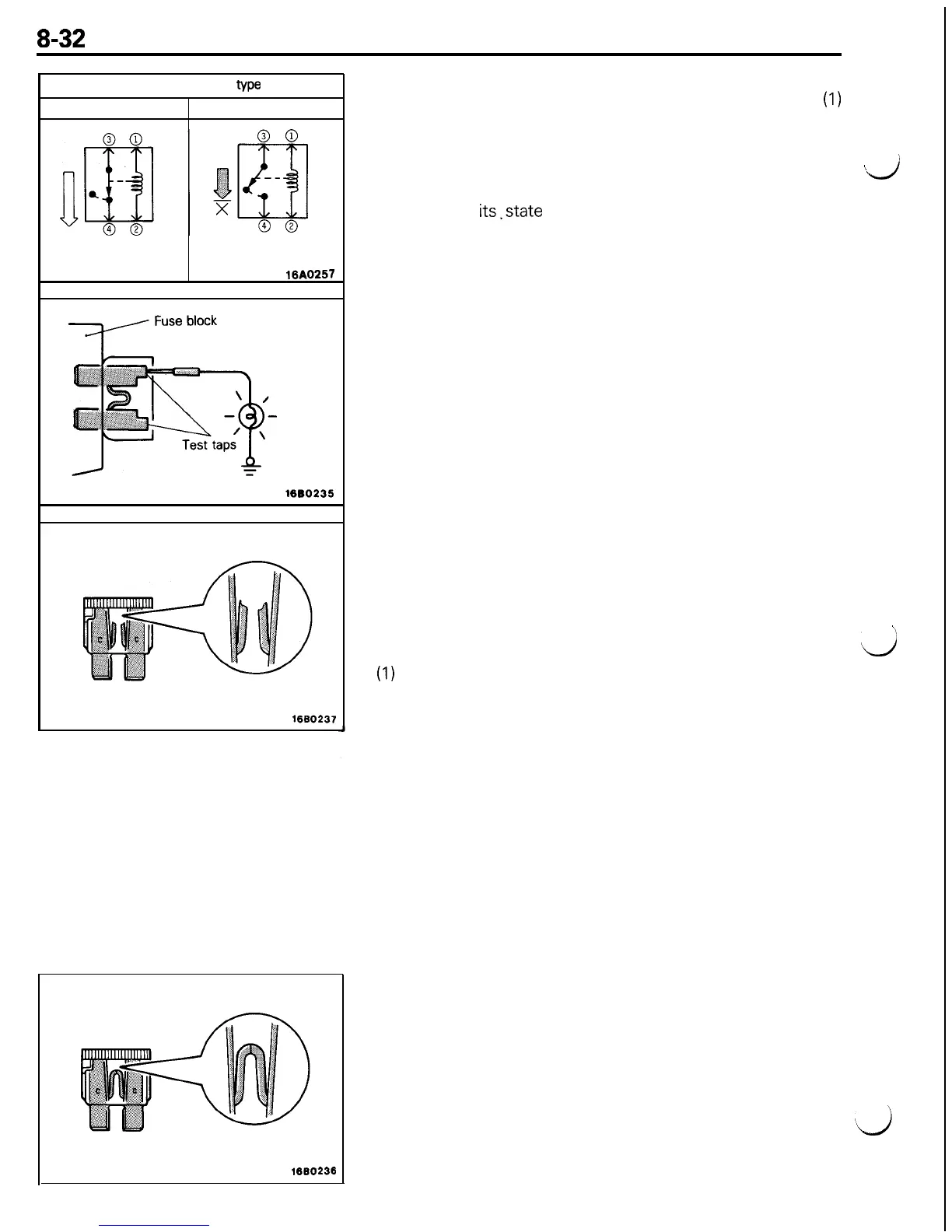
Normal close (NC)
type
Deenergized state
Energized state
Current flows
Current does not flow
16AO257
10BO235
State of fuse blown due to overcurrent
1680237
State of fuse blown due to thermal fatigue
1680236
When a normal close type relay as illustrated here is
checked, there should be continuity between terminals
(1)
and (2) and between terminals 3 and 4 when the relay is
deenergized, and the continuity should be lost between
terminals 3 and 4 when the battery voltage is applied to the
terminals 1 and 2. A relay can be checked in this manner
’
i
and it cannot be determined if a relay is okay or faulty by
checking its.state only when it is deenergized (or ener-
gized).
CHECKING FUSES
A blade type fuse has test taps provided to allow checking of
the fuse itself without removing it from the fuse block. The
fuse is okay if the test light comes on when its one lead is
connected to the test taps (one at a time) and the other lead is
grounded. (Change the ignition switch position adequately so
that the fuse circuit becomes live.)
CAUTIONS IN EVENT OF BLOWN FUSE
When a fuse is blown, there are two probable causes as
follows: One is that it is blown due to flow of current exceeding
its rating.
The other is that it is blown due to repeated on/off current
flowing through it. Which of the two causes is responsible can
_
be easily determined by visual check as described below.
d
(1)
Fuse blown due to current exceeding rating
The illustration shows the state of a fuse blown due to this
cause. In this case, do not replace the fuse with a new one
hastily since a current heavy enough to blow the fuse has
flowed through it. First, check the circuit for shorting and
check for abnormal electric parts. Only after the correction
of such shorting or parts, fuse of the same capacity should
be used as a replacement. Never use a fuse of larger
capacity than the one that has blown. If such a fuse is used,
electric parts or wirings could be damaged before the fuse
blows in the event an overcurrent occurs again.
(2) Fuse blown due to repeated current on/off
The illustration shows the state of a fuse blown due to
repeated current on/off. Normally, this type of problem
occurs after fairly long period of use and hence is less
frequent than the above type. In this case, you may simply
replace with a new fuse of the same capacity.
 Loading...
Loading...











