Appendix
A.4 Required memory for function blocks
Function blocks Instance 1 Instance 2
Note
OT
64
64
PM
72
56
+8 per support point
PO
96
96
PW
48
48
PT
40
40
RC
76
–
RE
128
112
+32 per record
as soon as a flag is used in the recipe, this
applies to every constant used in that recipe:
+4 per constant;
SC
20
–
SR(BIT)
96
96
SR(DWORD)
96
96
ST
24
–
T
52
52
TB
112
112
TC
76
76
VC
48
48
WT
84
84
+4 per channel
YT
96
96
+4 per channel
1) As soon as an interrupt module is used, +12 bytes of memory are required once
Required memory when connecting function blocks, using CP, T, D as an example
In order to estimate the required memory for a connected function block in LD/FBD,
you can assume a required memory space of eight bytes for each connected func-
tion block input and function block output. This applies regardless of whether the
function block inputs and/or outputs are digital or analog and of whether the con-
nection involves MB marker bytes or MD marker double words.
Depending on the complexity of the pre-wiring, the actual consumption can also be
higher. Each numerical constant used requires an additional 4 bytes in all pro-
gramming methods.
In EDP, each rung occupies 20 bytes, regardless of its content, while an input / output
circuit in the block diagram does not require any additional memory.
The following information was determined using the LD/FBD programming language.
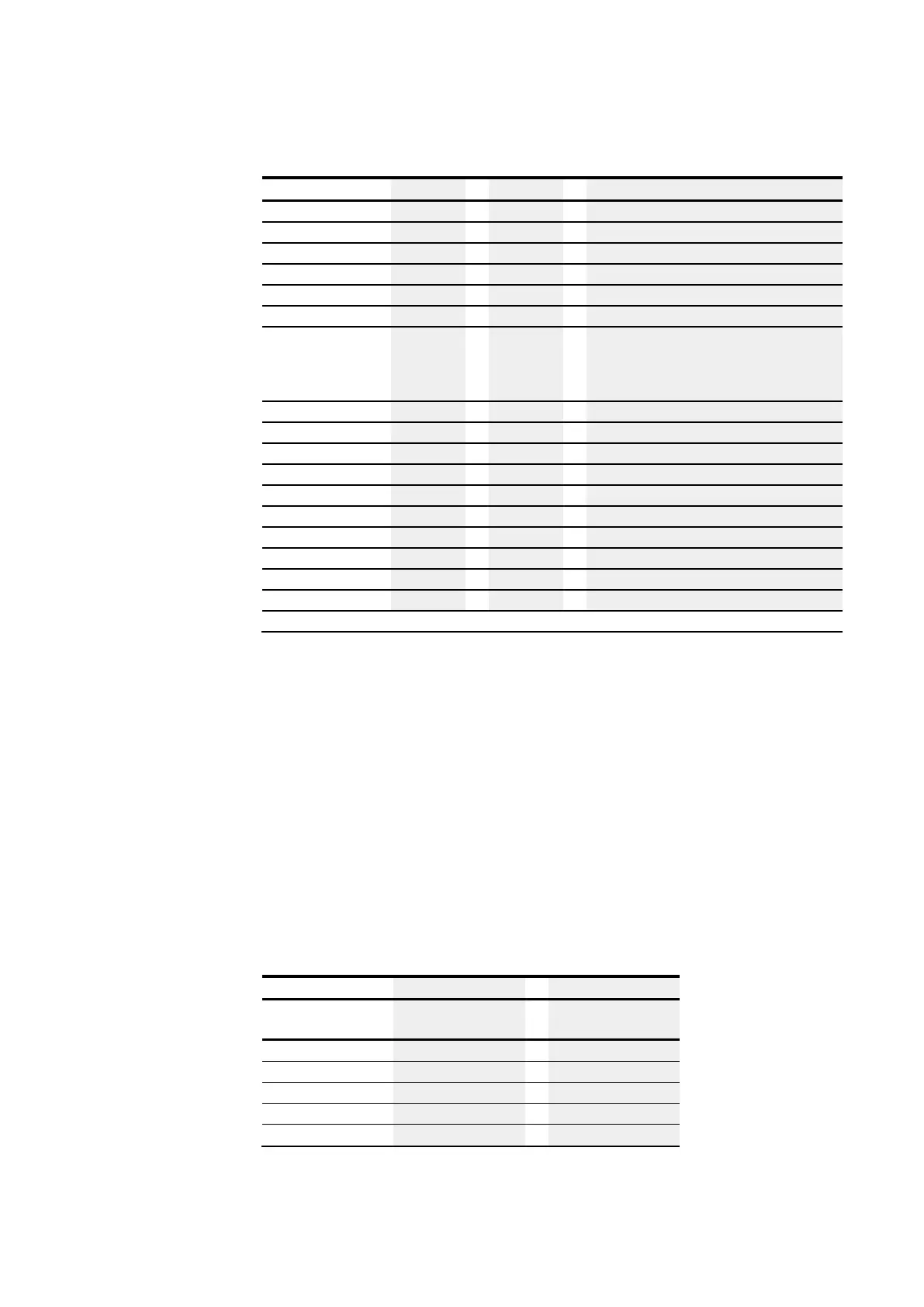
CP - Comparator Connected to
Memory Required
Function block input-
s/outputs
Operand
bytes
CP (not connected)
35
EN
I1
7
I1
IA1
7
I2
IA2
7
LT
Q1
7
Tab. 147: Memory Required FB CP
832
easyE402/24 MN050009ENEaton.com

 Loading...
Loading...











