DSG-423 ENGINE CONTROLS
08-9
Fuel Filter
The fuel filter is an inline filter assembly. Refer to
Section 4 for information on relieving fuel pressure,
disconnecting fuel lines and fuel filter replacement.
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit
When the key is first turned “ON”, the GCP energizes
the fuel pump relay for two seconds to build up the fuel
pressure quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the GCP shuts the fuel pump off and waits
until the engine is cranked. When the engine is cranked
and crankshaft position signal has been detected by the
GCP, the GCP supplies 12 volts to the fuel pump relay
to energize the electric fuel pump.
An inoperative fuel pump will cause a “no-start”
condition. A fuel pump which does not provide enough
pressure will result in poor performance.
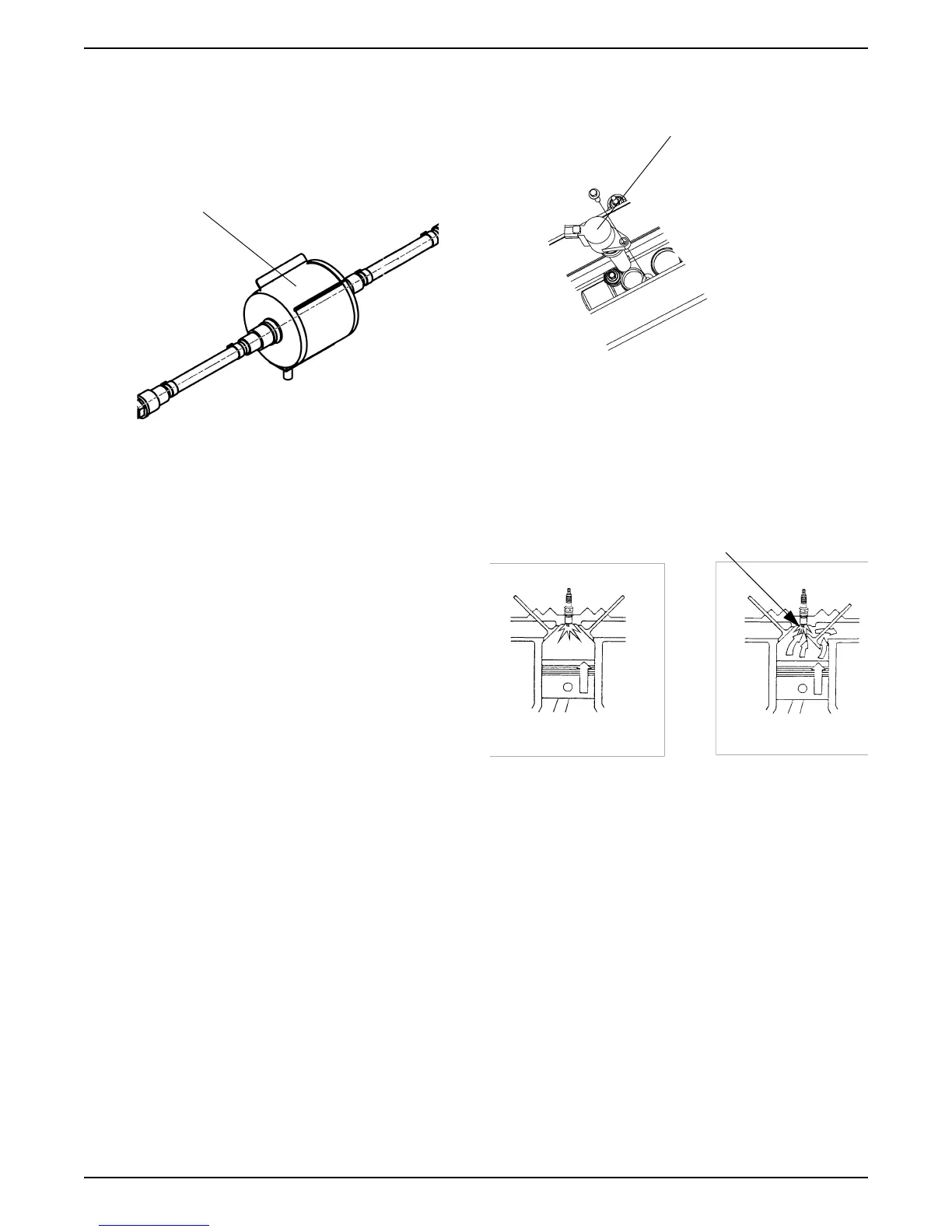
Coil-on-plug Ignition
The coil-on-plug ignition system controls fuel
combustion by providing a spark to ignite the
compressed air/fuel mixture at the correct time. To
provide optimum engine performance, fuel economy,
and control of exhaust emissions, the GCP controls the
spark advance of the ignition system. Coil-on-plug
ignition has the following advantages over a mechanical
distributor system:
• No moving parts
• Less maintenance
• Remote mounting capability
• No mechanical load on the engine
• More coil cooldown time between firing events
• Elimination of mechanical timing adjustments
• Increased available ignition coil saturation time
• Elimination of high tension wires
The coil-on-plug design has individual coils mounted
directly over each spark plug. Each cylinder is paired
with its opposing cylinder in the firing order, so that one
cylinder on compression fires simultaneously with the
opposing cylinder on exhaust. The spark that occurs in
the cylinder on the exhaust stroke is referred to as a
“waste spark”.
The primary coils in the coil pack are triggered by the
“ignition coil feed#1” and ignition coil feed #2” signals
from the GCP.
Ignition Coil
(coil-on-plug)
Power Stroke Exhaust Stroke
(waste spark)
 Loading...
Loading...