Chapter 9. Diagnostics
GFK-2950C February 2018 423
Interpreting the Fault Extra Data
Bytes 1 - 8: Ignored when decoding a security-related fault.
Byte 9: The operation during which the fault occurred.
▪ 01 (as in the example): Read
▪ 02: Write
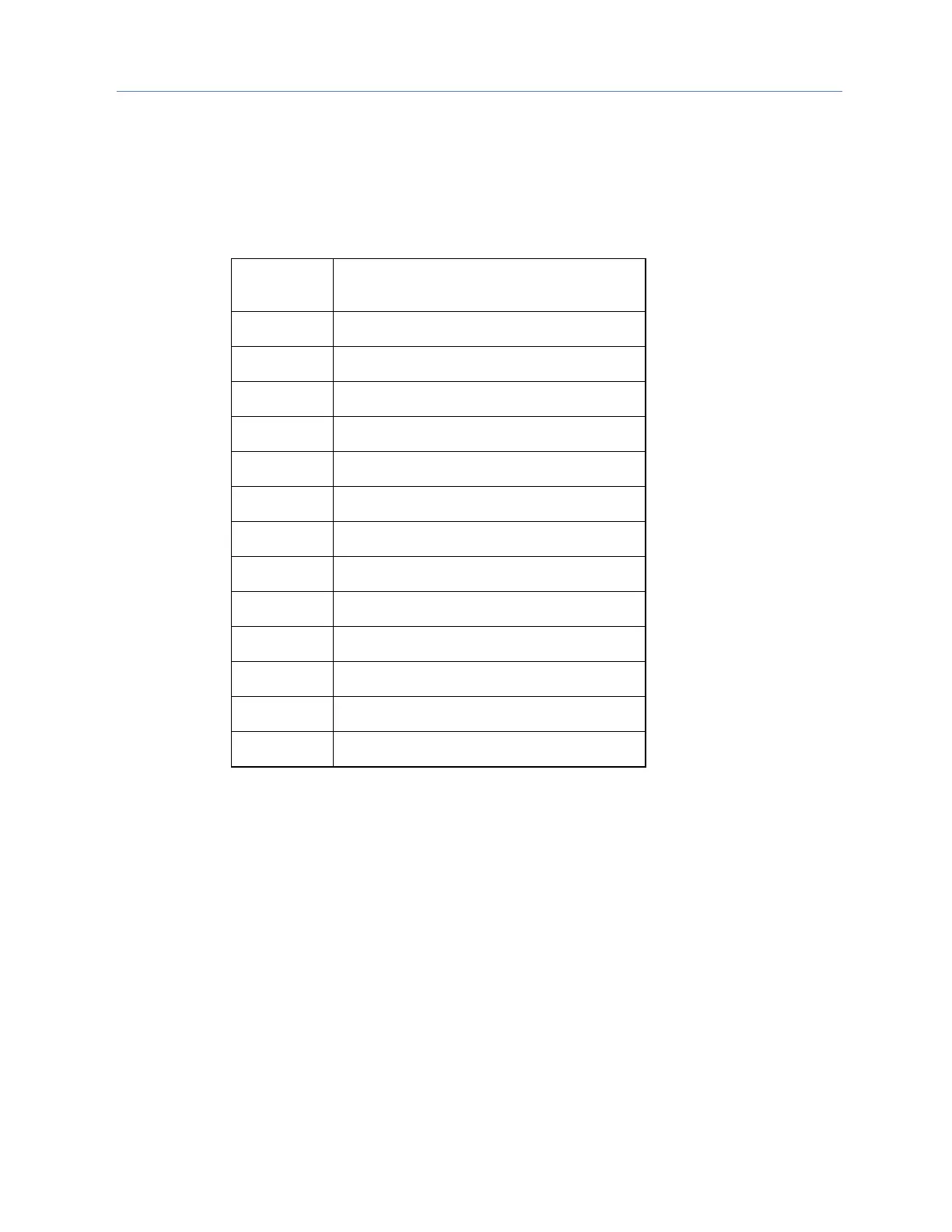
Byte 10: The hexadecimal value (HV) that specifies a CPU memory area.
%AI (Analog input memory)
%AQ (Analog output memory)
%I (Discrete input memory)
%Q (Discrete output memory)
%T (Discrete temporary status memory)
%M (Discrete momentary internal memory)
%SA (Discrete system memory A)
%SB (Discrete system memory B)
%SC (Discrete system memory C)
%S (Discrete system memory)
%G (Genius global memory)
Bytes 11–18: 0-based bit offset of the memory area being accessed. The 8-byte value is encoded in
little endian format, meaning that the byte values are reversed. In the example, the
value is 0x0000000000000006, which is equal to 1-based bit offset 7.
Bytes 19–22: The length in bits of data requested. In the example, 1 bit was requested.
Bytes 23–24: Ignored when decoding a security-related fault.

 Loading...
Loading...