Chapter 9. Diagnostics
GFK-2950C February 2018 391
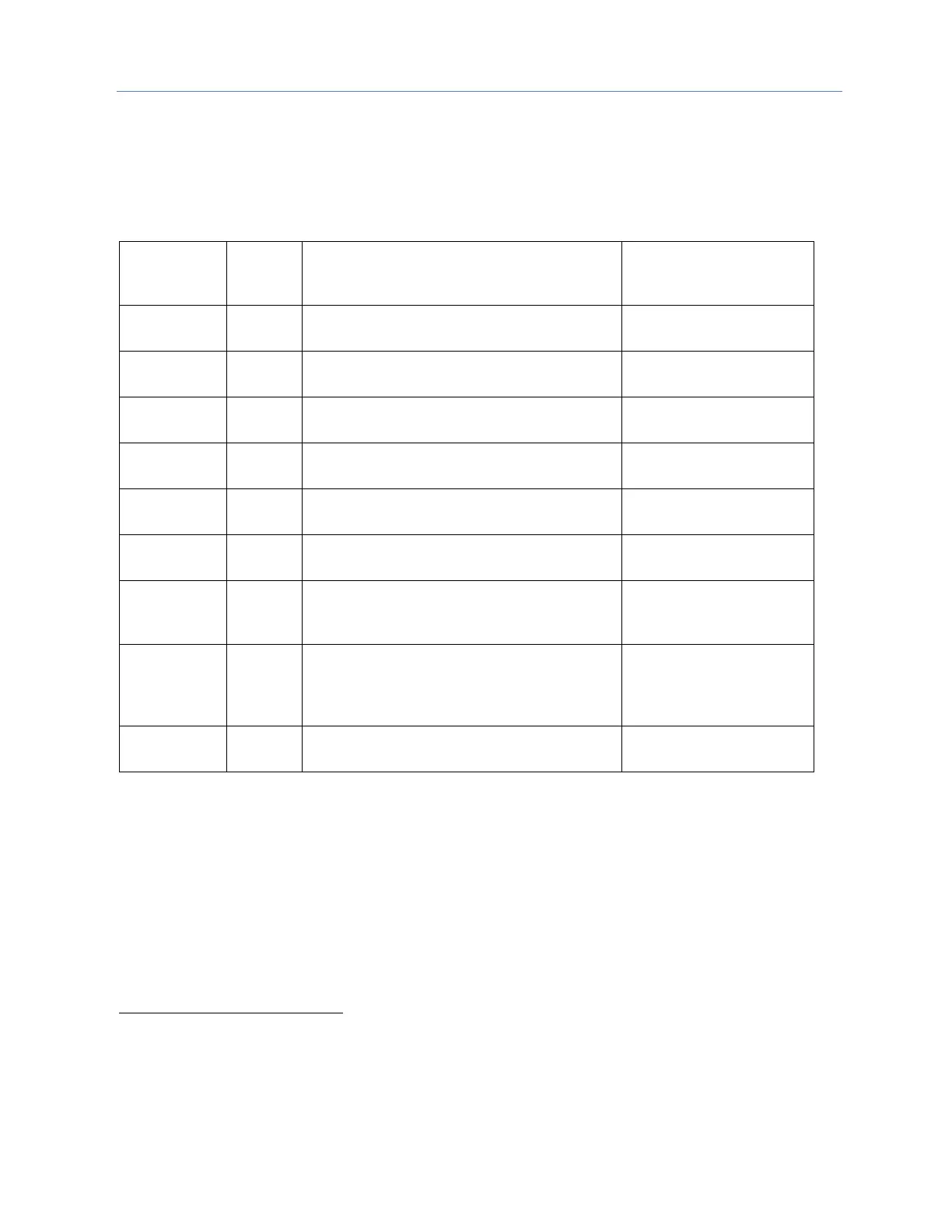
9.3.1 System Fault References
When a system fault reference is set, additional fault references are also set. These other types of
faults are listed in Fault References for Configurable Faults below and Fault References for Non-
Configurable Faults in the section which follows.
Fault References for Configurable Faults
System bus error. All system bus error faults
are logged as informational.
#HRD_FLT, #SY_PRES,
#SY_FLT
Non-recoverable software error in an I/O
Controller (IOC).
#IO_FLT, #IO_PRES,
#SFT_FLT
Loss of rack (BRM failure, loss of power) or
missing a configured rack.
#SY_FLT, #SY_PRES,
#IO_FLT, #IO_PRES
Loss of I/O Controller or missing a configured
Bus Controller.
Loss of I/O module (does not respond), or
missing a configured I/O module.
Loss of intelligent module (does not respond),
or missing a configured module.
Non-fatal bus or I/O Controller error, more than
10 bus errors in 10 seconds. (Error rate is
configurable.)
Configuration mismatch. Wrong module type
detected. The CPU does not check the
configuration parameter settings for individual
modules such as Genius I/O blocks.
CPU temperature has exceeded its normal
operating temperature.
Note: If the fault action for a fault logged to the fault table is informational, the configured action is
not used. For example, if the logged fault action for an SBUS_ERR is informational, but you
configure it as fatal, the action is still informational.
The #SFT_IOC software fault will have the same action as what you set for #LOS_IOC.
When a Loss of Rack or Addition of Rack fault is logged, individual loss or add faults for each module in that rack are
usually not generated.
Even if the #LOS_IOC fault is configured as Fatal, the CPU will not go to STOP/FAULT unless both GBCs of an internal
redundant pair fail.

 Loading...
Loading...