Goodrive30 Series VFD Function parameter list
-83-
When the set frequency is within the range of
jumping frequency, the VFD runs at the
boundary of jumping frequency.
The VFD can avoid the mechanical resonance
point by setting jumping frequencies. The VFD
supports the setting of three jump frequencies. If
the jump frequency points are set to 0, this
function is invalid.
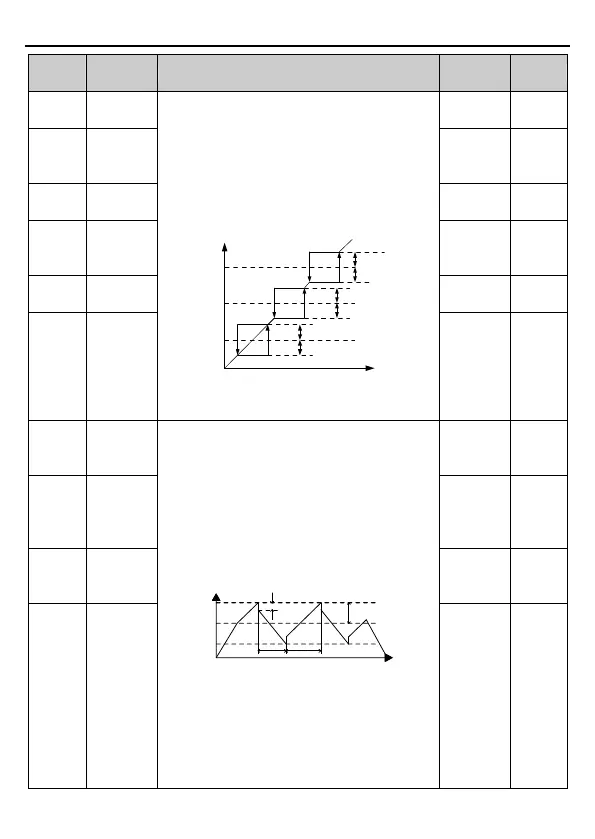
Set frequency f
Jump
frequency 3
Jump
frequency 2
Jump
frequency 1
½* jump frequency
amplitude 3
½* jump frequency
amplitude 3
½* jump frequency
amplitude 2
½* jump frequency
amplitude 2
½* jump frequency
amplitude 1
½* jump frequency
amplitude 1
Time t
Setting range: 0.00Hz–P00.03 (max. output
frequency)
Jump
frequency
amplitude 1
Jump
frequency
amplitude 2
Jump
frequency
amplitude 3
Amplitude
of wobbling
frequency
This function applies to the industries where
traverse and convolution function are required
such as textile and chemical fiber.
The traverse function means that the output
frequency of the VFD is fluctuated with the set
frequency as its center. The route of the running
frequency is illustrated as follows, of which the
traverse is set by P08.15 and when P08.15 is set
as 0, the traverse is 0 with no function.
Output frequency f
Jumping frequency
Accelerate per
ACC time
Decelerate per
DEC time
Amplitude of wobble
frequency
Fall time of
wobble frequency
Rise time of
wobble frequency
Center
frequency
Lower limit of
wobble frequency
Time t
Upper limit of
wobble frequency
Amplitude of wobbling frequency: The wobbling
frequency running is limited by upper and low
limits of the frequency.
Amplitude of wobbling frequency relative to the
center frequency (set frequency): amplitude of
wobbling frequency AW = center frequency ×
Amplitude
of sudden
jump
frequency
Rise time of
wobbling
frequency
Fall time of
wobbling
frequency

 Loading...
Loading...











