Filter types
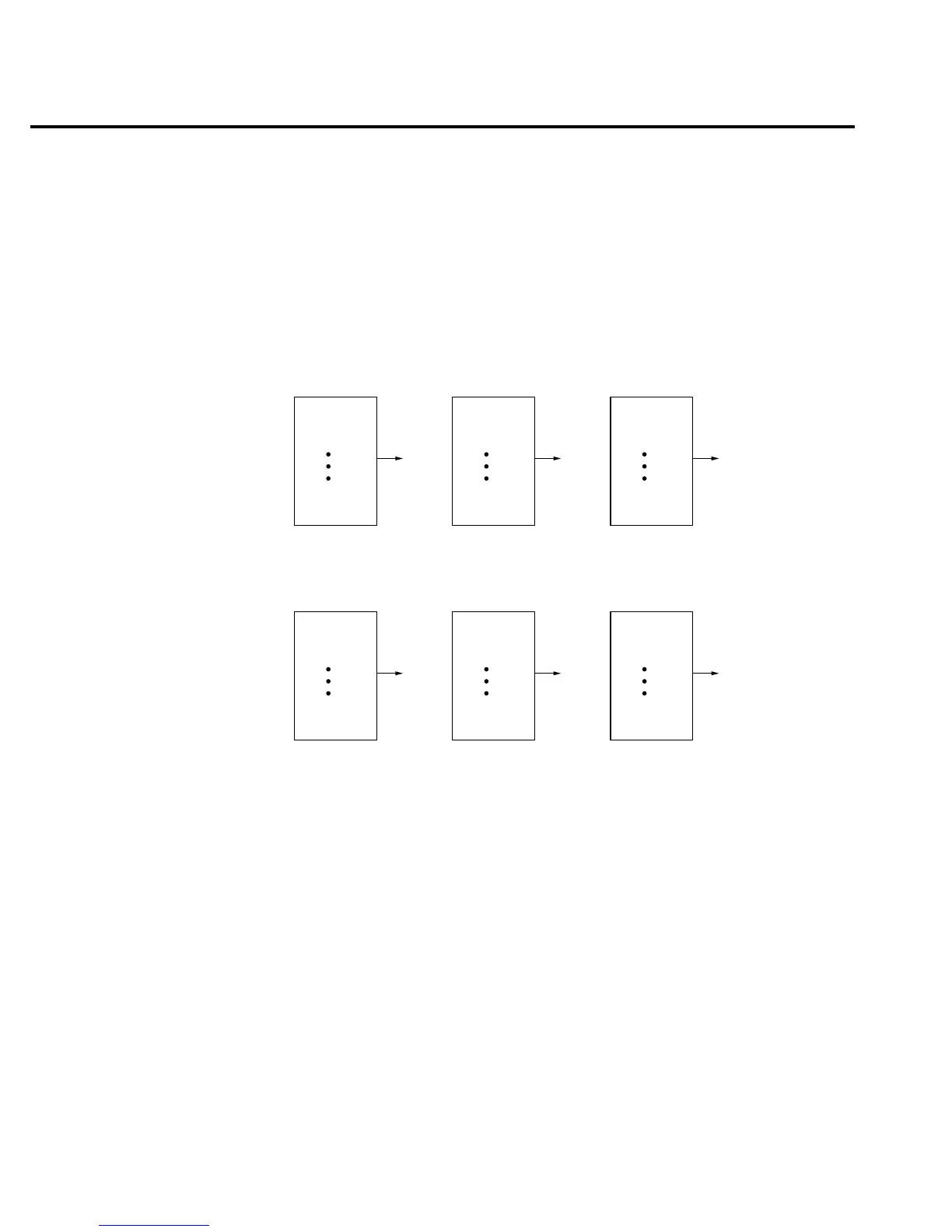
The moving average filter (Figure 3-1) uses a first-in, first-out stack. When the stack becomes
full, the measurement conversions are averaged, yielding a reading. For each subsequent con-
version placed into the stack, the oldest conversion is discarded, and the stack is re-averaged,
yielding a new reading.
For the repeating filter (Figure 3-1), the stack is filled and the conversions are averaged to
yield a reading. The stack is then cleared and the process starts over. Choose this filter for scan-
ning so readings from other channels are not averaged with the present channel.
Response time
The filter parameters have speed and accuracy tradeoffs for the time needed to display, store,
or output a filtered reading. These affect the number of reading conversions for speed versus
accuracy and response to input signal changes.
Conversion #10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
Conversion #1
Reading
#1
A. Type - Moving Average, Readings = 10
Conversion #11
#10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
Conversion #2
Reading
#2
Conversion #12
#11
#10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
Conversion #3
Reading
#3
Conversion #10
#9
#8
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
Conversion #1
Reading
#1
B. Type - Repeating, Readings = 10
Conversion #20
#19
#18
#17
#16
#15
#14
#13
#12
Conversion #11
Reading
#2
Conversion #30
#29
#28
#27
#26
#25
#24
#23
#22
Conversion #21
Reading
#3
igure 3-1
oving average and
repeating filters
3-4 Measurement Options

 Loading...
Loading...