Chapter 3 Engine Section 4 Inspection and maintenance of engine componenets
3—34
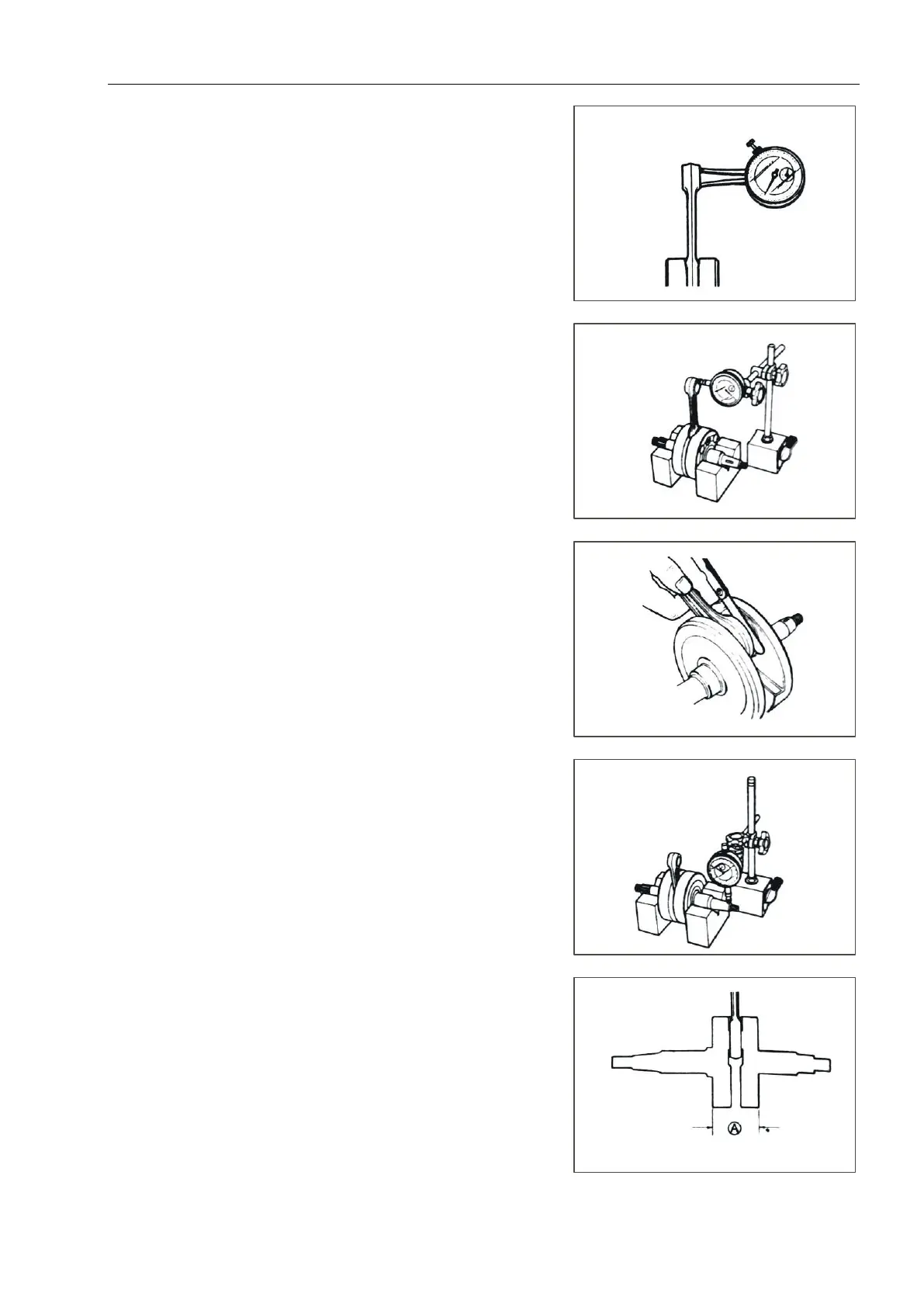
Inner diameter of small end of connecting rod
Measure the inner diameter of the small end of the
connecting rod with an inner diameter micrometer.
If the inner diameter of the small end of the connecting rod
exceeds the service limit, replace the connecting rod.
As in Fig.3.4.63
Tools: inside micrometer
Use limit:φ
012.0
004.0
14
mm
Deflection of connecting rod and big end backlash
of connecting rod
The wear of the large end of the connecting rod can be
determined by examining the movement of the small end of
the connecting rod.
The wear degree of the big end of the connecting rod
can also be checked by this method. As Fig. 3.4.63
Tools: magnetic rack Dial meter (1/100mm)
V-shaped block (100 mm) Limit of use: 1.2mm
Push the large end of the connecting rod to one side
and measure the backlash using a feeler gauge. As in
Fig.3.4.64
Tools: feeler gauge Standard: 0.10 -- 0.45 mm
Limit of use: 1.0 mm
If the service limit is exceeded, the crankshaft
assembly may be replaced or the deflection and backlash
may be limited by replacing worn parts (e.g., connecting
rods, big-end bearings and crankshaft pins).
Crankshaft deflection
Support the crankshaft with a V-shaped block as
shown.Position the dial gauge and slowly turn the
crankshaft to read its yaw.
If the yaw is greater than the service limit, the
crankshaft should be corrected or replaced. As Fig. 3.4.65
Tools used; Magnetic rack
Dial meter (1/100mm) V-shaped block (100 mm)
Limit of use: 0.05mm
reassemble
When reassembling the crankshaft, the width between
arm A shall be within the standard range.
As Fig. 3.4.63
Standard crank width: 53.0 ± 0.1 mm
Fig.3.4.62
Fig.3.4.63
Fig.3.4.64
Fig.3.4.65
Fig.3.4.66
 Loading...
Loading...











