The second knee of the tripping characteristic is defined by the setting at
DIFF: Idiff> PSx.
The characteristic equations for the three different ranges are given below.
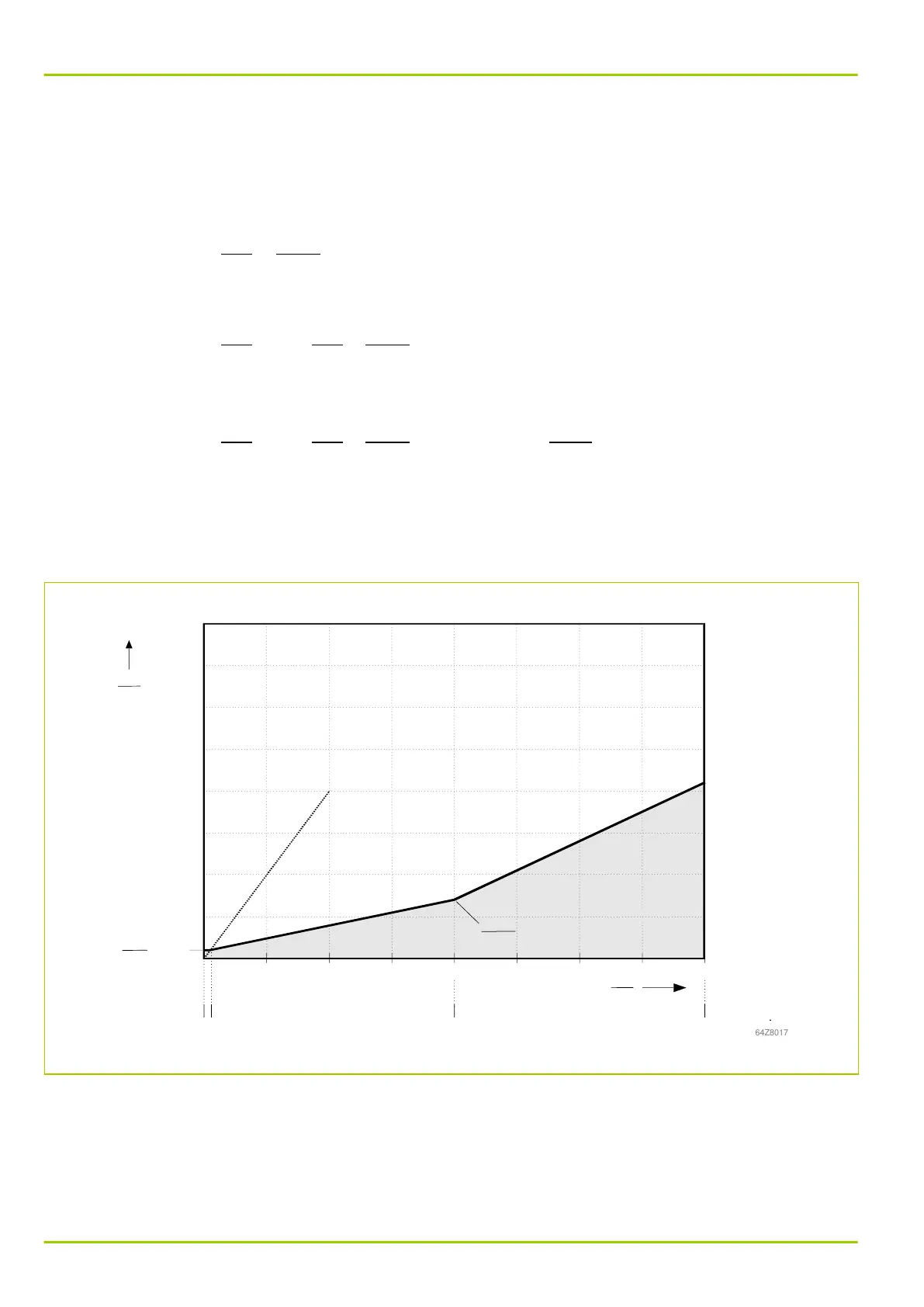
Fig. 3-82, (p. 3-116) shows the tripping characteristic.
Characteristics equation for the range 0 ≤ I
R
≤ 0.5I
diff >
:
I
d
I
ref
=
I
diff >
I
ref
Characteristics equation for the range 0.5I
diff >
< I
R
≤ I
R,m
2
:
I
d
I
ref
= m
1
⋅
I
R
I
ref
+
I
diff >
I
ref
⋅
(
1 − 0.5 ⋅ m
1
)
Characteristics equation for the range
I
R,m
2
< I
R
:
I
d
I
ref
= m
2
⋅
I
R
I
ref
+
I
diff >
I
ref
⋅
(
1 − 0.5 ⋅ m
1
)
+
I
R,m
2
I
ref
⋅
(
m
1
− m
2
)
I
ref
: reference current
m
1
: gradient of the characteristic in range 0.5I
diff >
< I
R
≤ I
R,m
2
m
2
: gradient of characteristic in range I
R,m
2
< I
R
2
4
6
8
0
2 4 6 8
I
IIIII
64Z8017
Tripping area
m1 = 0.3
m2 = 0.7
= 0.2
Id>
Iref
IR
Iref
Id
Iref
IR,m2
Iref
= 4.0
Blocking area
Fault current characteristic
for single-side feed
Fig. 3-82: Tripping characteristic of differential protection
If the current transformer supervision (CTS) function is used, the basic pick-up
sensitivity DIFF: Idiff> PSx can be increased to a value set at
DIFF: Idiff>(CTS) PSx.
P631
3 Operation
3-116 P631/EN M/R-11-C // P631-310-650
 Loading...
Loading...