Configure Switching
132
S350 Series 8-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Managed Pro Switch Models GS308T and GS310TP
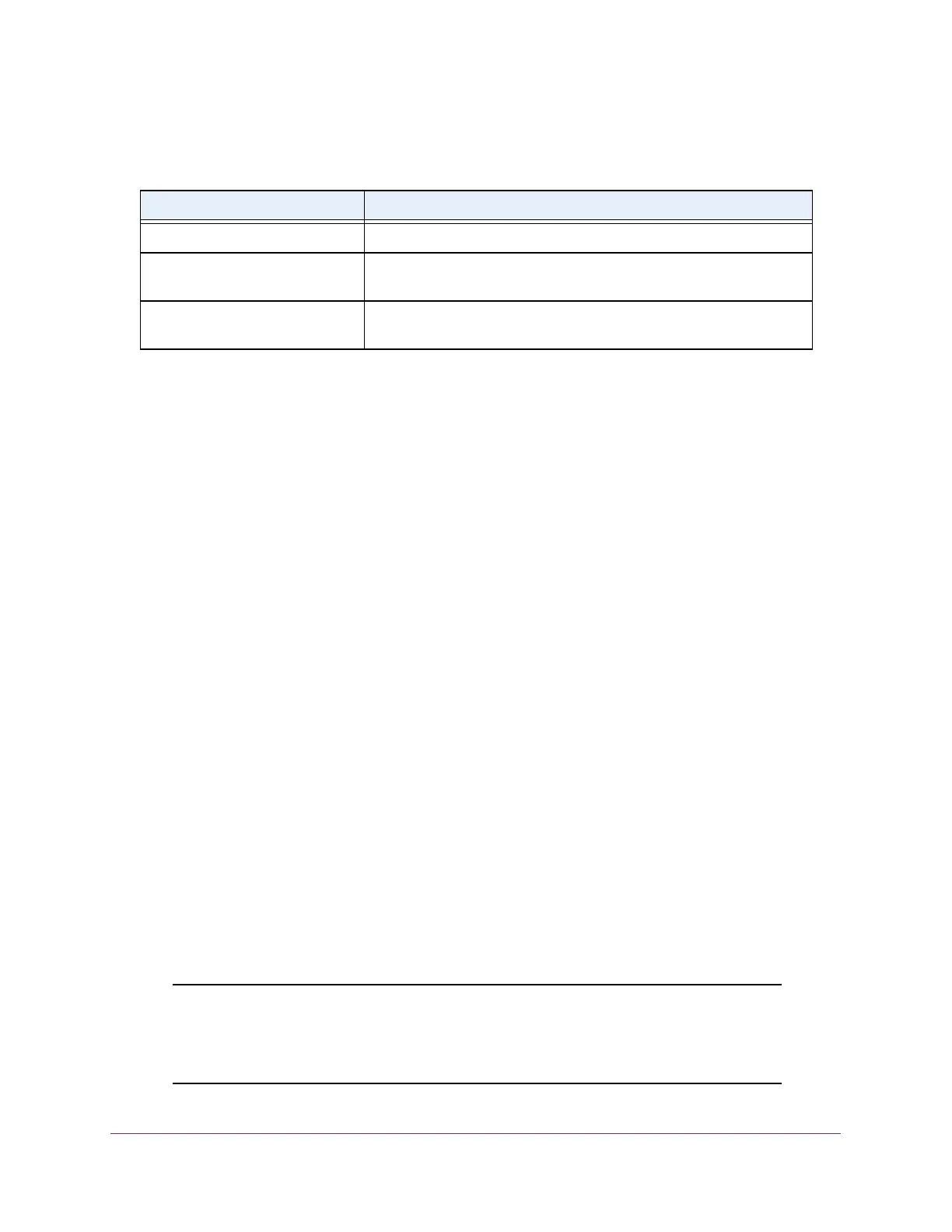
The following table describes the nonconfigurable Auto-VoIP status information.
Table 25. Auto-VoIP status
Field Description
Auto-VoIP VLAN ID The Auto-VoIP VLAN ID.
Maximum Number of Voice
Channels Supported
The maximum number of voice channels supported.
Number of Voice Channels
Detected
The number of VoIP channels prioritized successfully.
Configure Spanning Tree Protocol
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides a tree topology for any arrangement of network
devices. STP also provides one path between end stations on a network, eliminating loops.
STP (also referred to as “classic” STP) provides a single path between end stations, avoiding
and eliminating loops. For information about configuring the global STP settings for the
switch, see Configure STP Settings on page 133.
The switch support the following spanning tree versions:
• CST. Common STP
. For information on configuring CST, see Configure CST Settings on
page 135 and Configure CST Port Settings on page 136.
• MSTP. Multiple Spanning
Tree Protocol (MSTP, also referred to as MST) supports
multiple instances of spanning tree to efficiently channel VLAN traffic over different
interfaces. For information on configuring MSTP, see Manage MST Settings on page 141
and Configure MST Port Settings on page 144.
• RSTP. Rapid STP
. Each instance of the spanning tree behaves in the manner specified in
IEEE 802.1w, Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP), with slight modifications in the working but
not the end effect (chief among the effects is the rapid transitioning of the port to the
forwarding state). For information on viewing the RSTP state, see View Rapid STP
Information on page 140.
The difference between the RSTP and the traditional STP (IEEE 802.1D) is the ability to
configure and recognize full-duplex connectivity and ports that are connected to end
stations, resulting in rapid transitioning of the port to the forwarding state and the
suppression of
Topology Change Notification. These features are represented by the
parameters pointtopoint and edgeport. MSTP is compatible with both RSTP and STP. It
behaves in a way that is appropriate for STP and RSTP bridges. An MSTP bridge can be
configured to behave entirely as an RSTP bridge or an STP bridge.
Note: For two bridges to be in the same region, the force version must be
802.1s and their configuration names, digest keys, and revision levels
must match. For additional information about regions and their effect
on network topology, refer to the IEEE 802.1Q standard.

 Loading...
Loading...