Configure Switching
111
S350 Series 8-Port Gigabit Ethernet Smart Managed Pro Switch Models GS308T and GS310TP
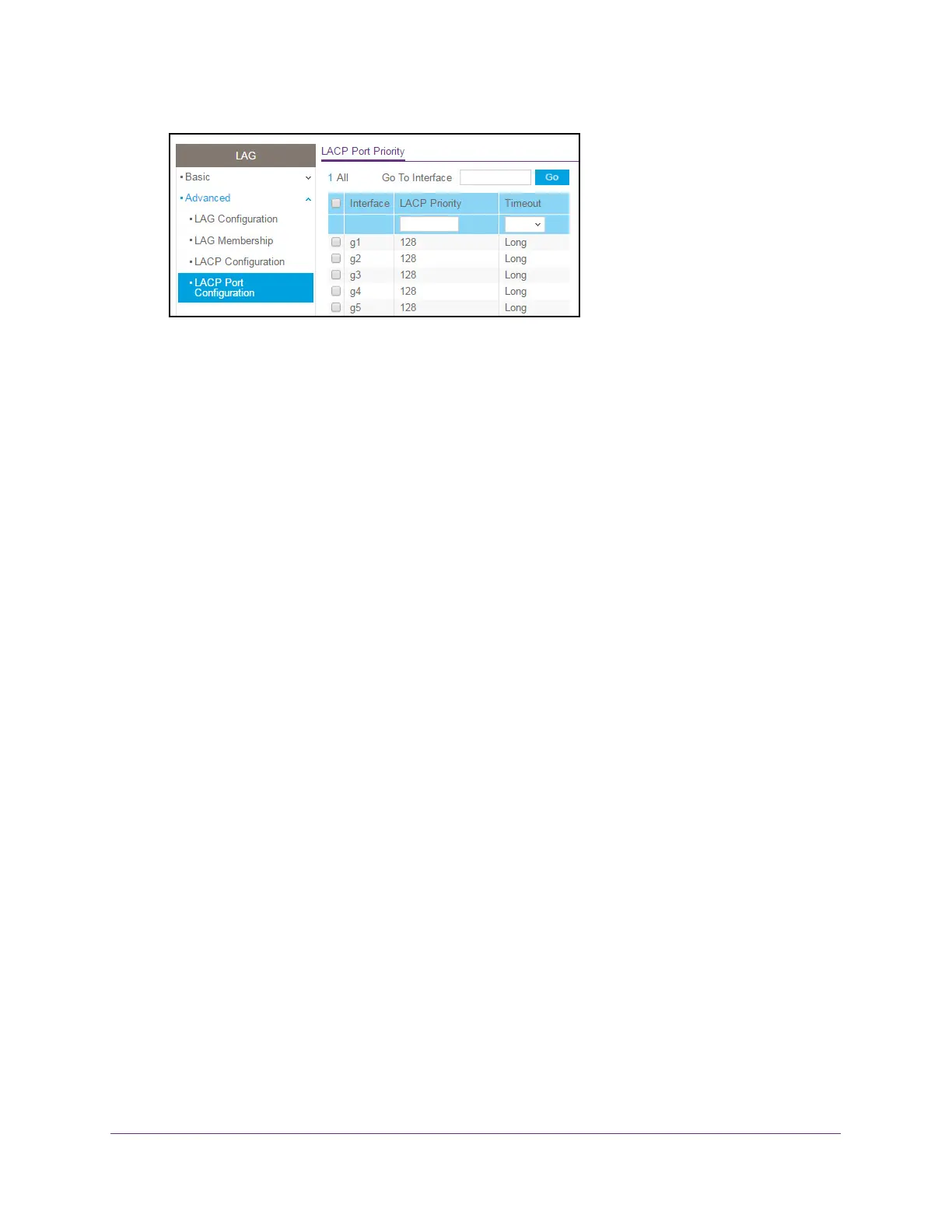
6. Select one or more interfaces by taking one of the following actions:
• T
o configure a single interface, select the check box associated with the interface, or
type the interface number in the Go To Interface field and click the Go button.
• T
o configure multiple interfaces with the same settings, select the check box
associated with each interface.
• T
o configure all interfaces with the same settings, select the check box in the heading
row.
7. In the LACP Priority field, specify the LACP priority value for the selected interfaces.
This value specifies the interface’s link aggregation priority relative to the devices at the
other ends of the links on which link aggregation is enabled.
A higher value indicates a
lower priority. The range is 1 to 65535. The default value is 128.
8. In the T
imeout field, configure the administrative LACP time-out value:
• Long. Specifies a long time-out value.
• Short. Specifies a short time-out value.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Configure VLANs
Adding virtual LAN (VLAN) support to a Layer 2 switch offers some of the benefits of both
bridging and routing. Like a bridge, a VLAN switch forwards traffic based on the Layer 2
header, which is fast, and like a router, it partitions the network into logical segments, which
provides better administration, security, and management of multicast traffic.
By default, all ports on the switch are in the same broadcast domain. VLANs electronically
separate ports on the same switch into separate broadcast domains so that broadcast
packets are not sent to all the ports on a single switch. When you use a VLAN, users can be
grouped by logical function instead of physical location.
Each VLAN in a network is assigned an associated VLAN ID, which appears in the IEEE
802.1Q tag in the Layer 2 header of packets transmitted on a VLAN.
An end station can omit
the tag, or the VLAN portion of the tag, in which case the first switch port to receive the
packet can either reject it or insert a tag using its default VLAN ID. A port can handle traffic
for more than one VLAN, but it can support only one default VLAN ID.

 Loading...
Loading...